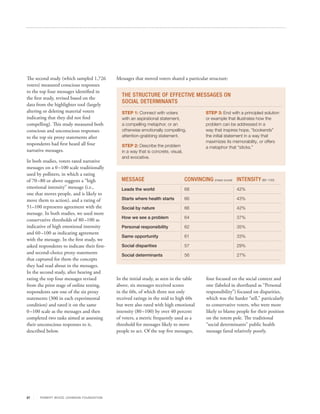
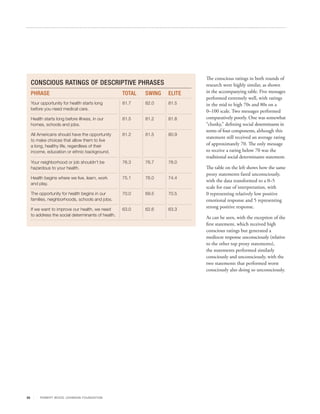
This document discusses research conducted to develop effective messaging around social determinants of health. Through focus groups and surveys of over 3,000 Americans, researchers tested various messages and identified best practices. The most persuasive message discussed how, despite U.S. leadership in healthcare, Americans do not have as long life expectancies as other countries, but framing it in a way that doesn't trigger political biases. The research showed the importance of priming audiences, offering potential solutions, incorporating personal responsibility, and focusing on shared experiences rather than specific disparities.


















![The Democratic privilege by virtue of birth,” and goes on affected by social determinants of
Frames for Social to discuss how unequal levels of health health. Broadly, containers keep
based solely on the zip code in which things in and keep things out; they are
Determinants of Health a person was born contradicts this physical, psychological, or social places.
and Health Disparities foundational principle of American society. Containers can protect us or trap us;
Across Populations The second level on which the deep
they can be open or closed, positive
or negative.
metaphor system operates is that
SYSTEM Democrats view poor levels of health For Democrats, low‐income communities
The deep metaphor of system forms as emerging from a complex and are isolated and self‐contained on all
the fundamental underpinning for the interrelated system of social, cultural, three levels—physical, psychological,
Democratic view of social determinants economic, and biological factors. and social. They are physically isolated
of health. Broadly, the system-deep One Democrat states, “It’s all tied in locations that lack resources
metaphor refers to the unification and together—housing, health care, energy, necessary to live a healthy life such
organization of separate entities into food.” Consequently, changing any one as easily accessible doctors’ offices,
a whole. The unity of a system means factor, such as access to insurance, is grocery stores with fresh foods, and
that the parts are interdependent; these not going to fix the problem of health places to exercise safely. One Democrat
connected parts often operate in a disparities. There are numerous social says “it’s like living within your own
predictable and recurrent pattern with determinants that we must address little world…the reality for poor
certain results. simultaneously and comprehensively people is never leaving their culture
in order to overcome the system of of poverty.” On a psychological level
For Democrats in particular, the interrelated factors that results in poor this “culture of poverty” traps them
system frame operates on two levels. levels of health, in certain communities. in a mentality that they can never
First, American society as a whole Because this frame of a complex system get ahead, they are unable to take
is a complex system that unifies all permeates the Democratic view of advantage of the opportunities in
citizens. As such, all individuals, from health they often feel the need to discuss broader society. Democrats describe
the poorest person in the Bronx to a multitude of issues and factors the poor as “a self‐contained group
the wealthiest person in Manhattan, simultaneously, quickly moving from at the bottom of the pyramid with
are interdependent, even if this is not one cause to another cause. This high unemployment, low job status.”
readily apparent. When poor levels of makes their discussions seem complex Solving health-related problems seems
health exist in some communities it and, at times, muddled. Even though particularly hopeless. The poor have
eventually affects everyone and weakens comprehensively addressing all social watched grandparents and parents
the entire system that is America. determinants of health makes perfect die of diabetes-related complications
What holds this American system sense to individuals operating in the or heart disease and it has become
together is a foundation of rights such world of public health and policy who almost an expected life outcome. There
as freedom, opportunity, and equality. hold the same system frame, it may be exists a psychological and cultural
For Democrats, health is itself a right; cumbersome and frustrating to those barrier to reaching out to the medical
all Americans have the right to health who hold a different frame, as we will community. A common Democratic
care and the right to lead a healthy life. see with the Republican world-view. manifestation of the container frame
One Democrat states, “Health care is a involves barriers. They bring images
right, it’s so fundamental to being able CONTAINER of blockades and “significant barriers
to have a healthy lifestyle. [What makes Where the deep metaphor system related to health care [exist between the
it a right are] the values of society, of underpins the Democratic view of Latino community/African-American
federal government.” Another states American society and health-related community and White folks.”]
that “one of the real founding principles issues, the deep metaphor container
[of America] was the notion of absence of frames the way they view communities
V U L N ER A B L E P O P U L AT I O N S P O RT F OL I O 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdh2010-13133485910494-phpapp01-110814140409-phpapp01/85/Sdh-2010-19-320.jpg)
![Finally, on a social level, the poor are that they are hard to separate at times)
left out of the larger social system are a reflection of extreme imbalance in
that Democrats see as underpinning American society between the “haves”
America. This is particularly troubling and the “have nots.” For Democrats, a
for Democrats as part of their situation where “it would take this chief
fundamental view of society is that executive two hours to earn enough to
everyone is interconnected, so having fund a community kitchen for three
some groups left out of this system is years” is morally wrong —“Something
not only morally wrong, it weakens is wrong there, it’s out of balance.”
the overall view of America as a well This is an important touch point
functioning system of inclusion. One for Democrats. As we will see later,
Democrat states, “Individuals at the Republicans have a more optimistic
bottom of society’s rungs, economically, view of Americans’ health status,
socially, etc., they’re the ones who whereas Democrats are angered by this
get left out when it comes to access profound social imbalance, “It makes
to affordable, quality health care. me very angry…it’s unjust and unfair
…we leave a sixth of Americans outside and profoundly disturbing.” “[I feel]
the system…we as a society have a really angry, I mean really angry…I
responsibility, an obligation, and it’s didn’t realize how angry I was about
in our best interests to bring them in.” that until you asked me.” Or, in the
Consider the digital collage that one collage below, “This woman who’s
Democrat created, which exemplifies screaming [represents that] she’s angry
the way low‐income communities trap that these problems existed for so long.”
individuals in “containers” that separate Fig. 1 Collage created by a Democrat to
them from the larger social system, as The second way that the balance-deep
show the separation of poor communities from
represented by the well‐dressed white metaphor frames how Democrats view wealthy White society.
students at the bottom of the image issues related to health disparities is
Fig. 2 Collage created by a Democrat
(see Figure 1). in their discussion of remedies and highlighting anger over persistent social
outcomes. Democrats seek equality— imbalance with regards to health levels.
BALANCE balanced distribution of resources, the
The balance-deep metaphor encompasses same health care treatment for everyone,
ideas of equilibrium, adjusting, and (ideally) equal outcomes in that all
maintaining or offsetting forces, and communities would have roughly the
things being as they should. Balance same levels of health. The language of
themes can structure peoples’ thinking equality has been a cornerstone of
about social, moral, psychological Democratic discussions of a multitude
and emotional domains. Democrats of social issues, from health disparities
predominantly express the negative side to employment to education. Statements
of balance. Having an interconnected like, “Equality assumes that we are
social system while simultaneously all going to end up at the same level.
tolerating pockets of isolated, self- Equity to me presumes a fair and
contained, impoverished citizens leaves even distribution of resources” pepper
Democrats with a profound sense the Democratic discussion of social
of imbalance. Health disparities and determinants of health. Critically, this
wealth disparities (issues that are so is not the language that is effective
deeply interconnected for Democrats
15 R OB ER T WOOD J OH NSON F OUN DAT ION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdh2010-13133485910494-phpapp01-110814140409-phpapp01/85/Sdh-2010-20-320.jpg)

![The difference in base level of optimism
versus anger between the Republicans
and Democrats could be a real source of
tension between the two groups when it
comes to discussing social determinants
of health. Understanding these basic
differences in emotional response to the
issue could help anticipate touch points
in a conversation where communication
might break down.
Much as they see America and health
care as a whole on a journey through
time, Republicans see individuals as
on their own health journeys. Echoing
the common theme of “individual
Fig. 3 Collage created by a Republican to show different choices along the journey of health and how
responsibility,” Republicans view poor they lead to either positive or negative life outcomes.
health as arising from bad choices along
one’s path and the inability to overcome
obstacles to health that one encounters would lead him to a lower path, which The second Republican expression of
along the way. Rather than employing is disadvantage. Or the baby could take resource highlights an important aspect
the Democratic frame of externally‐ the upper path where they don’t have of this deep metaphor. Physical resources
imposed barriers that trap communities a care about anything.” Thus, where are finite; we use up natural resources,
in poverty and low levels of health, Democrats view American society and we spend money, we consume food.
Republicans frame poor levels of health the causes of low levels of health in Replenishing a resource takes time and
in terms of a failure to give individuals certain populations as interconnected effort, and some resources can never be
in a community “a road map of how systems, Republicans view both as replaced. For Republicans, American
to achieve [health].” However, in the unpredictable journeys. society has a finite amount of resources,
same line of thought they feel they both monetary and service‐related.
must acknowledge that “…some of RESOURCE We need to be realistic that every person
these differences we create because… While Republicans focus on personal cannot have everything; we simply do
we lead ourselves to places.” In other responsibility for choices made not have enough to go around equally.
words, Republicans feel it is important along one’s health journey, they also One Republican states, “because of this
to give individuals the opportunity and acknowledge that people living in world of scarce resources, there’s always
the tools to make good choices in their low‐income communities may lack rationing…balancing out how you’re
health journey, but at the same time the means and ability to choose the going to ration things with how much
we must acknowledge that they will right path toward health. This is redistribution you want.” Another says,
also make their own, sometimes bad, an activation of the resource-deep “If we had unlimited resources, it’d be
choices. The following collage portrays metaphor. Resources are essential to our great to say that everybody deserves and
the common Republican theme of survival. They can be physical—such can have access to Cadillac health care,
a divergent path that individuals as a tool, person, or an organization, but we don’t.”
encounter in their health journey. This or intangible—such as a skill, a
Republican states, “We start down the body of knowledge, or a network of Because of American’s limited resources,
road…as the baby progresses, there relationships. Resources act as agents Republicans focus more intensely on
are two paths that he could take. One enabling us to achieve important goals. getting the most “bang for the buck,”
17 R OB ER T WOOD J OH NSON F OUN DAT ION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdh2010-13133485910494-phpapp01-110814140409-phpapp01/85/Sdh-2010-22-320.jpg)
![meaning that they want to be certain “[Democrats] would be just as happy the government and what is expected
that they infuse resources into the most bringing the high end down as you of the individual. Neither one of these
critical programs and services that would bringing the low end up…I care entities should bear the sole burden
demonstrate effectiveness in helping about bringing the low end up and of raising levels of health in poor
individuals in low‐income communities the fact that this reduces disparities communities. “Government makes
make better health choices. Where is great, but it’s not the disparity that decisions…and there has to be some
Democrats tend to see resources going worries me, it’s the low end people not balancing of altruistic motivation to
into a system where they circulate doing well.” As illustrated very clearly redistribute and efficiency,” meaning
through different communities and by this participant, Republicans are that we should infuse resources
programs without necessarily being concerned about social determinants of into the best places, but we should
exhausted, Republicans see a zero‐sum health and low levels of health in poor expect individuals to take personal
game. If you pour all of your resources communities, but they immediately responsibility in using them.
into low‐income communities, there object to any plan that uses the
is less for the rest of America, and you language of equality or creating equal
simultaneously have not guaranteed levels of health because it activates the
that you actually help that community deep metaphors of limited resources
because you did not necessarily pinpoint and creating balance by taking things
the most strategic uses of those funds away from the “haves” to give to the
and services. “have nots.”
BALANCE Another important expression of
The final deep metaphor that frames balance for Republicans is their
the issue of social determinants of conviction that it is unrealistic to expect
health for Republicans is balance, that everyone is going to have the same
but it is expressed in a very different levels of health. In a free society where
way than the Democratic framing of individuals make their own choices
social imbalance. Where Democrats (again, relating back to the journey
see equality as both a solution (giving theme), it is natural that there will be
everyone equal services and access) and differences in individual’s health. We
a desired outcome (equal levels of health should, however, establish a minimum
across all communities), the language acceptable level, providing enough
and ideas around equality are extremely resources that people are able to achieve
off‐putting to Republicans. They health goals they set for themselves. A
understand equality quite differently Republican states, “There [are] bound
than Democrats. While Democrats to be differences in health outcomes,
see equality as raising the bottom so there are good reasons why some people
everyone is at the same level (lifting should be healthier than others. As long
people out of the entrapping holes of as we are willing to live in a society
poverty), Republicans view equality where people are different and given
as more of a scale where you have to different levels of income, [we] will have
take things away from the people who to have different levels.”
are well‐off in order to give them to
Finally, Republicans frame the best
the poor. This frame directly relates to
solution to health disparities as a
the zero‐sum view of resources held by
balance between what is provided by
Republicans. One Republican states,
V U L N ER A B L E P O P U L AT I O N S P O RT F OL I O 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdh2010-13133485910494-phpapp01-110814140409-phpapp01/85/Sdh-2010-23-320.jpg)