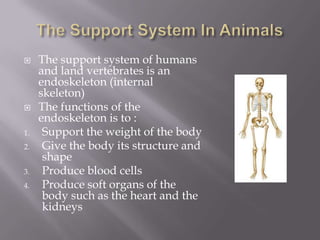
Land vertebrates and humans have an endoskeleton that provides structure, supports weight, and protects organs. It gives shape and supports the weight of land vertebrates while aquatic vertebrates are supported by buoyancy. Invertebrates have exoskeletons or hydrostatic skeletons for shape and organ protection. Plants have woody tissue, turgor pressure, or are buoyant to provide structure and support above and below water.