1. Studies of biological contributions to homosexuality face difficulties due to ethical and practical limitations of research on humans as well as differences between humans and animal models.
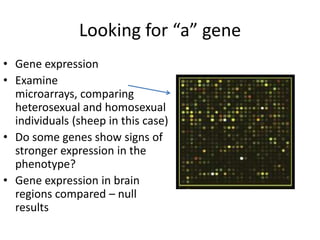
2. Genetic research has used linkage analysis and association studies to search for genes related to homosexuality, but results so far only suggest regions rather than specific genes due to complexity of multiple genetic and environmental factors.
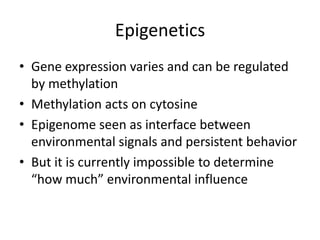
3. Epigenetics offers a framework to study gene-environment interactions through examining methylation differences between identical twins who differ in sexual orientation, but causes of those methylation differences remain unknown.













![Clinical and Research Issues
•- Robert L. Spitzer: Reparative Therapy Works [?]
– Scales of sexual orientation:
•attraction, identity, sexual behavior
• Critiques:
–no follow-up or face to face interviews
–retrospective accounts
–recruitment and sample bias
–NO peer review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/section10-130316233413-phpapp01/85/Section-10-16-320.jpg)

