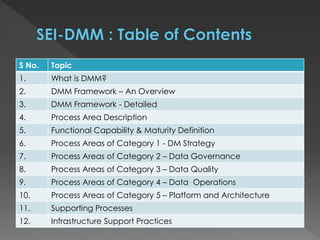
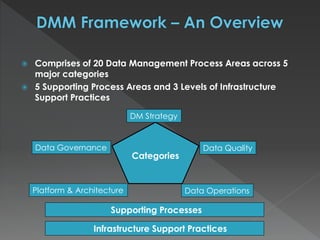
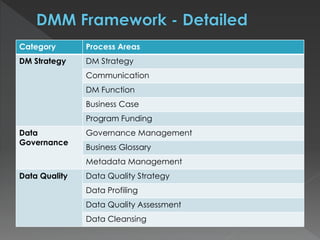
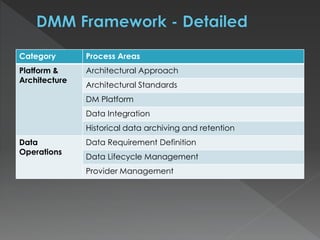
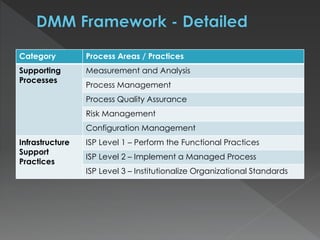
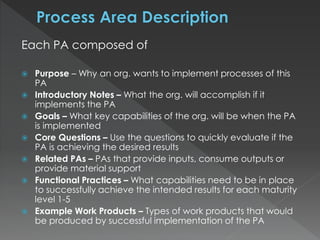
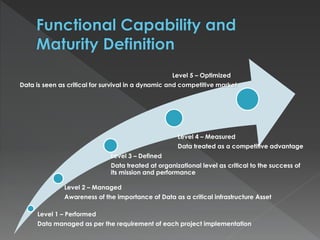
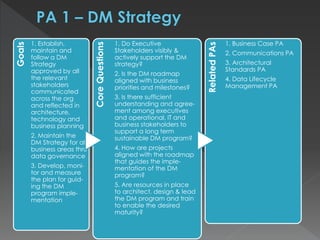
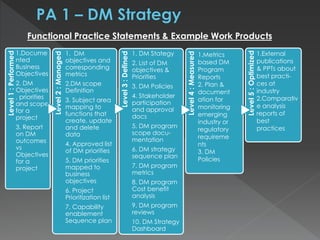
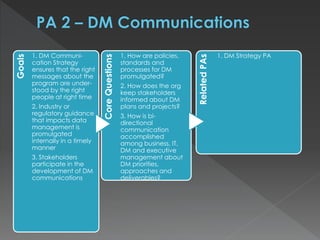
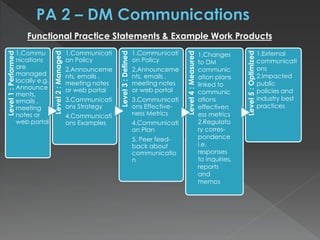
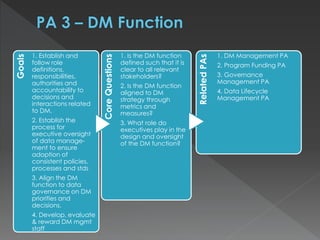
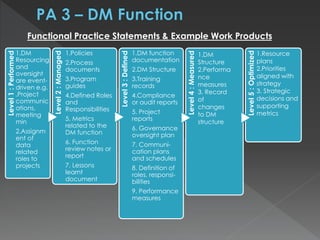
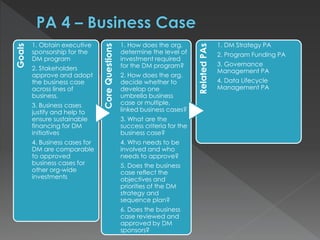
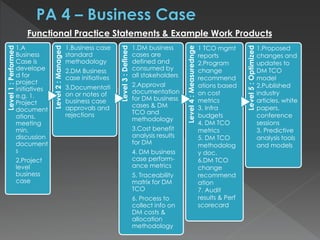
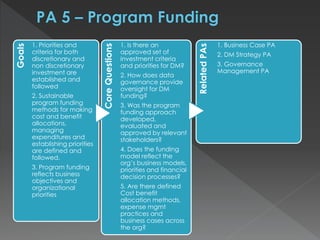
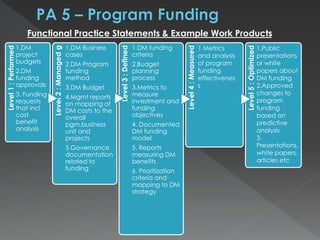
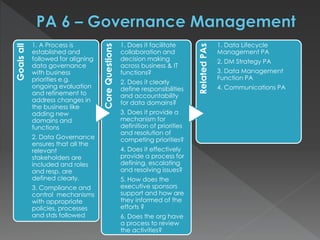
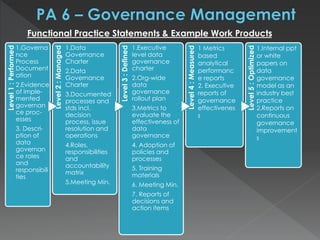
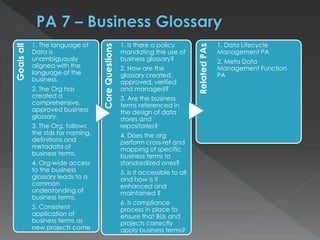
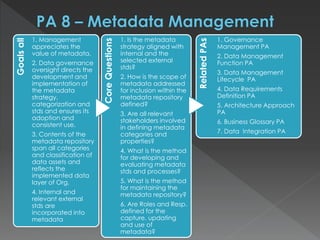
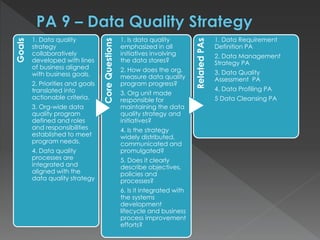
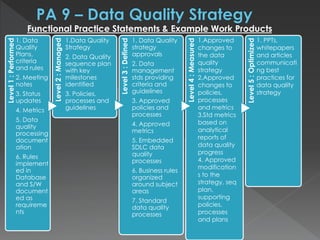
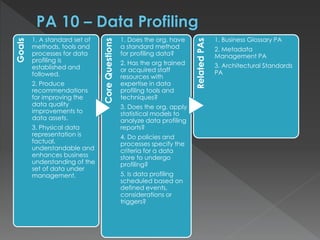
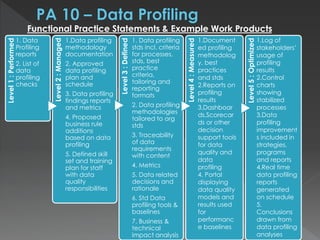
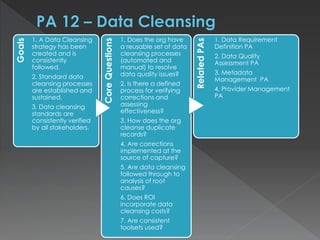
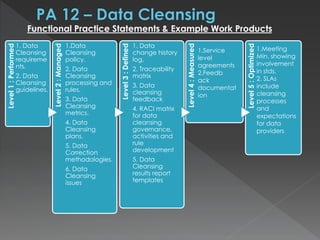
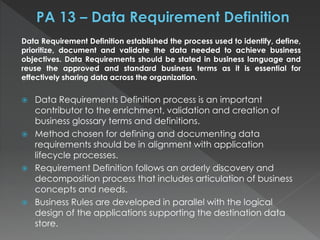
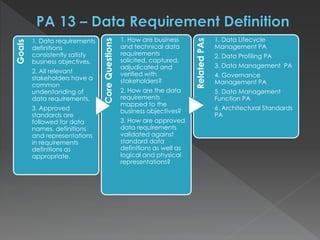
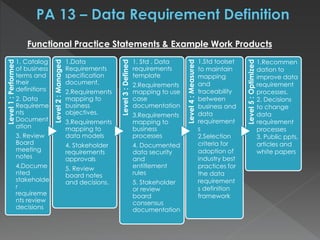
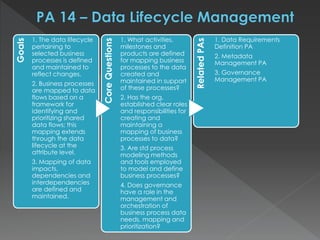
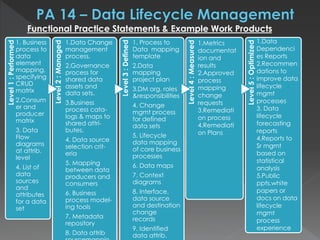
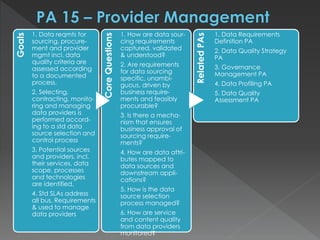
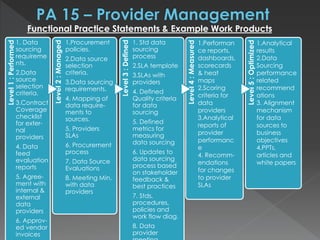
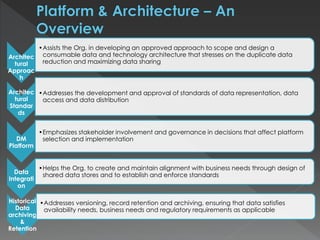
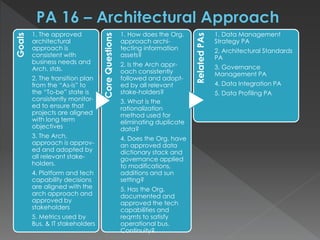
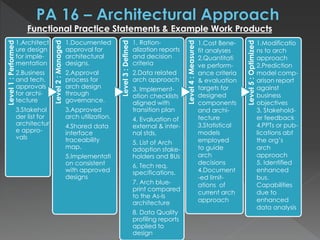
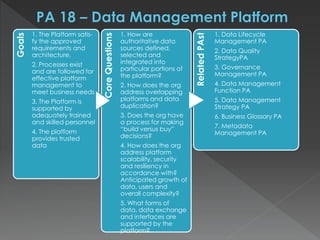
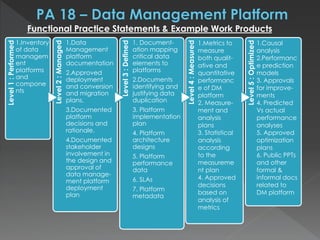
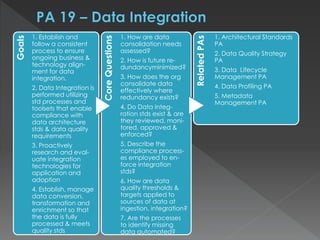
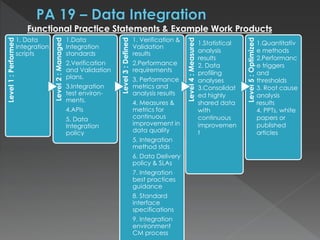
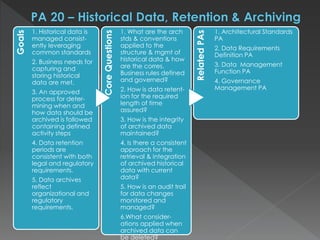
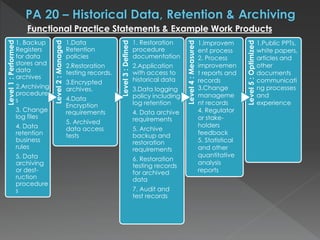
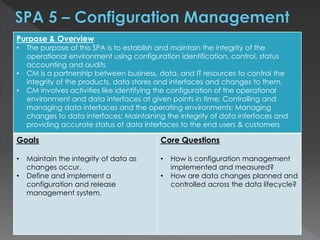
The document discusses the Data Management Maturity (DMM) framework, which defines best practices for data management across five categories: data strategy, data governance, data quality, data operations, and platform/architecture. It describes the goals and key questions for each of the 20 process areas within these categories. For each process area, it provides example work products and functional practices at different maturity levels (performed, managed, defined, measured, optimized). The document is intended as a comprehensive reference for organizations to evaluate and improve their data management capabilities.