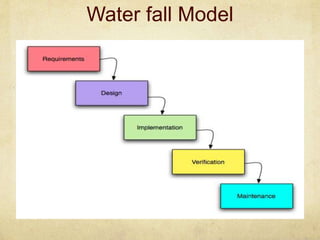
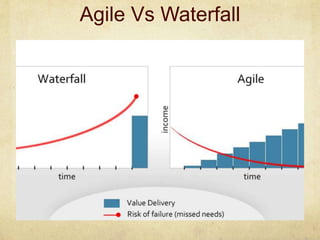
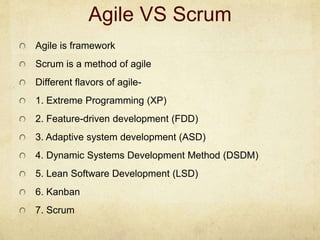
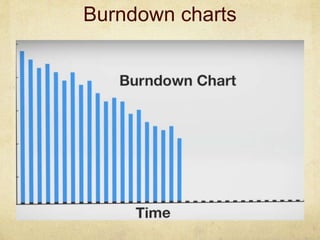
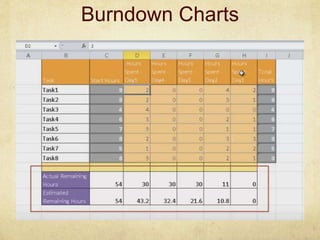
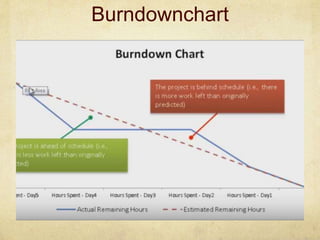
This document provides an overview of Scrum and its key concepts. It defines the waterfall and agile models of software development. Scrum is described as an agile method that uses cross-functional teams, product backlogs, sprints, daily stand-ups, and sprint reviews. Key Scrum roles like the Product Owner and Scrum Master are explained. The document also discusses estimating techniques, burndown charts, and how Scrum compares to other agile frameworks.