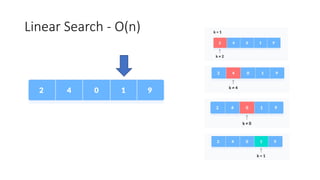
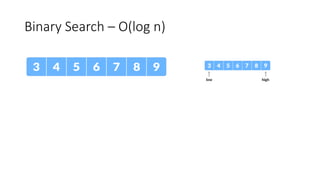
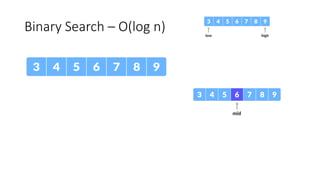
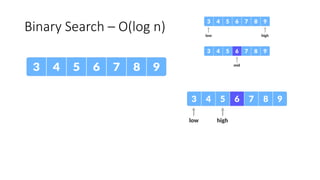
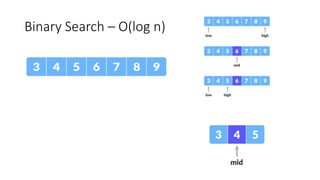
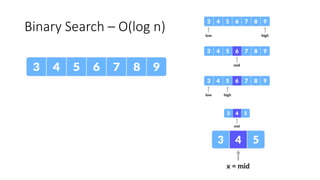
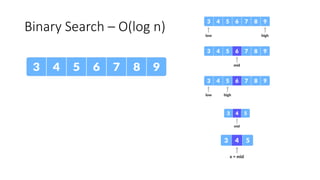
The document discusses two search algorithms: linear search, which is simple and effective for small datasets but slow for larger data due to its O(n) time complexity, and binary search which is faster at O(log n) but requires sorted data and contiguous memory. It also briefly covers various sorting algorithms including bubble sort, which functions by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements to sort the array. The document emphasizes the specific use cases, advantages, and drawbacks of each algorithm.