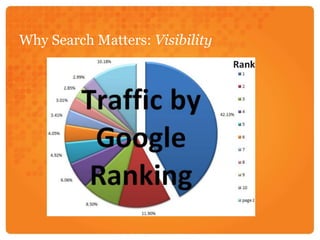
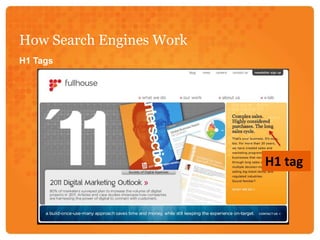
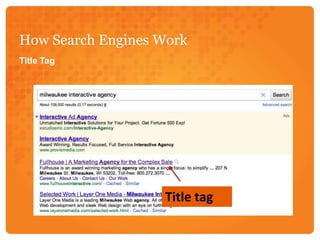
Search engine optimization (SEO) involves optimizing web pages to increase traffic from search engines. SEO is important because search engines are the second most popular internet activity and people trust search results. Search engines use spiders that crawl and index web pages, storing content in an index used to return relevant results. Key aspects of SEO include optimizing content, site architecture like URLs and navigation, and building internal and external links. Effective SEO involves an initial audit, keyword research, optimizing pages, implementation, link building, and analyzing metrics like traffic, bounce rate, and conversions over time.