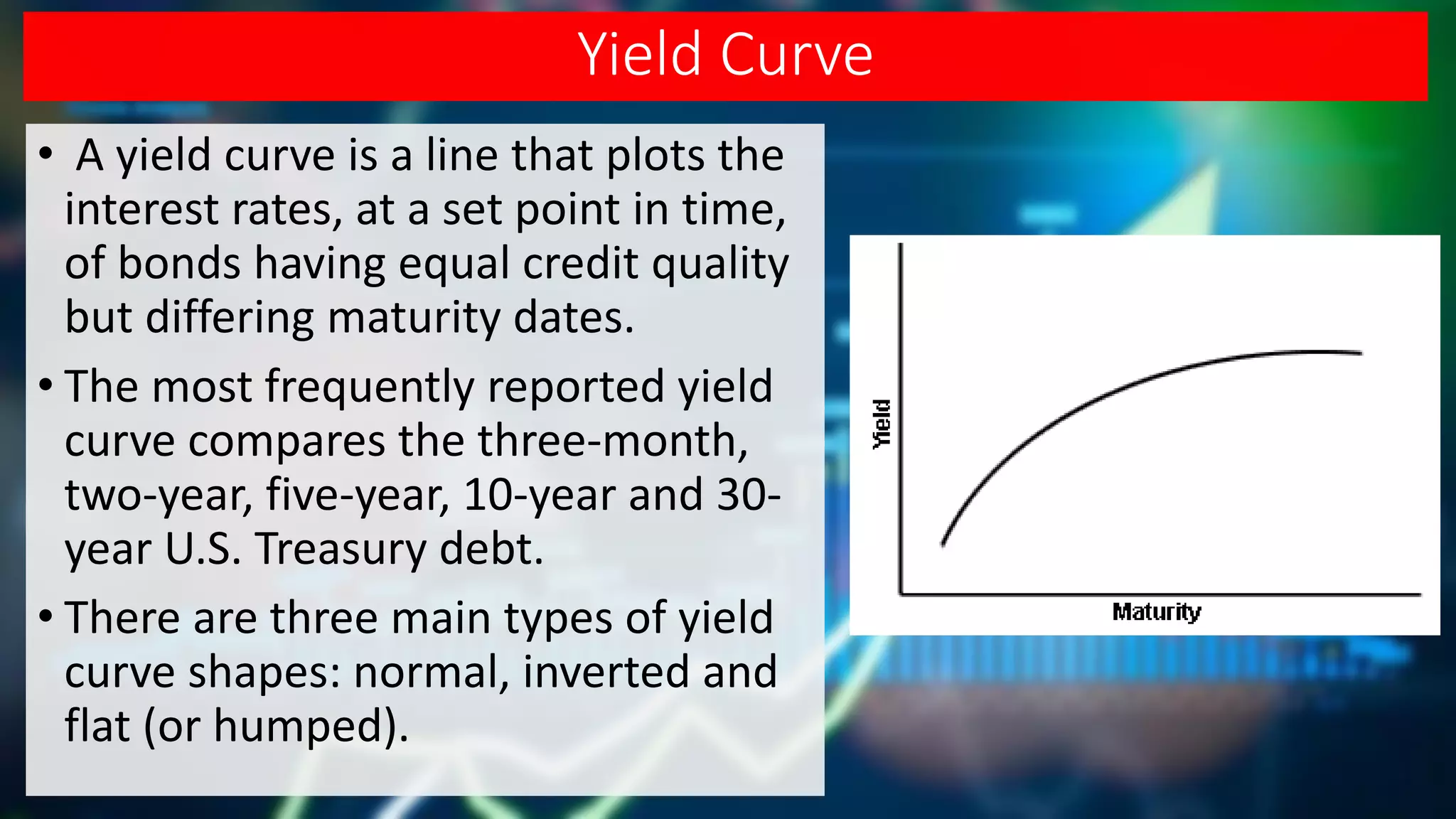
Bonds are fixed income instruments that represent loans to borrowers like corporations or governments. Bondholders are creditors who receive interest payments and repayment of principal at maturity. Key bond components include maturity date, coupon rate, credit rating, and yield measures like yield-to-maturity. Bond prices are inversely related to interest rates and face risks like default, inflation, and changes in interest rates. A yield curve plots bond yields of the same credit quality against maturity and can be normal, inverted, or flat depending on economic conditions.