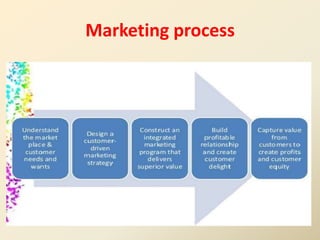
The marketing process involves understanding customer needs and creating value for customers through products and services to build relationships. The goal is to attract new customers by meeting needs better than competitors and keeping current customers satisfied. Marketing management determines target customer segments and designs a value proposition to meet their needs. The marketing concept orientation focuses on knowing customer needs and fulfilling them better than others.