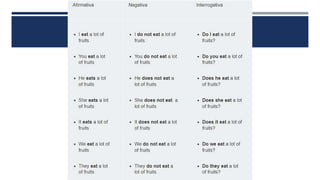
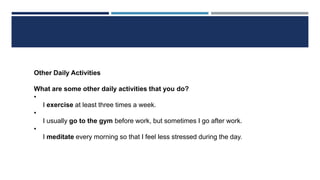
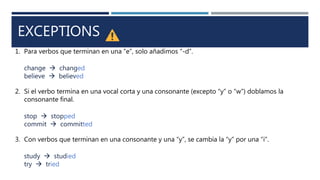
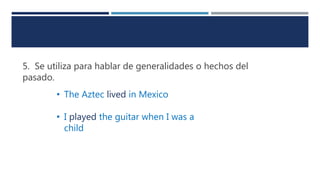
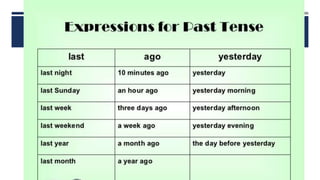
The document discusses English verb tenses and their importance for clear written and spoken communication. It explains that verb tenses identify when an action occurs in the past, present, or future. The simple past tense is then examined in more detail, noting that it is used to talk about completed actions or situations in the past. Both regular and irregular verbs are discussed, with examples provided of how to form the simple past of regular "-ed" verbs and common irregular verb forms. Guidance is given on using the simple past tense to talk about specific past events, series of past actions, repeated past habits, and general past facts.