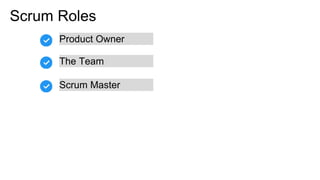
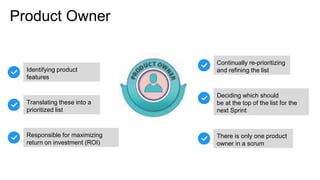
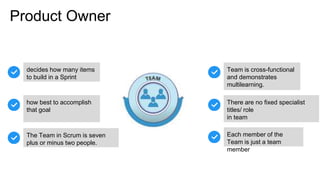
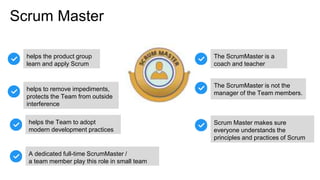
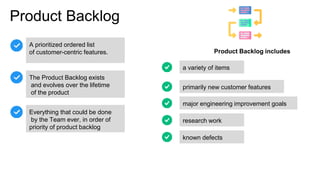
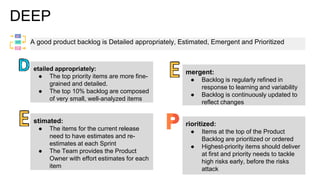
Scrum is an iterative development framework where cross-functional teams work in timeboxed cycles called sprints, typically lasting up to four weeks. Key roles include the Product Owner, responsible for maintaining the prioritized product backlog, and the Scrum Master, who facilitates the process but does not manage the team. Essential practices include defining a 'Definition of Done' for product increments and conducting sprint planning meetings to set objectives and determine work allocations.