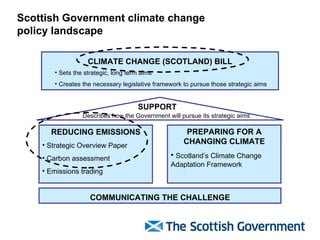
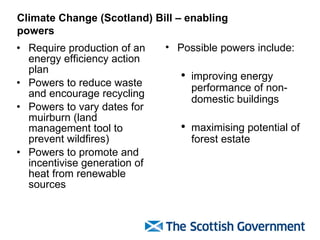
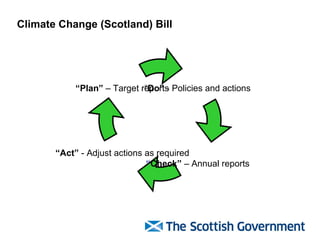
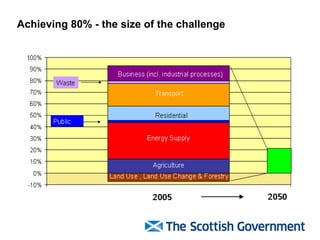
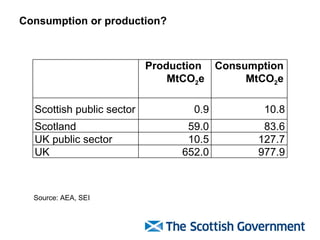
The document discusses Scotland's policies and targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change. It outlines the Climate Change (Scotland) Bill which sets long-term targets of reducing emissions by 80% by 2050 and interim targets of 50% by 2030. It also discusses using carbon assessment tools to evaluate the climate impacts of government spending and policies in order to help meet emission reduction goals.