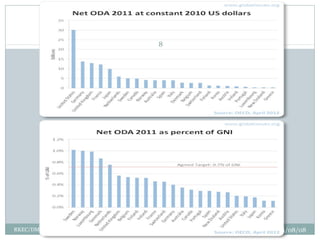
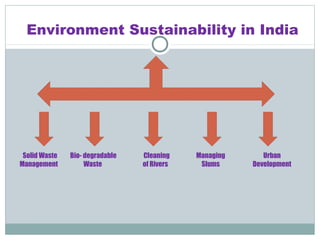
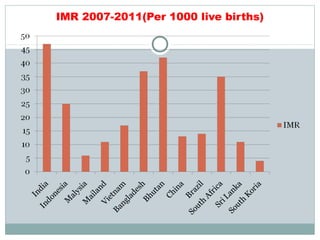
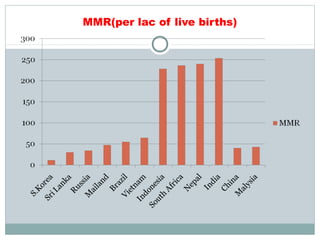
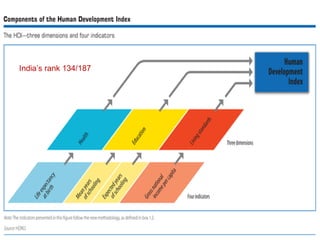
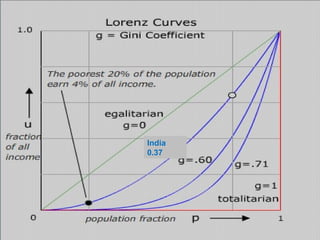
The document discusses several topics related to sustainable development. It first discusses the Pareto principle, which notes that 20% of the world's population controls 80% of resources, leading to unequal quality of life. It then lists several environmental damages caused by overconsumption and population growth, such as deforestation, pollution, and loss of biodiversity and natural resources. The term "sustainable development" is defined as development that meets current needs without compromising future generations, as coined by the UN World Commission on Environment and Development. The document also discusses focus areas for sustainable development like green jobs, sustainable cities, and water management.