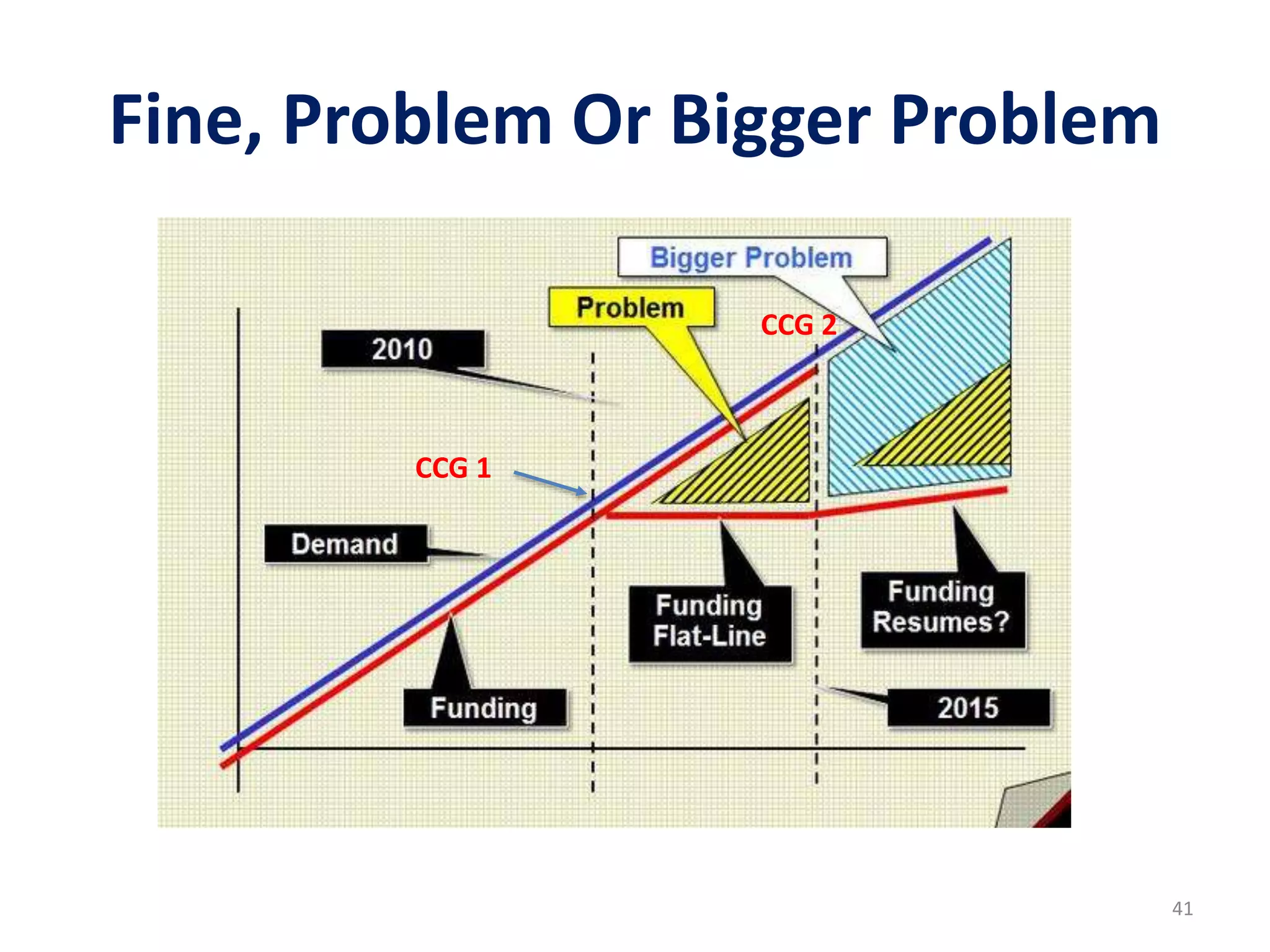
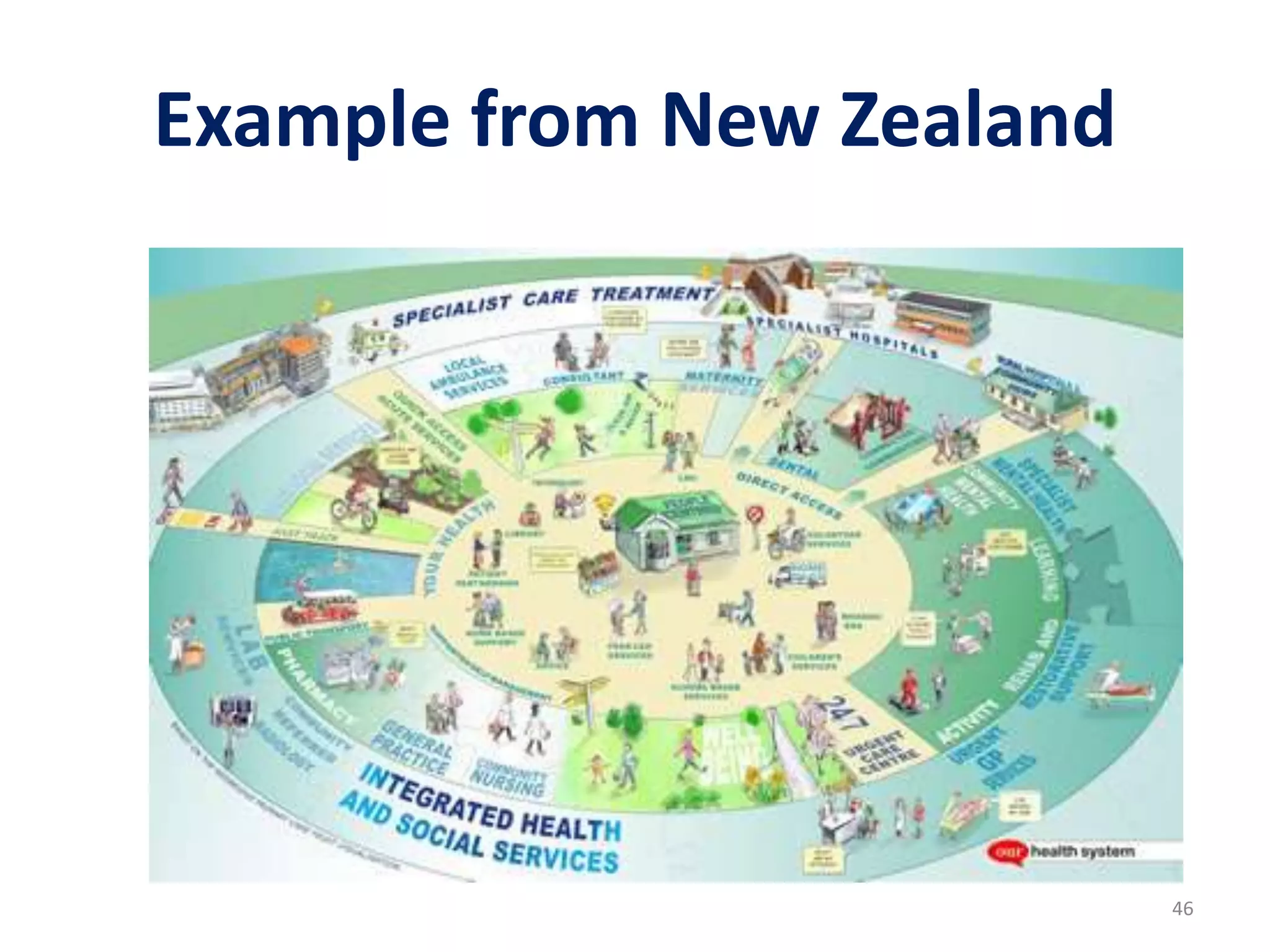
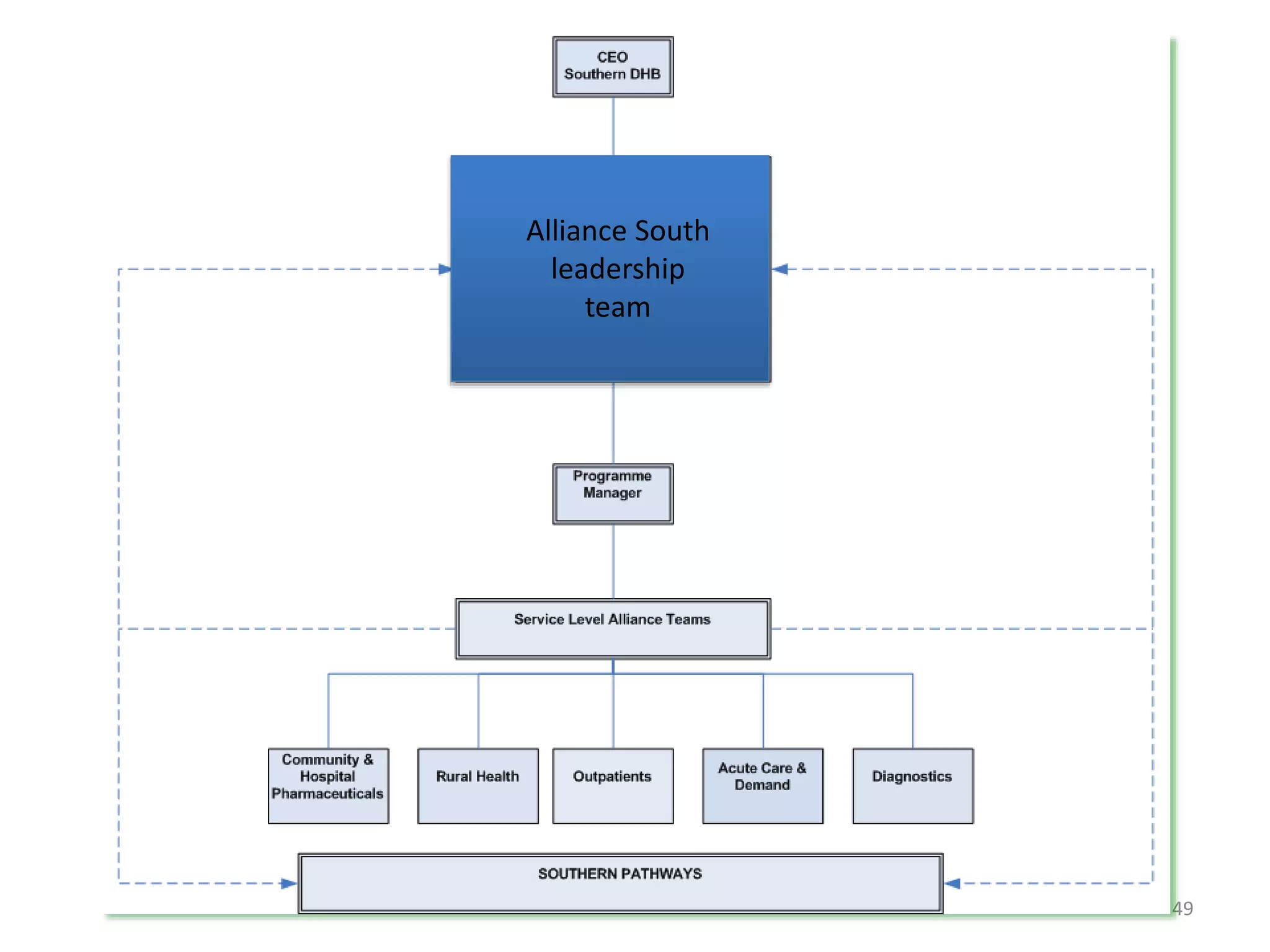
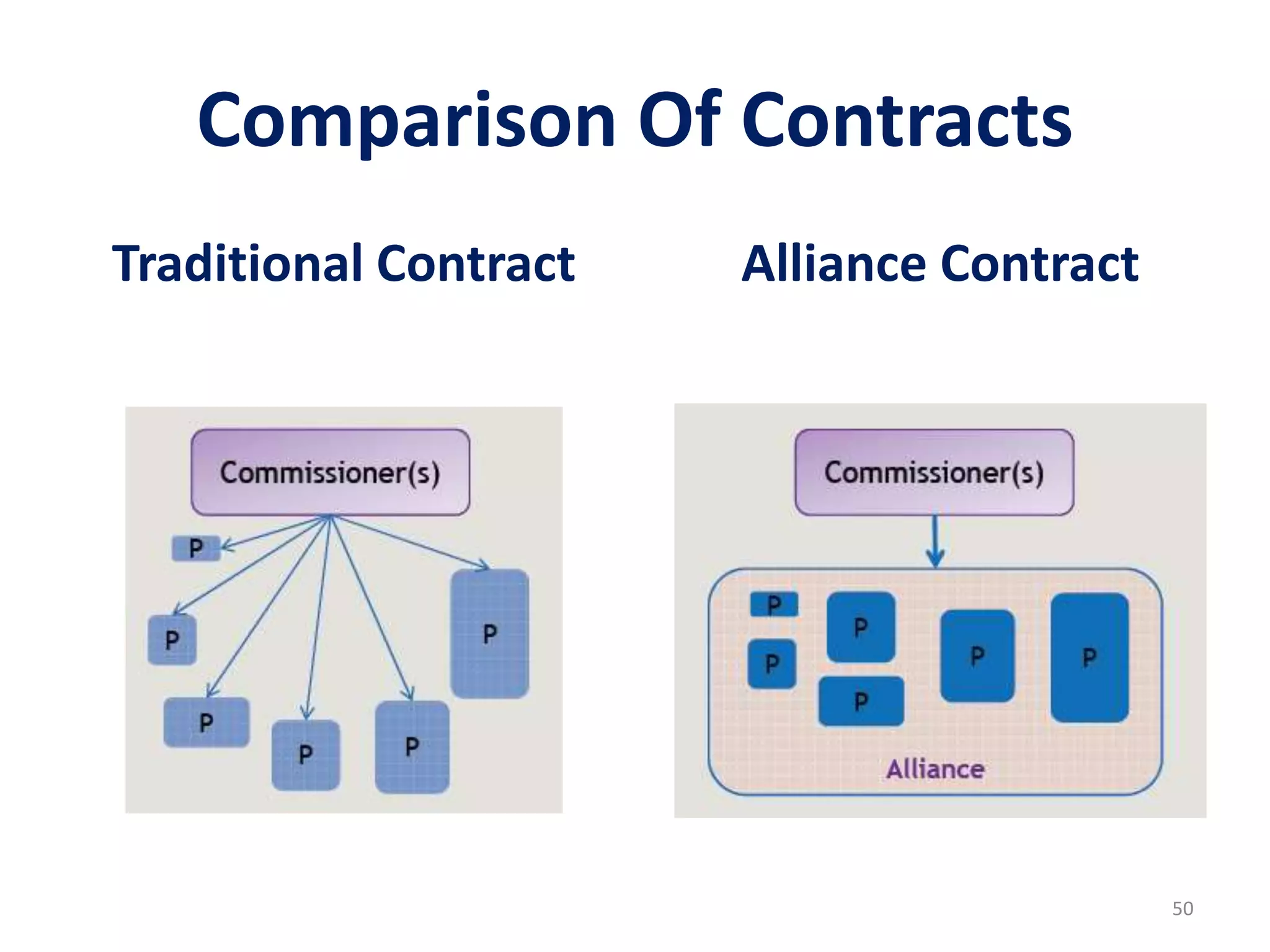
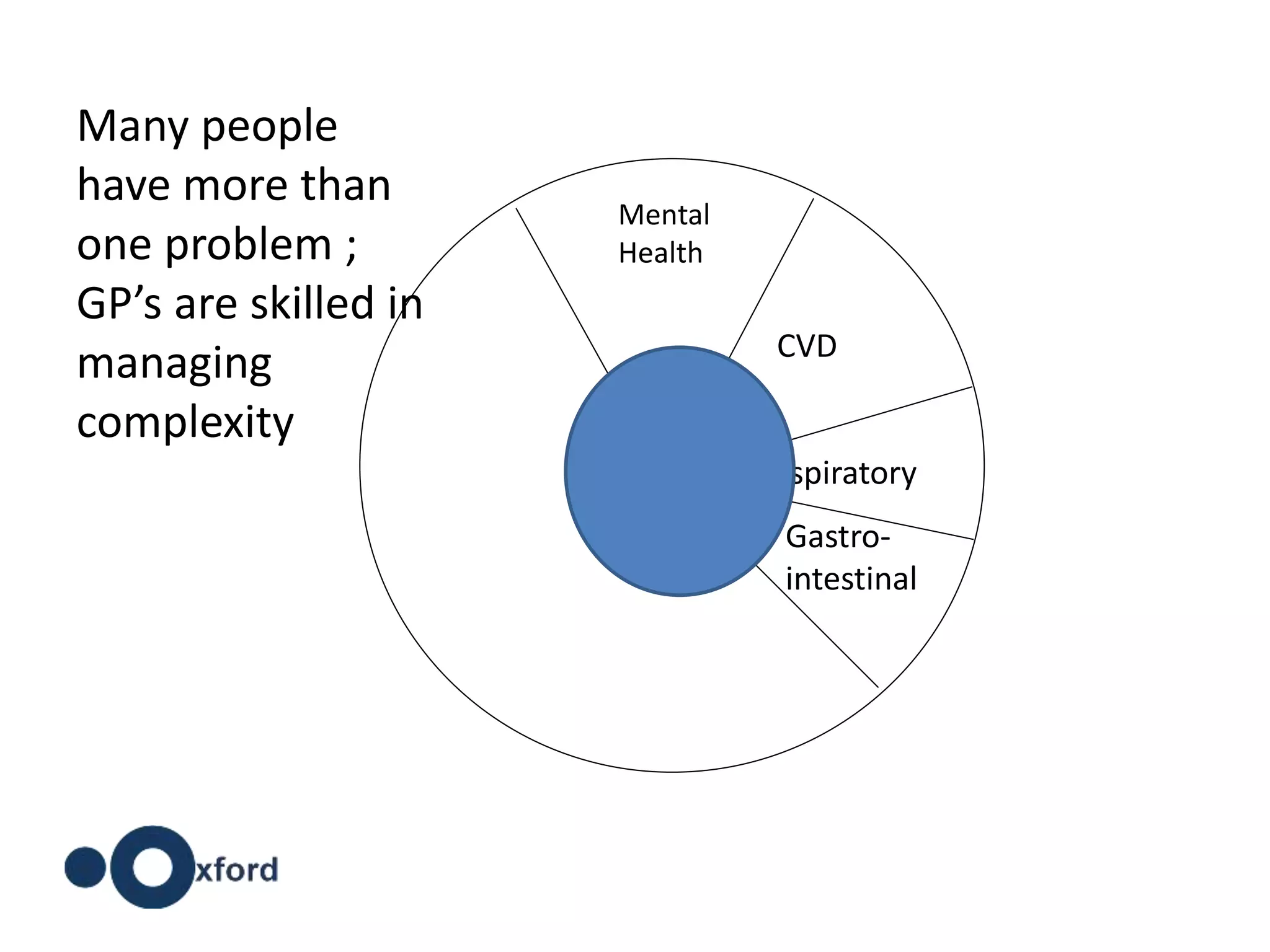
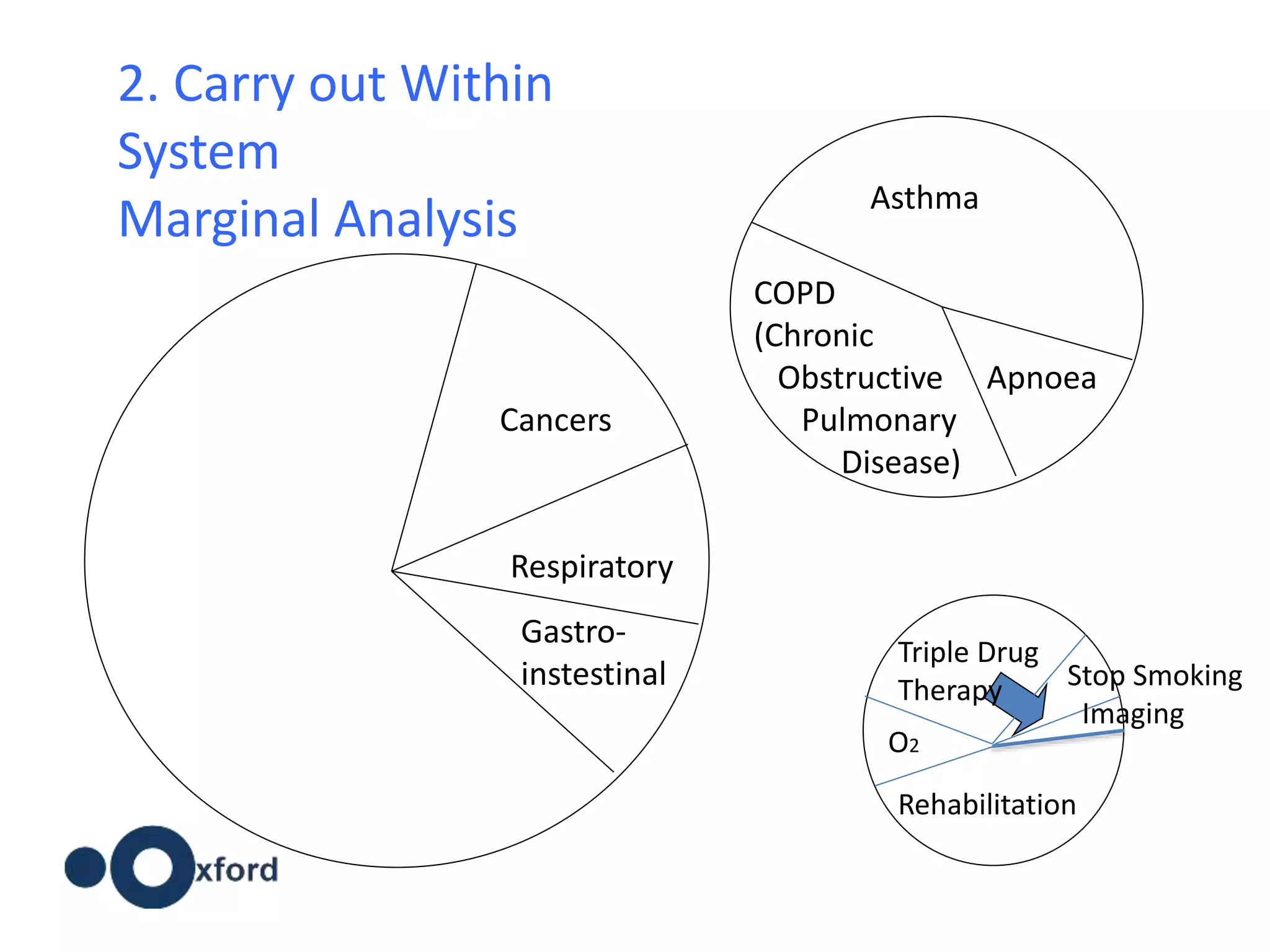
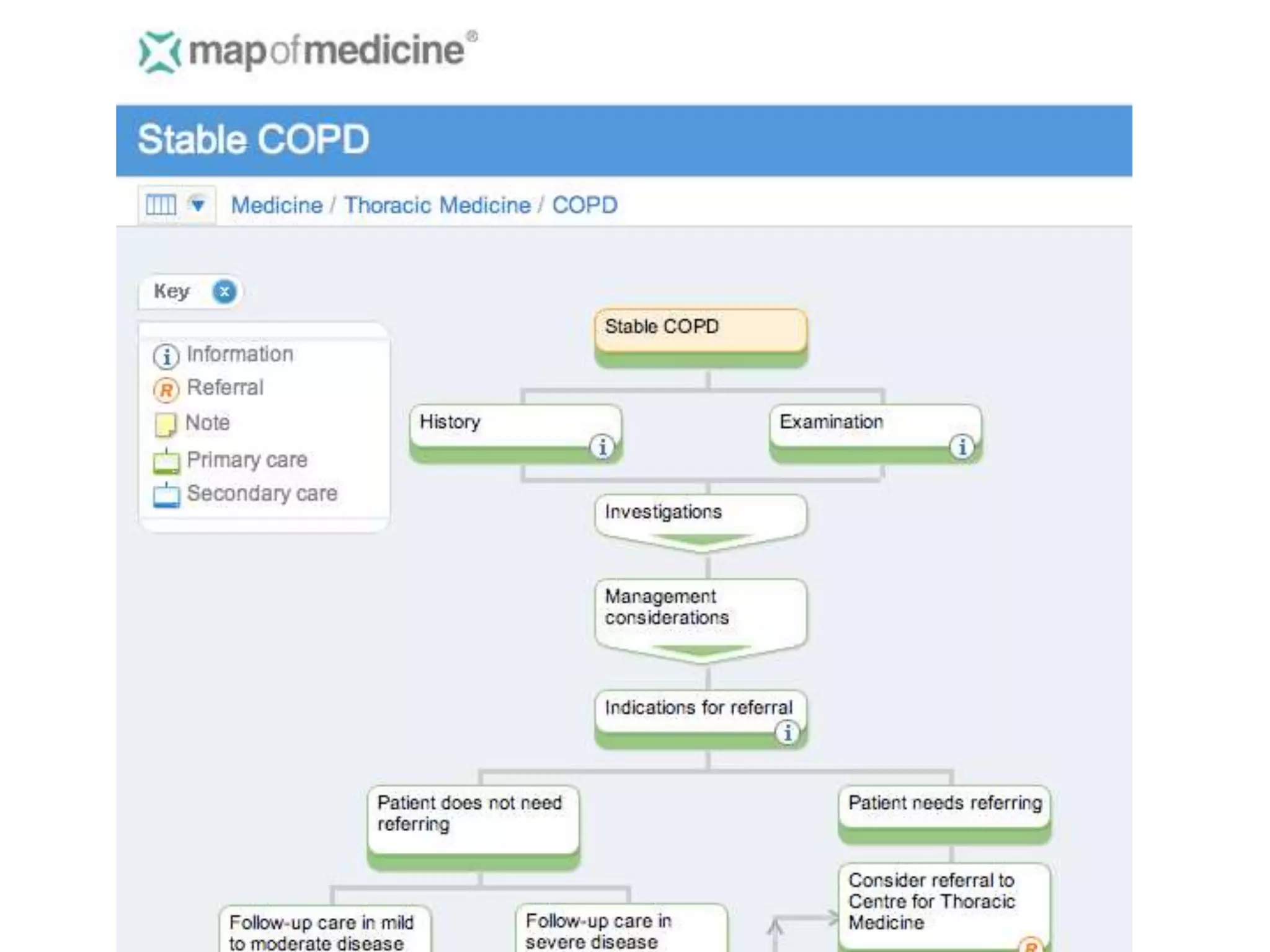
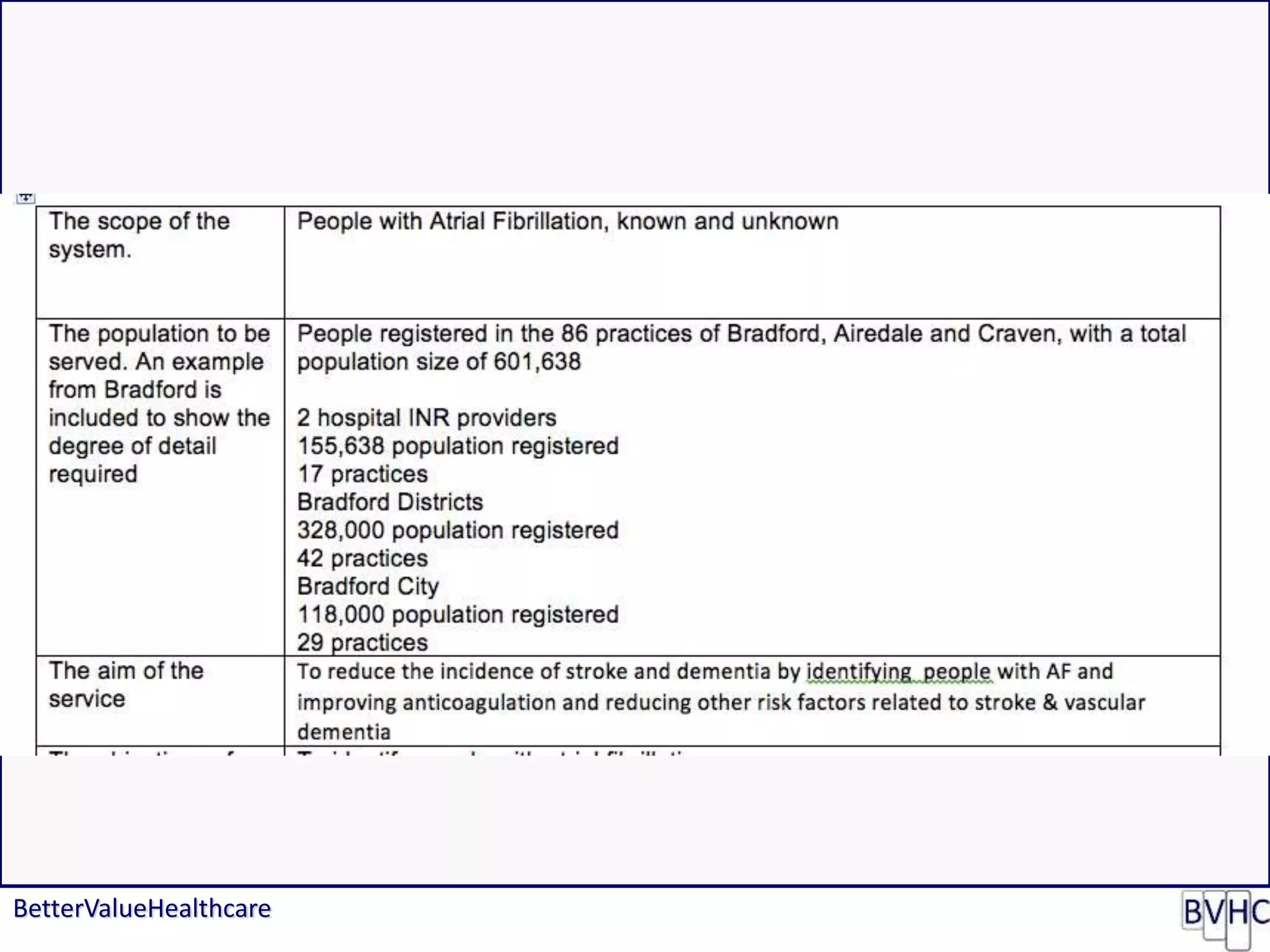
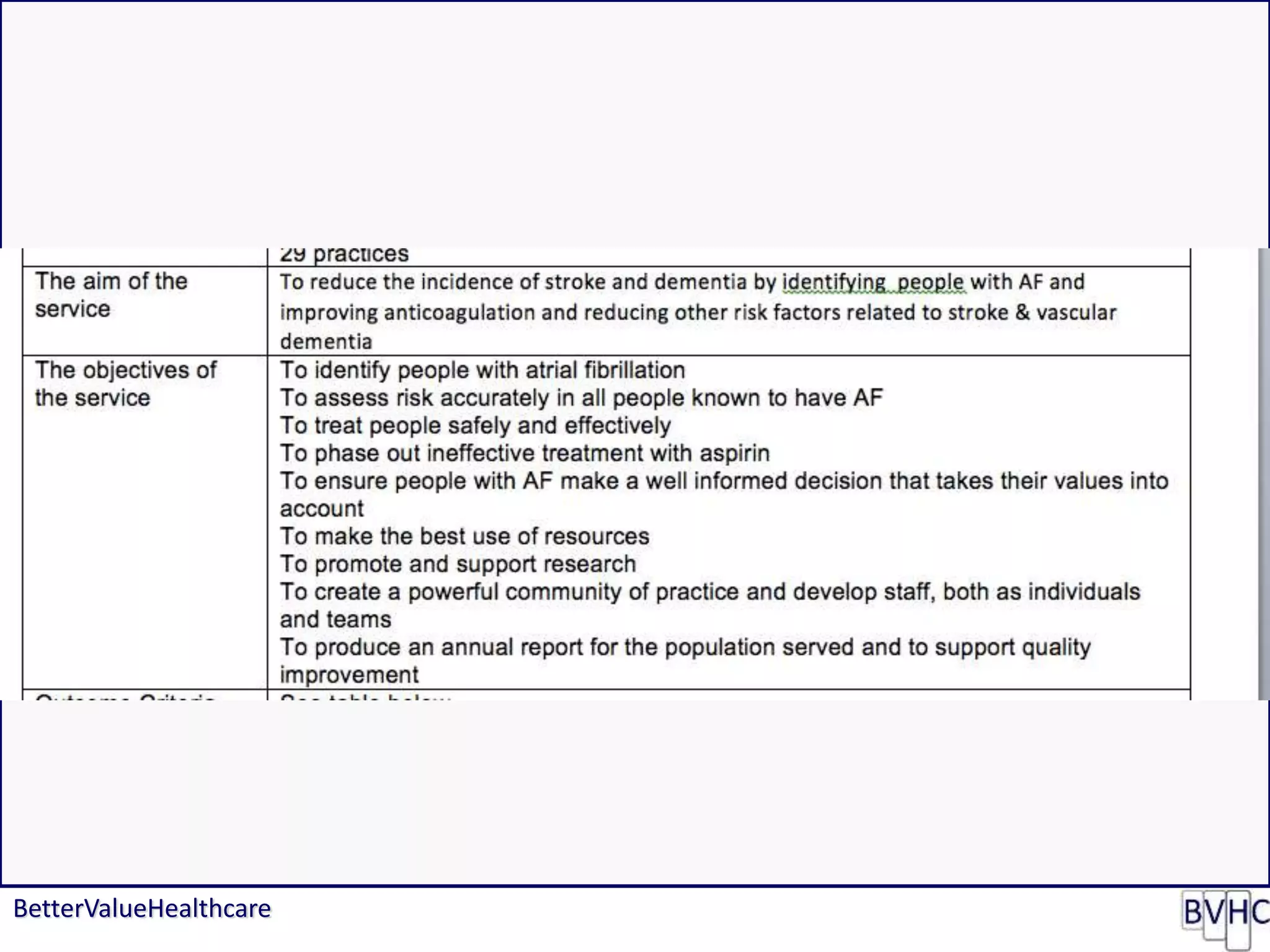
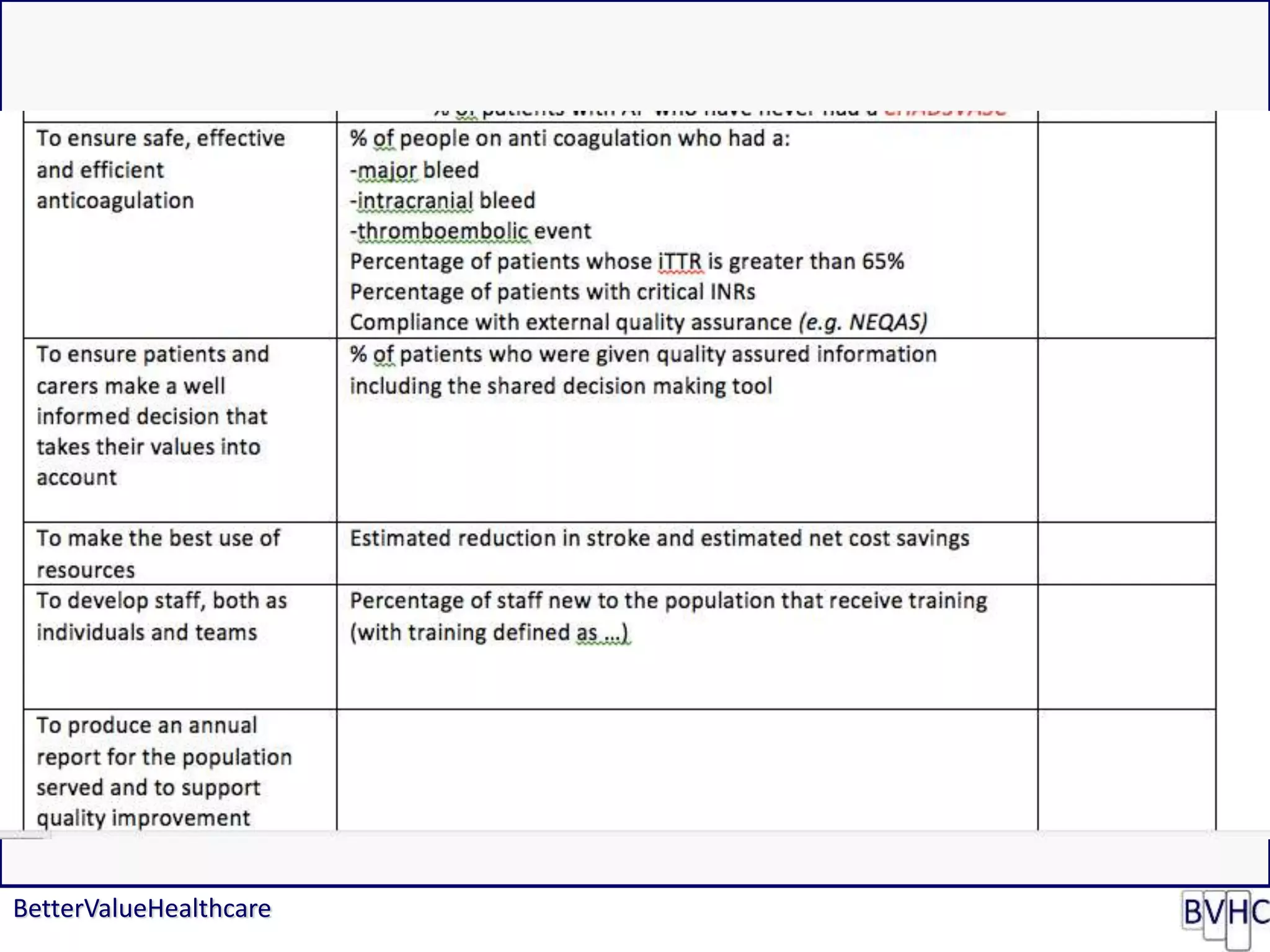
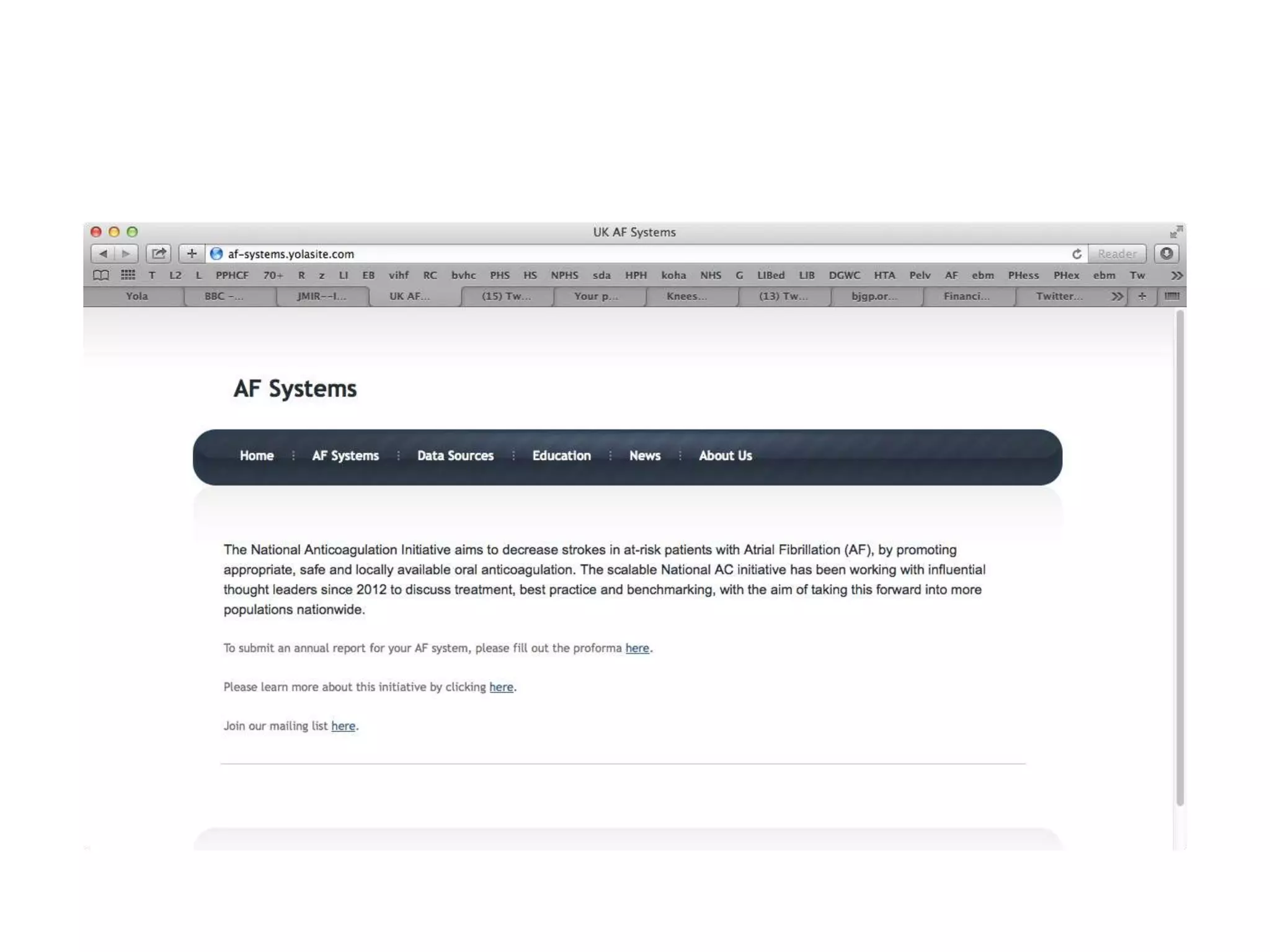
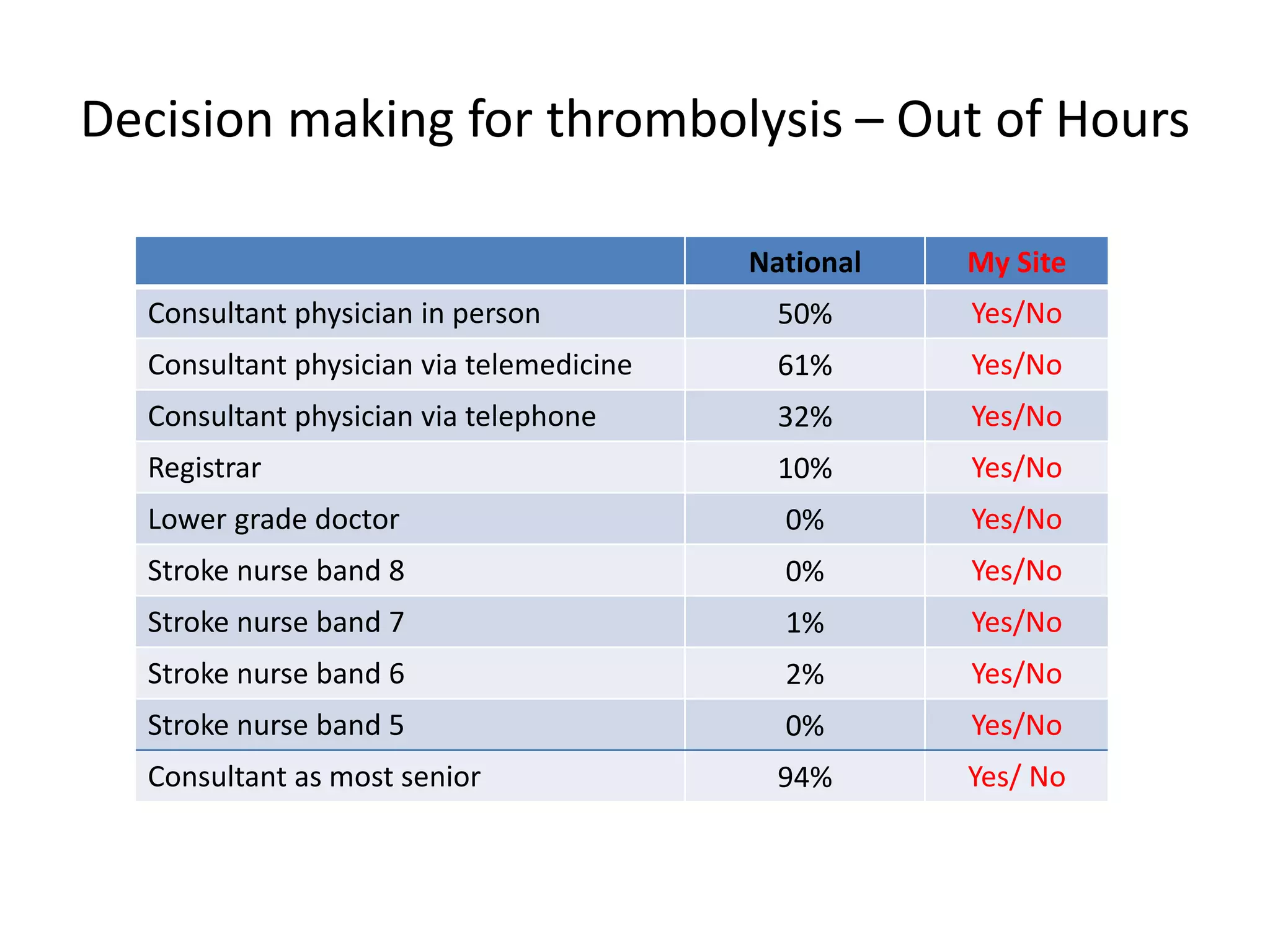
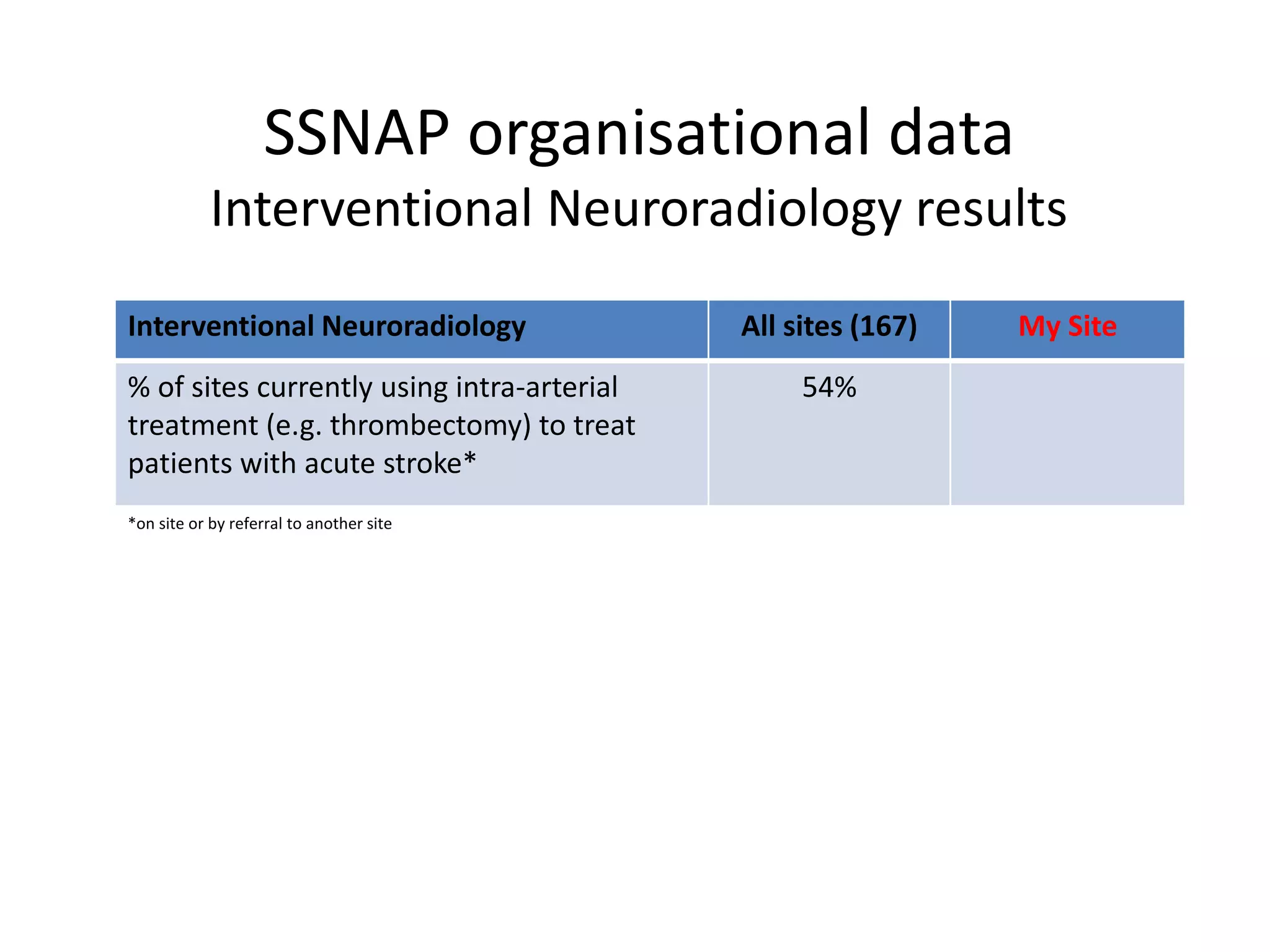
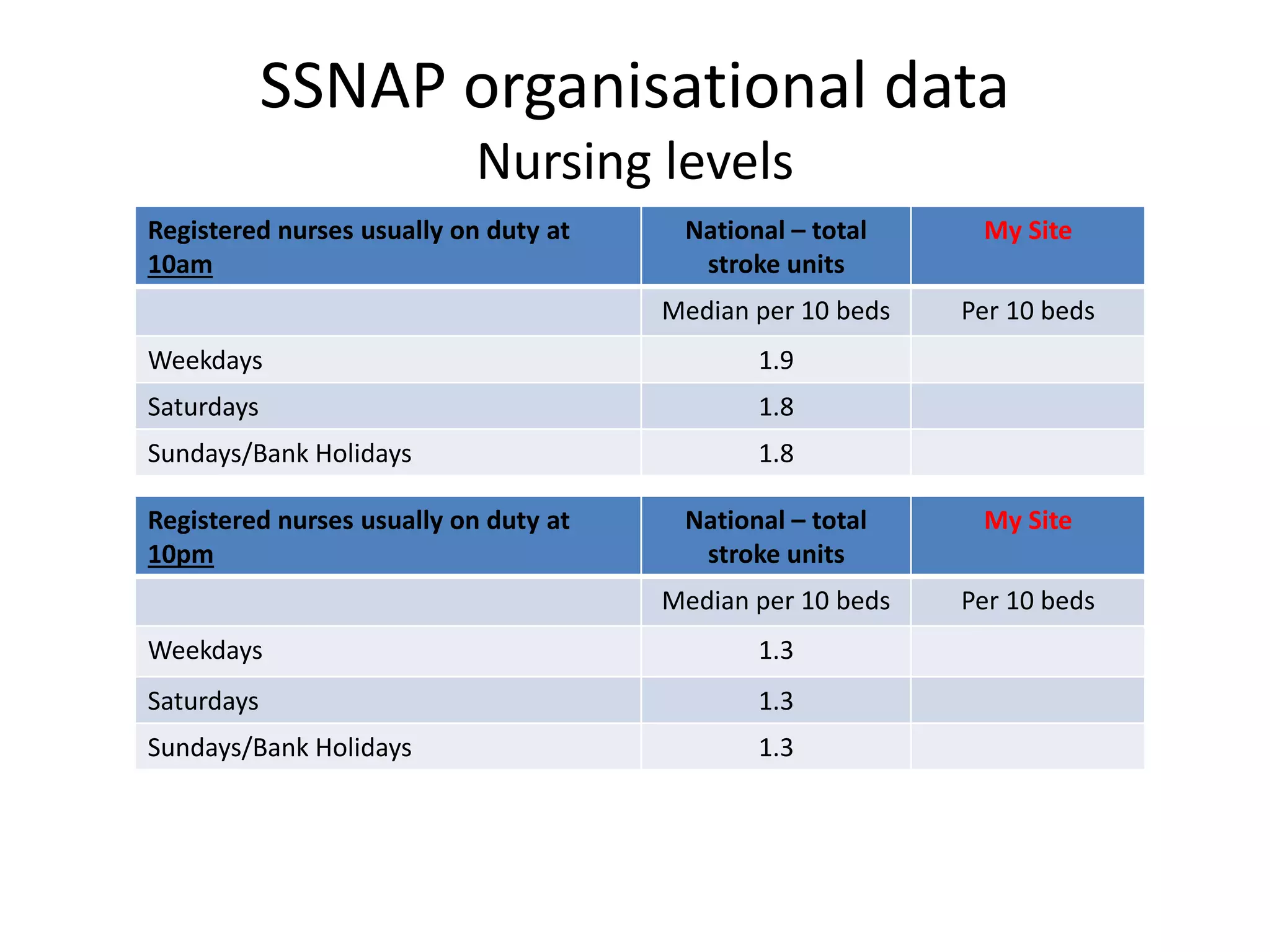
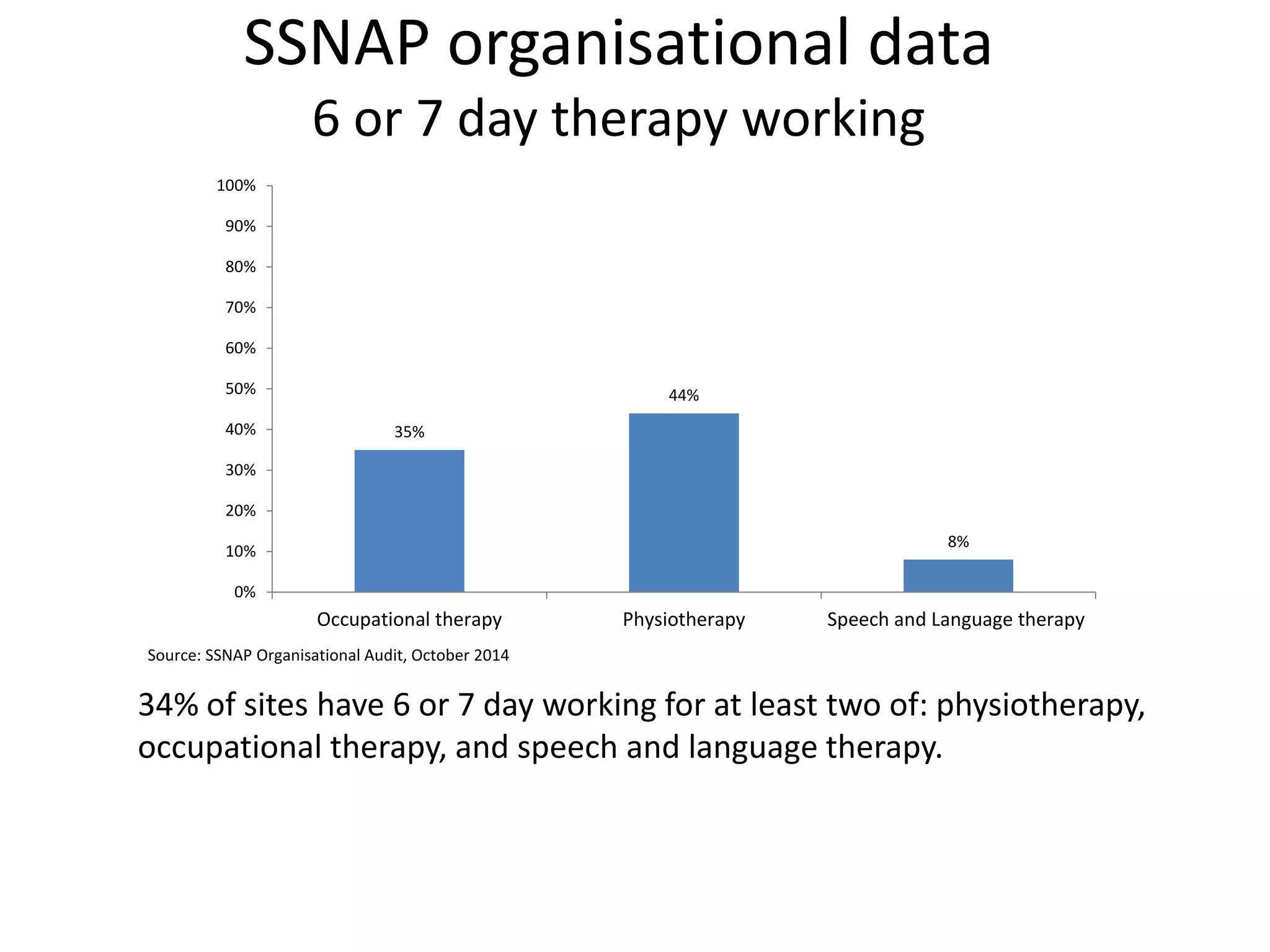
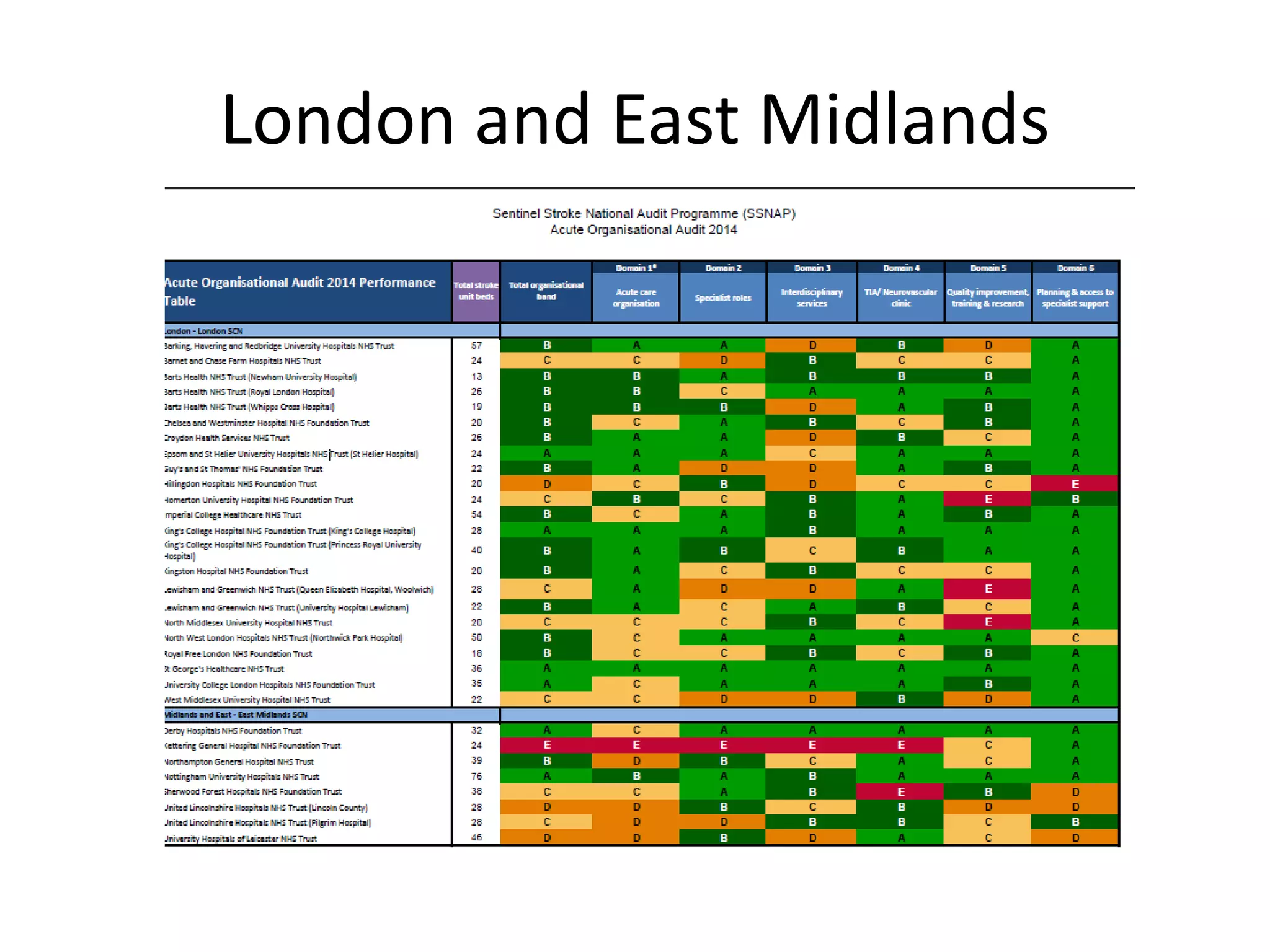
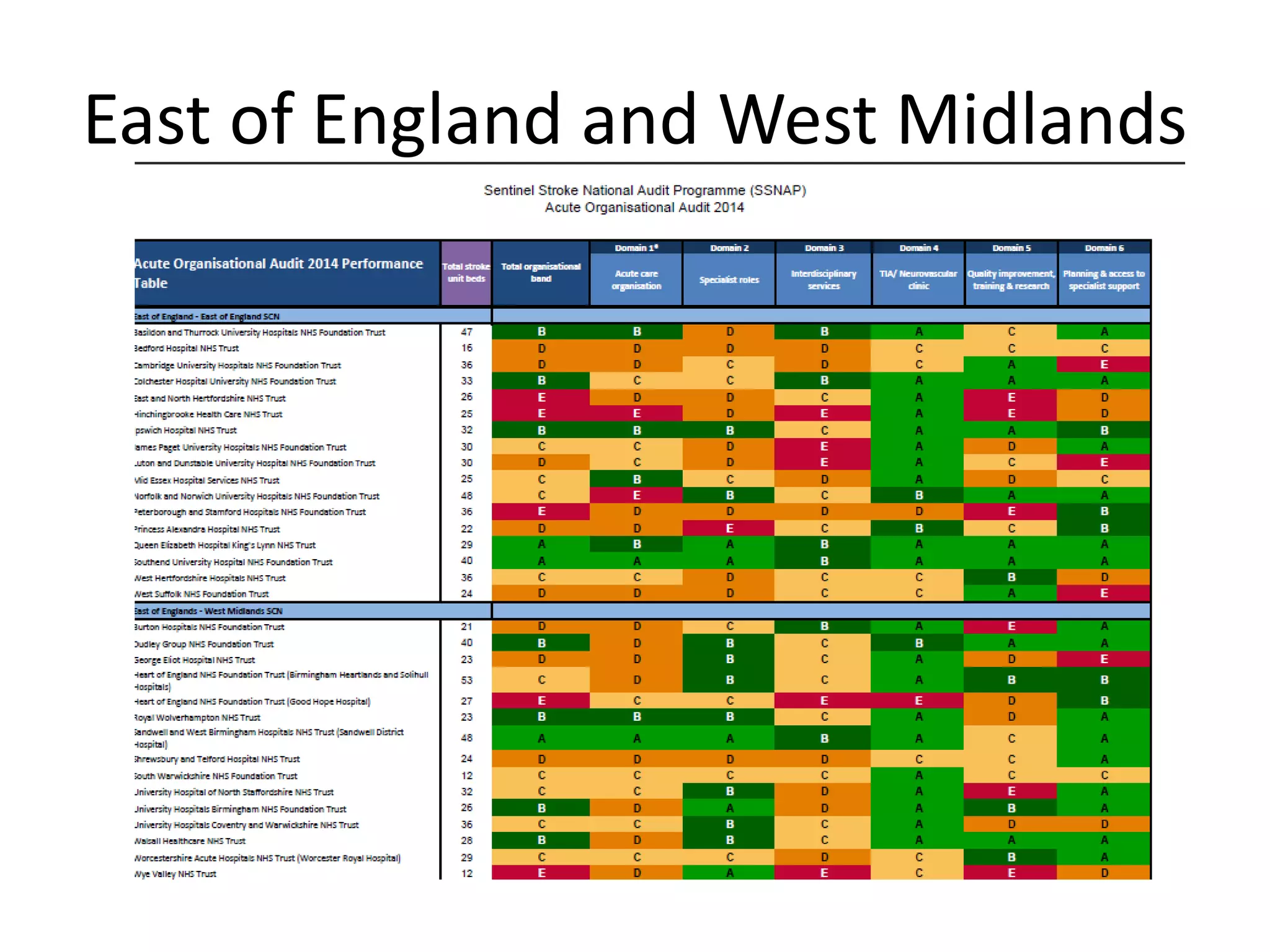
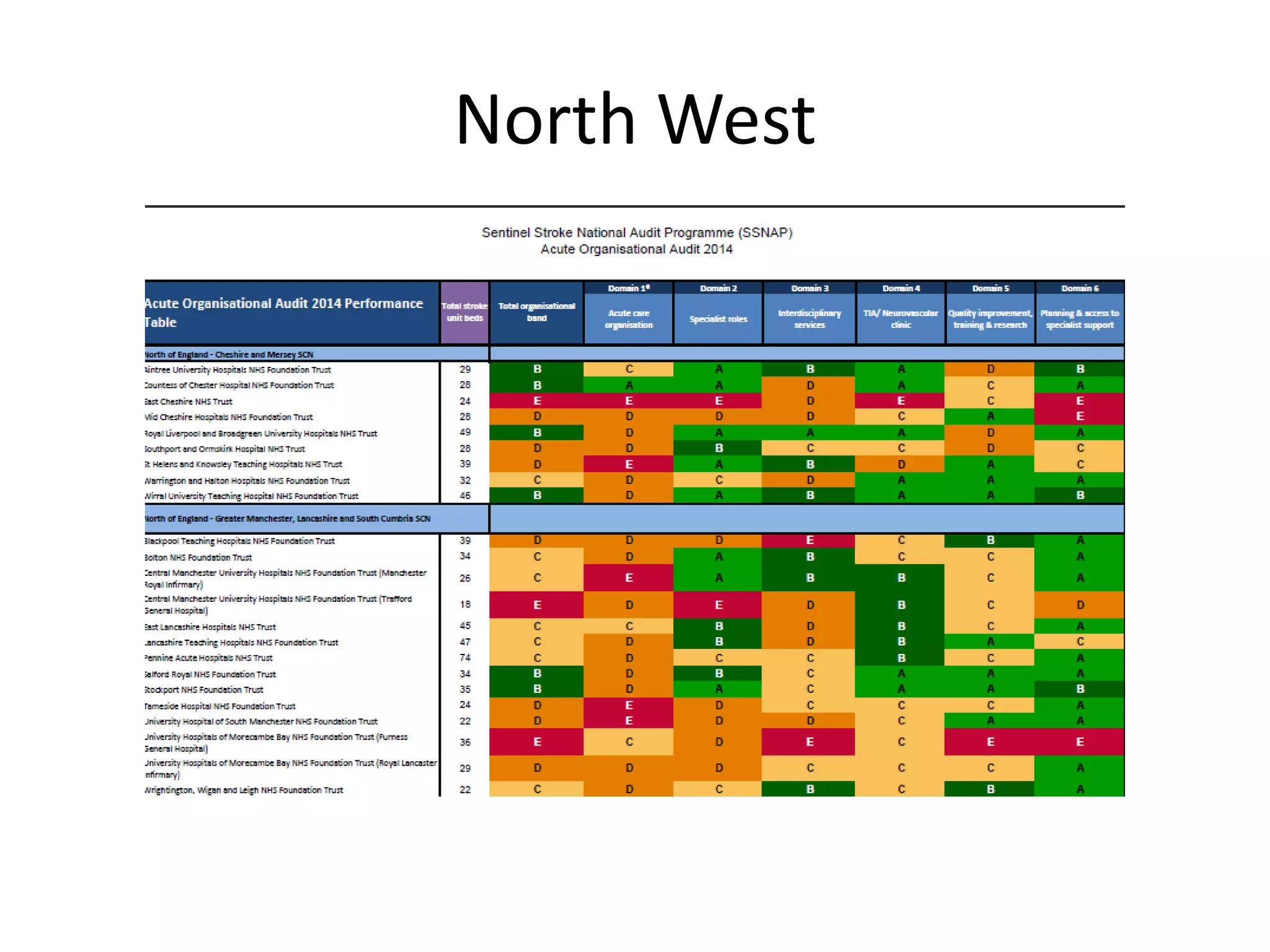
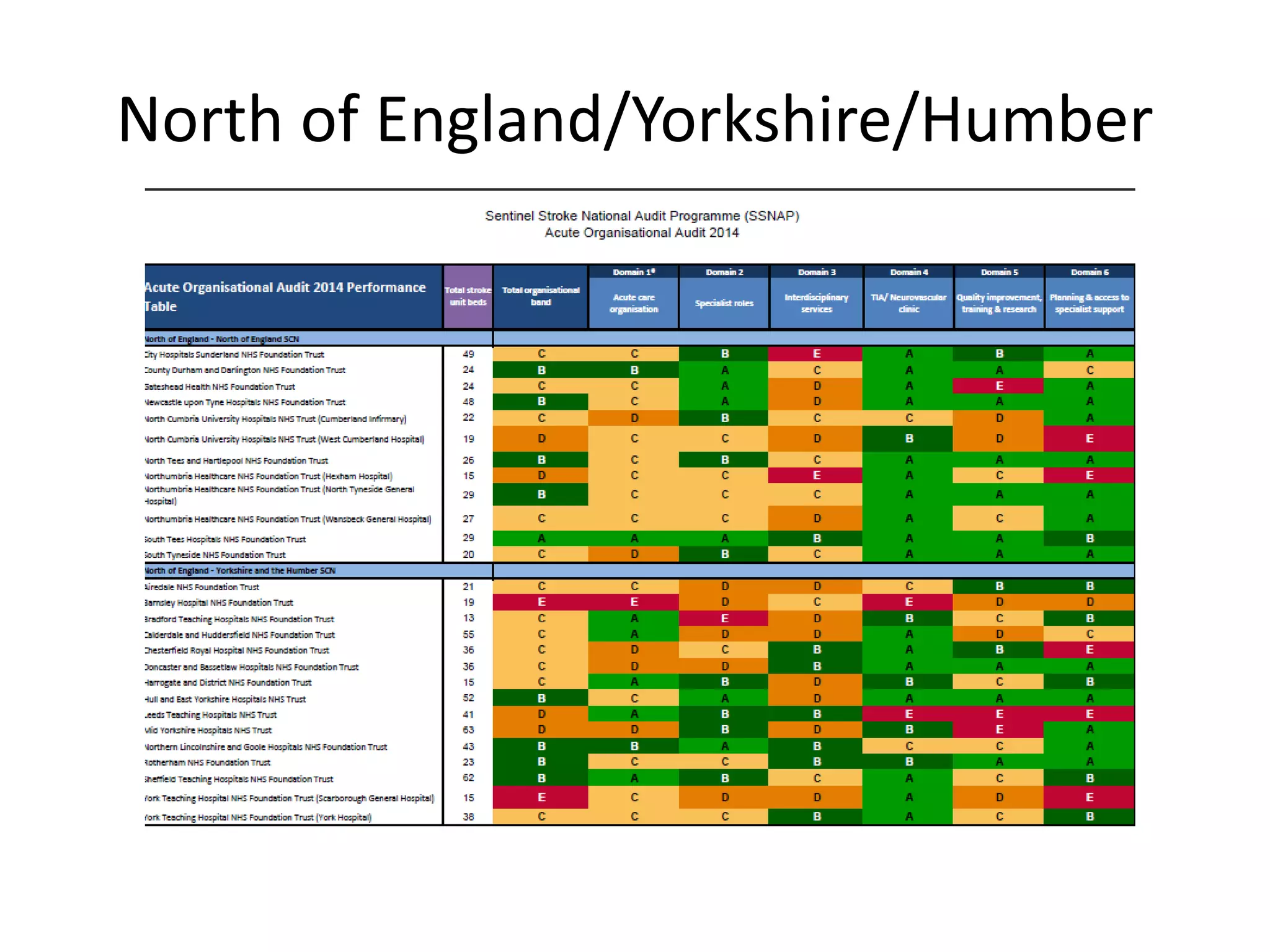
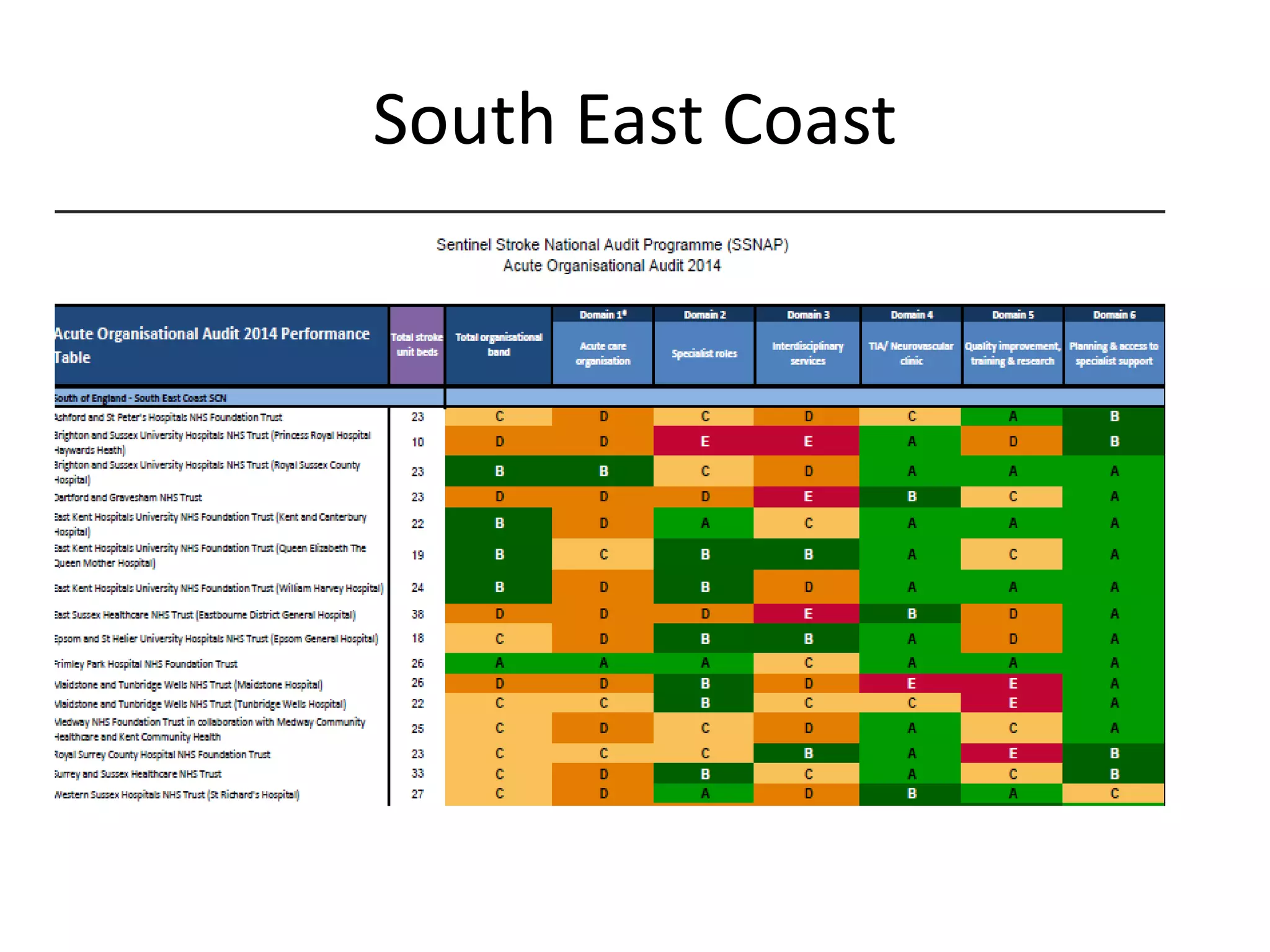
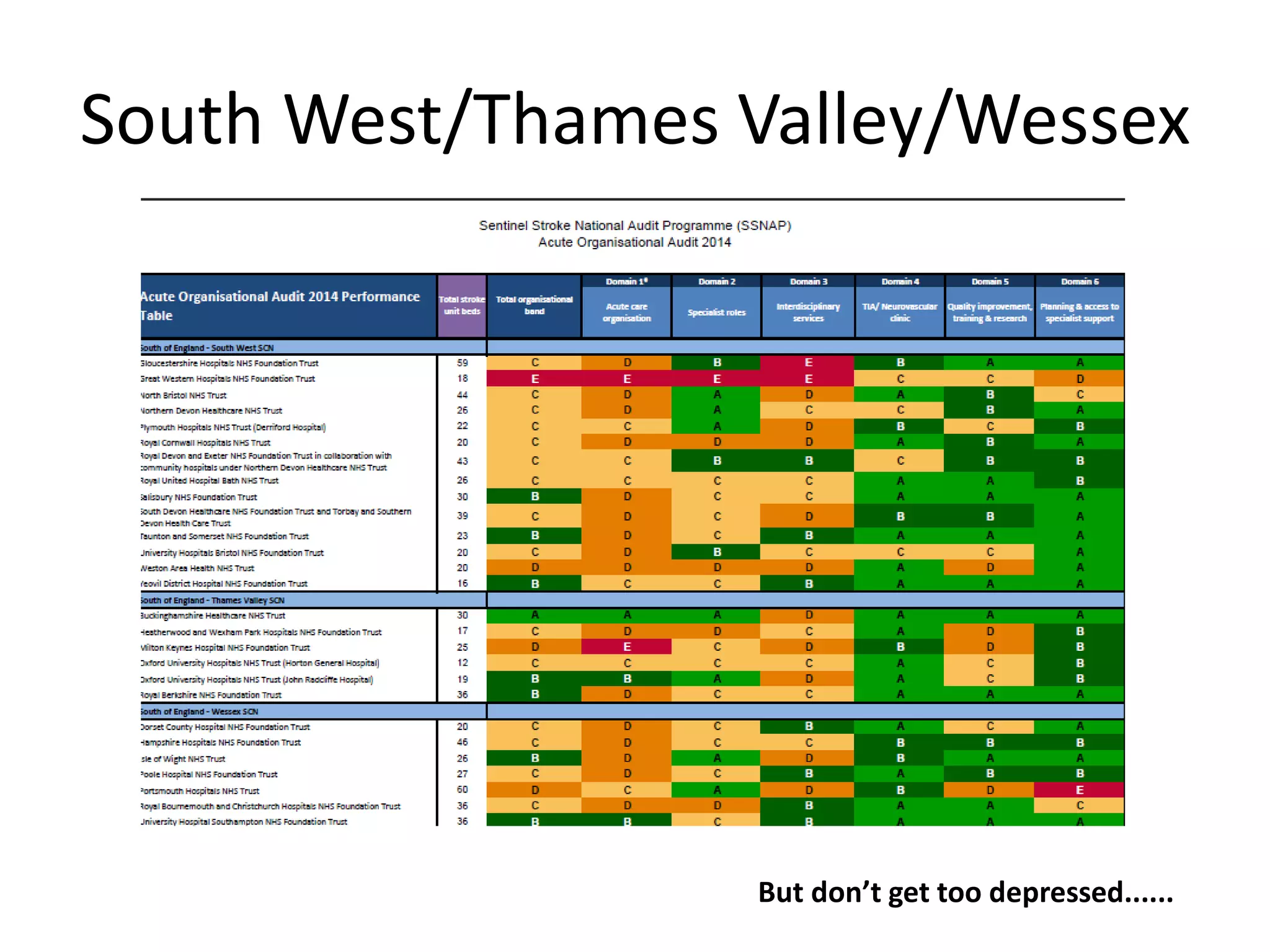
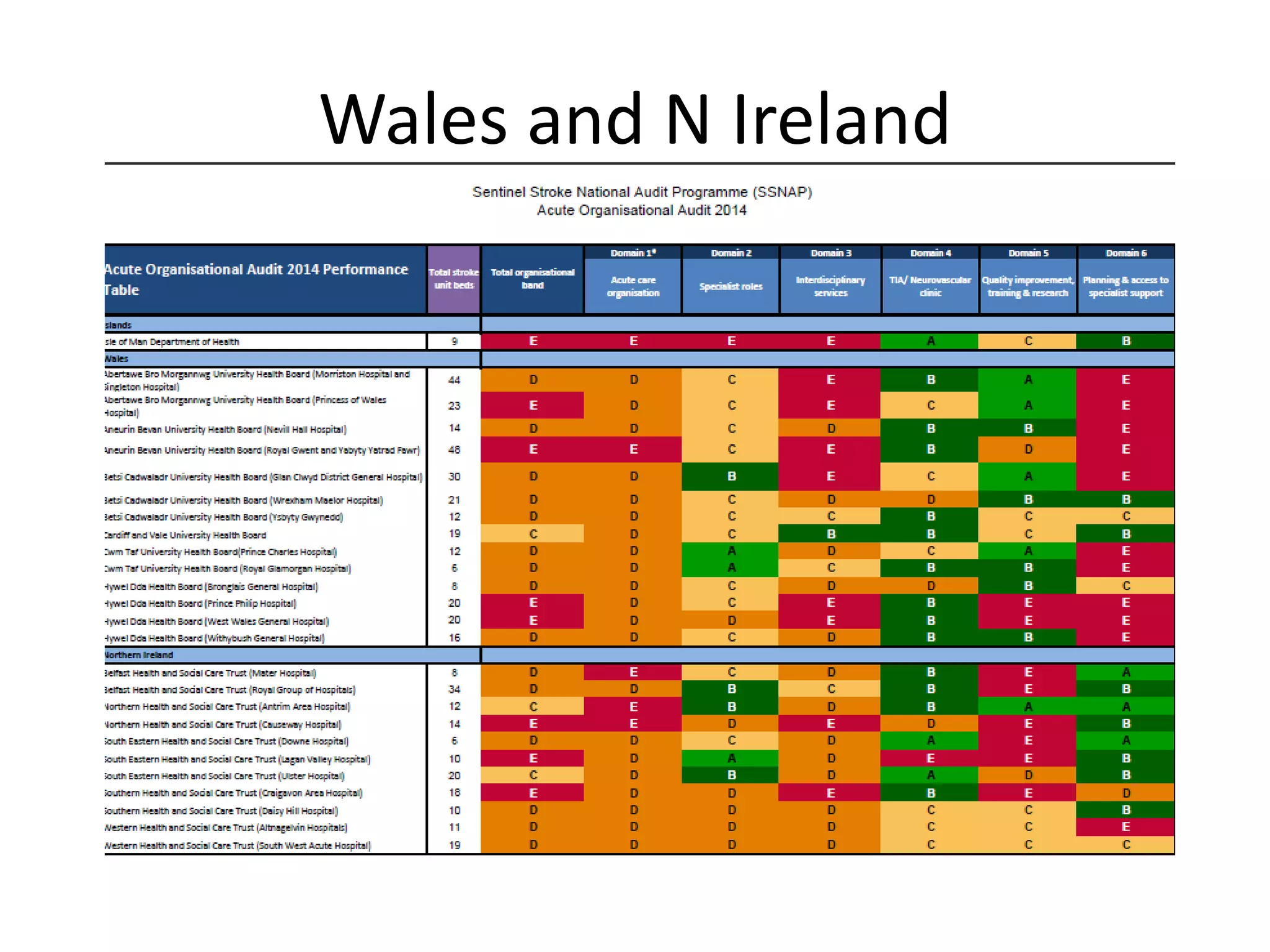
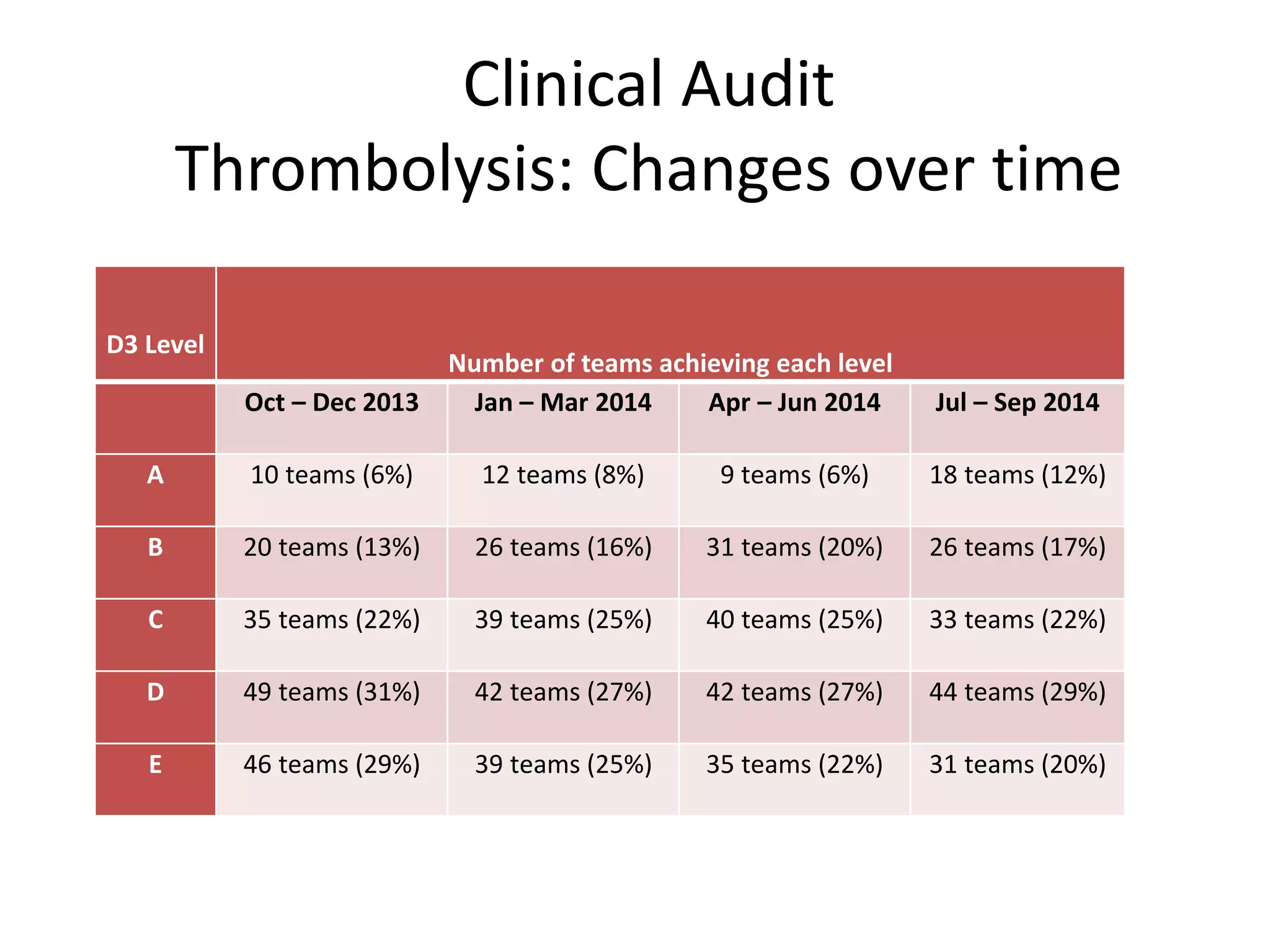
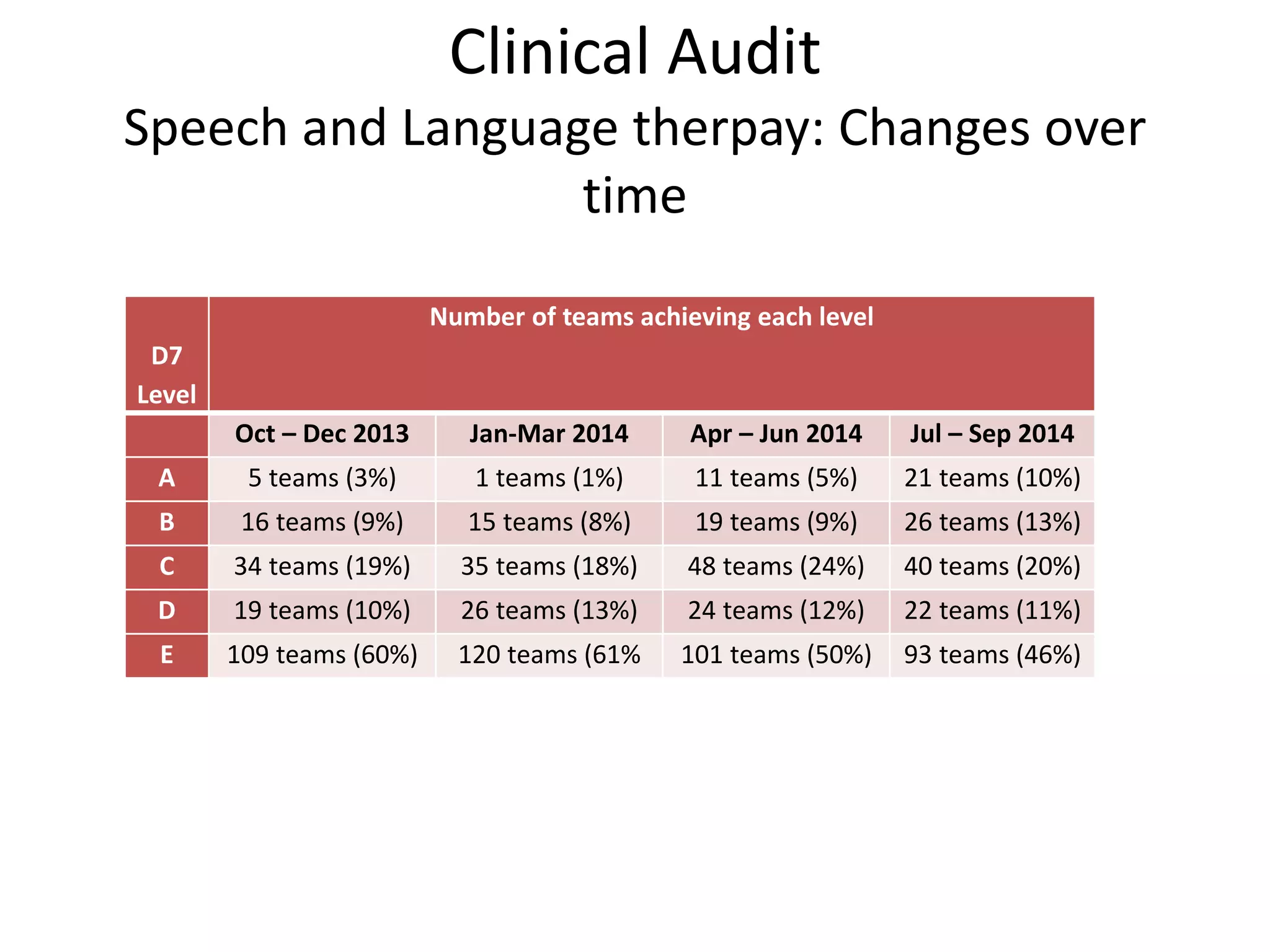
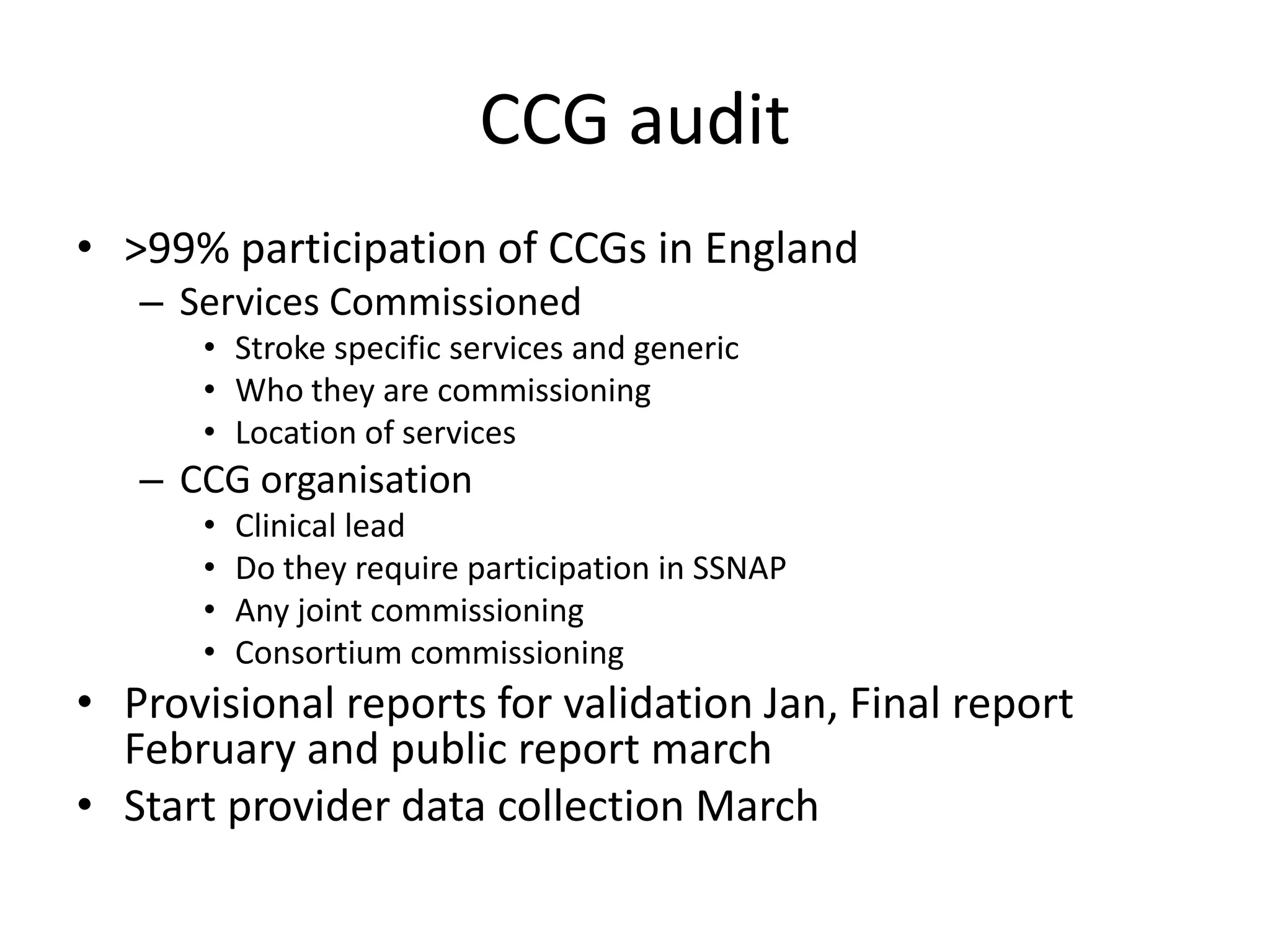
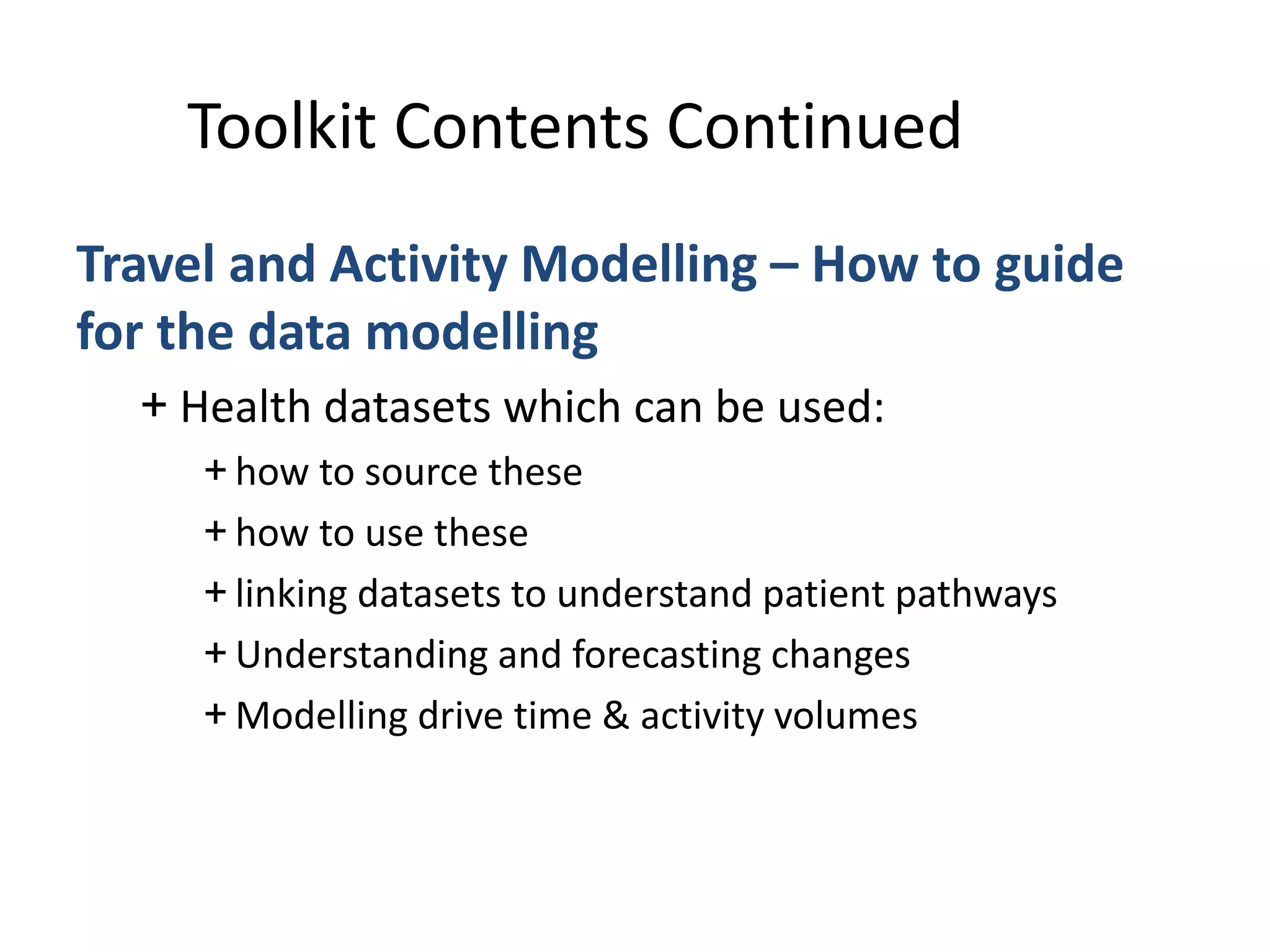
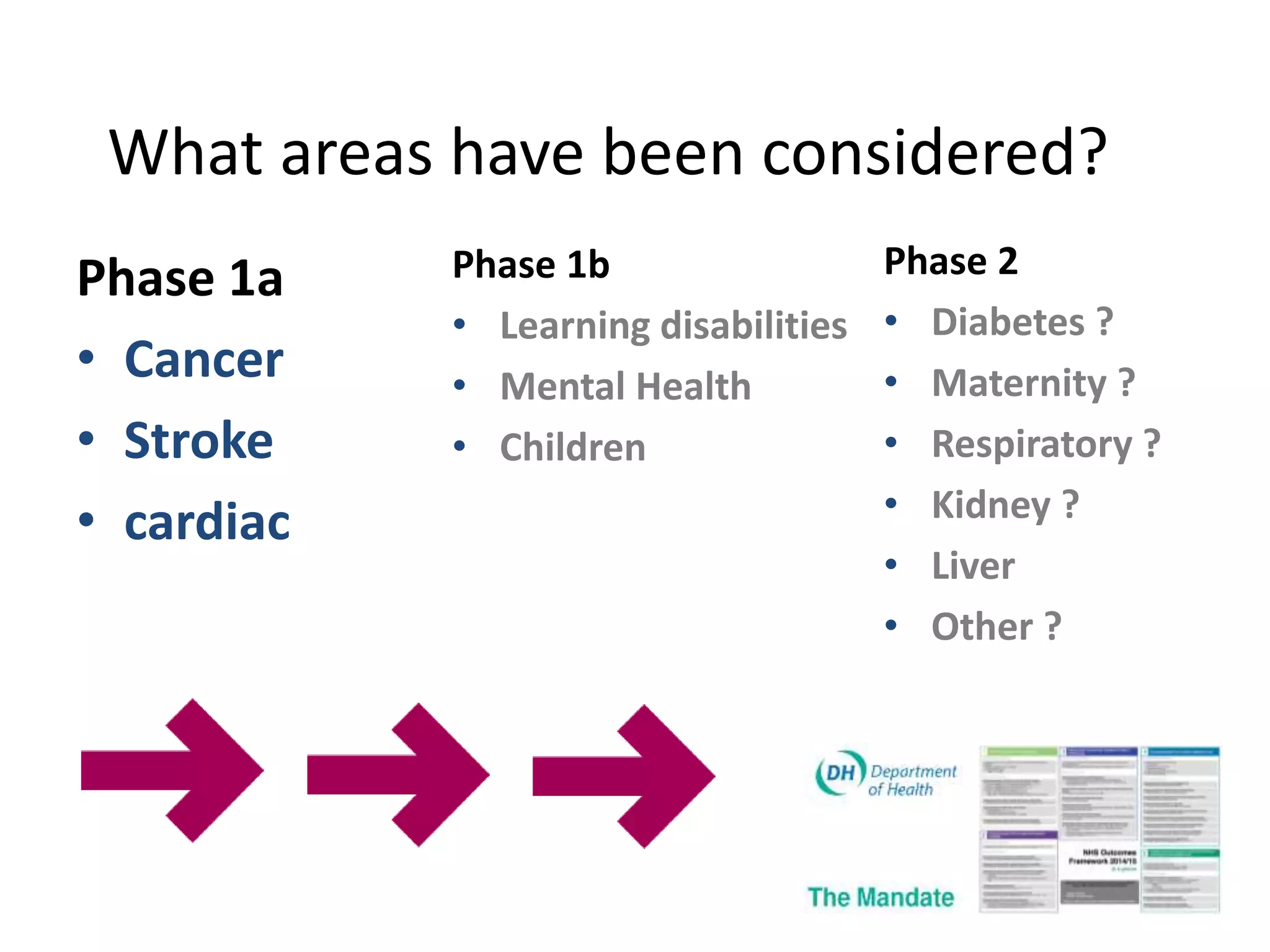
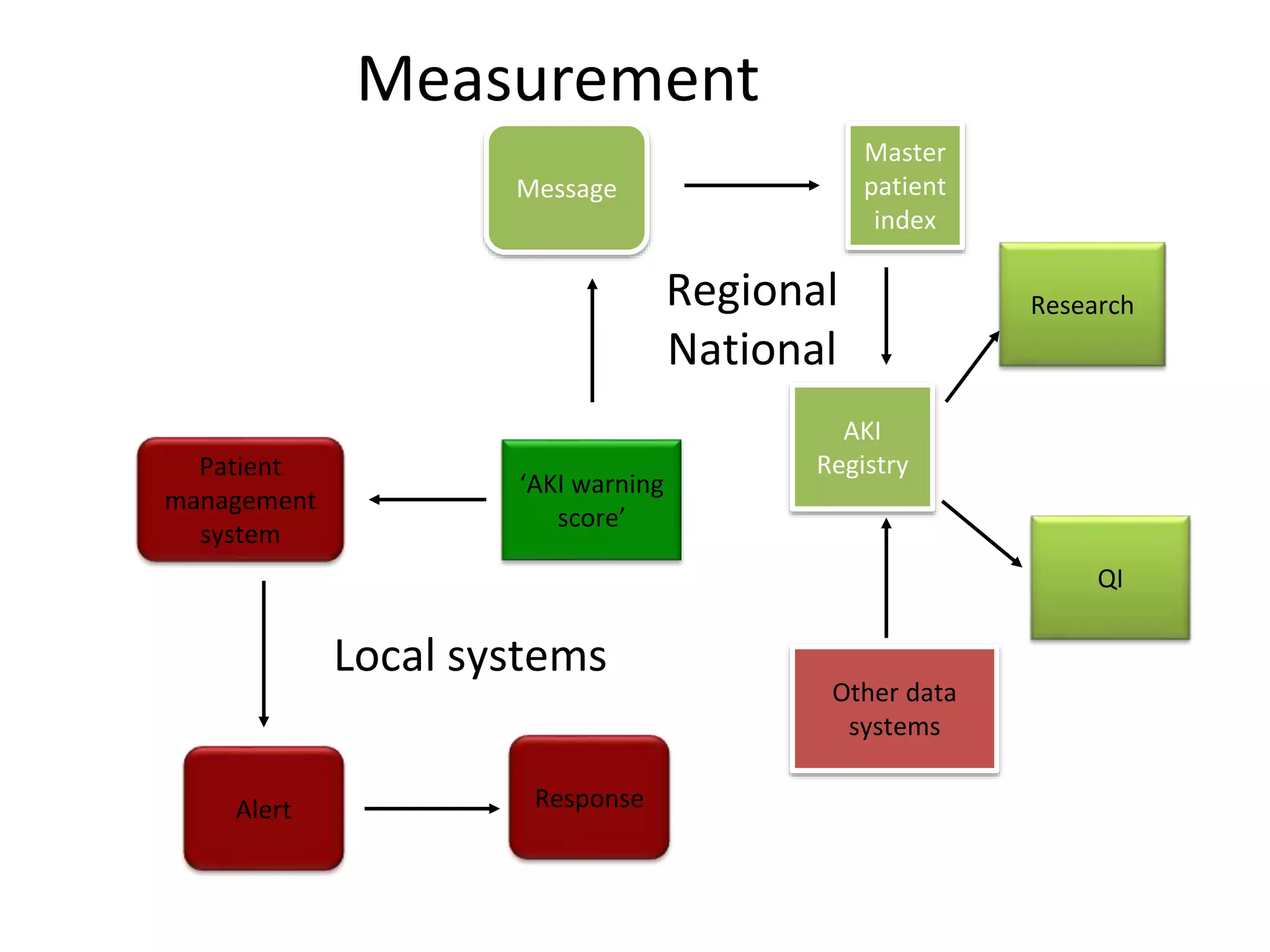
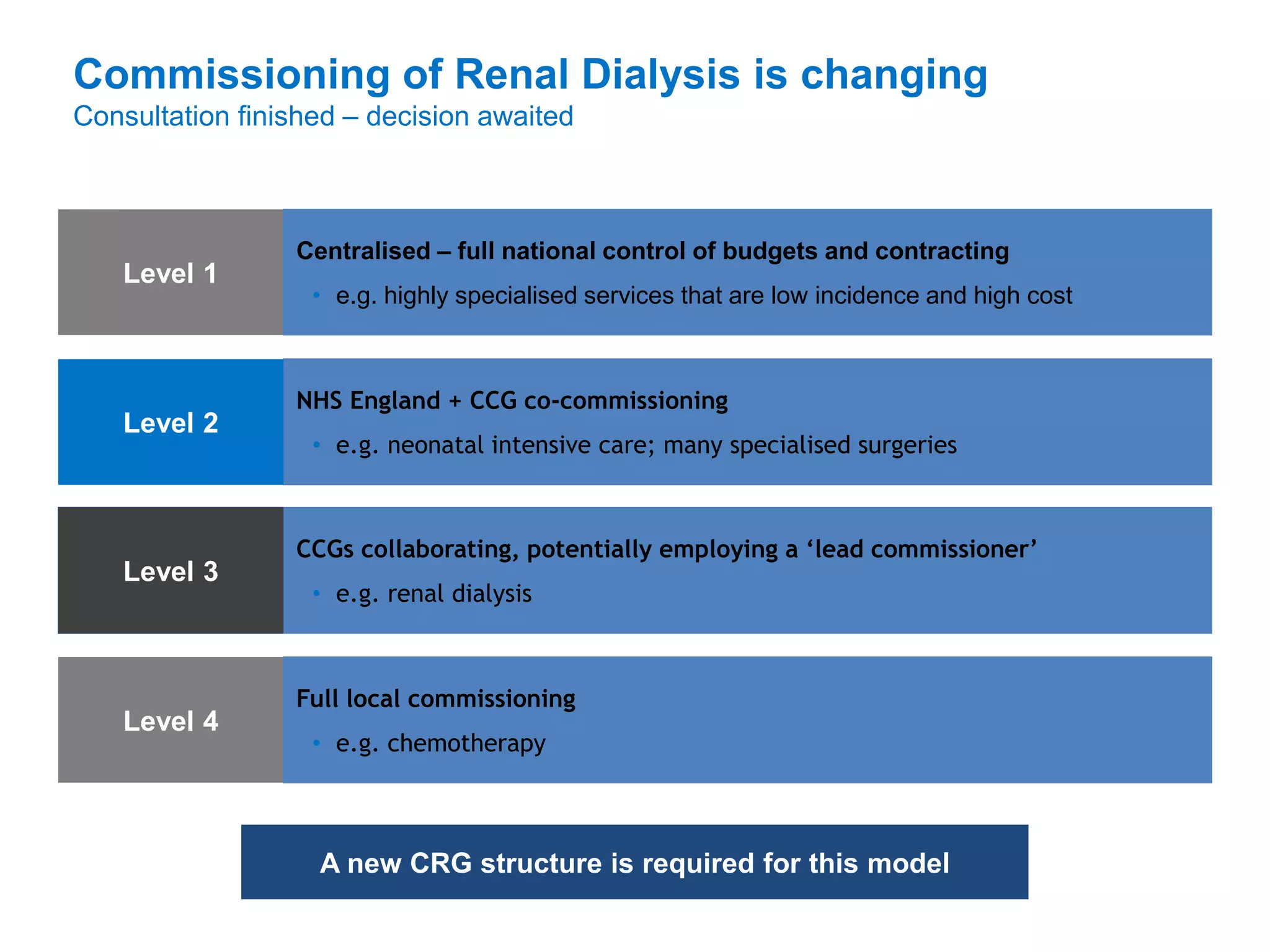
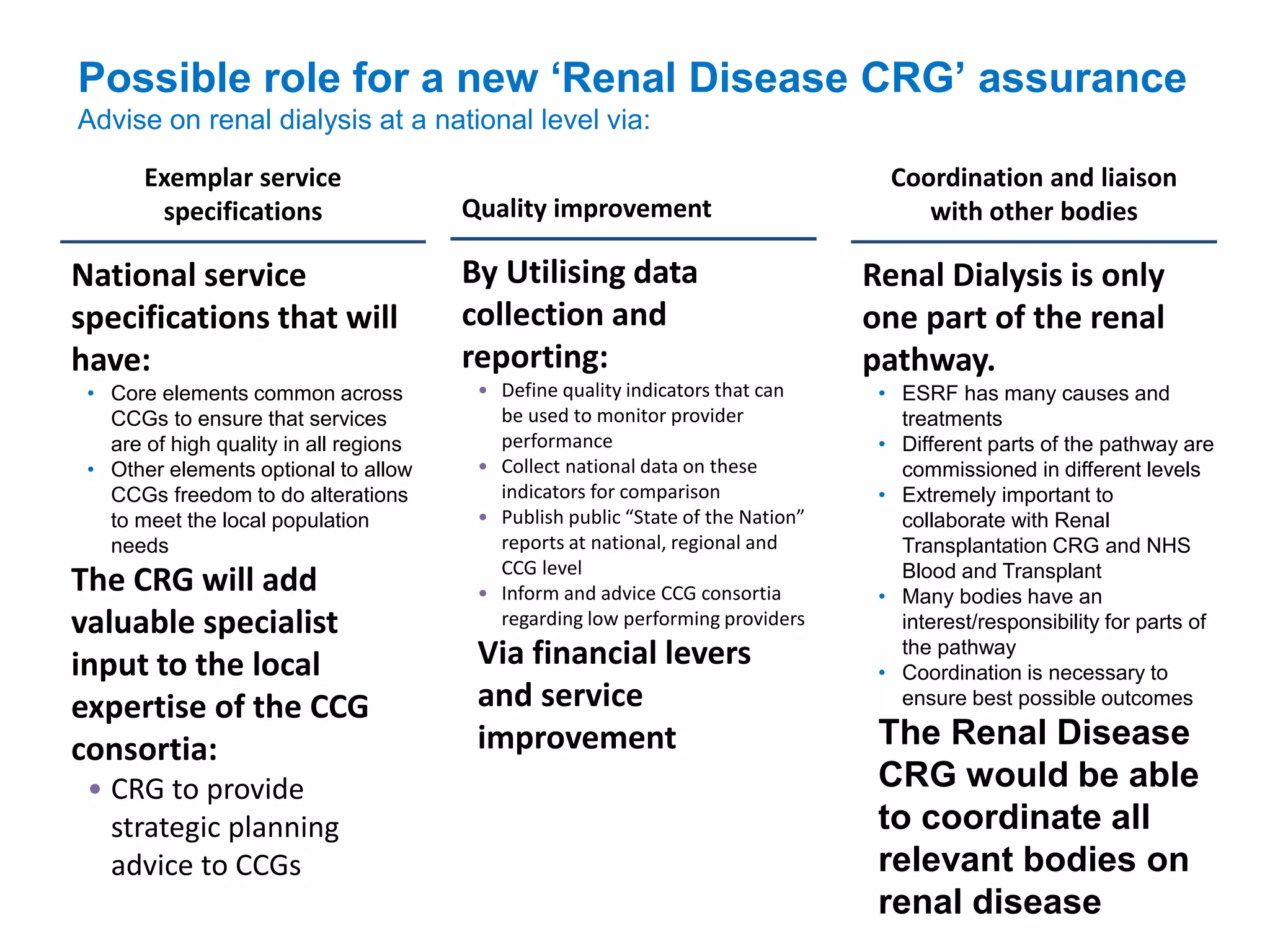
The document discusses attempts to improve health outcomes across England, focusing on cardiovascular disease and local leadership initiatives. Key themes include the empowerment of patients, innovation in care models, and the importance of effective commissioning and community engagement. The findings emphasize collaboration and systemic improvements in healthcare delivery as critical to achieving better health outcomes.






































![One Hackney Performance Metrics – Payment Basis
l
METRIC MEASURE/PAYMENT BASELINE TARGET
March 2015
TARGET
September 2015
TARGET
March 2016
1 Increase effectiveness of
reablement/rehabilitation
12 month period to target month.
Payment based on % achieved.
Payment baseline 90.4% (12 month period)
90.5% still at home
91 days after
discharge
1 additional
patient still at
home
90.5% - 100% paid
90.7% still at home
91 days after
discharge
8 additional
patients still at
home
90.6% - 50% paid
90.7% - 100% paid
91.2% still at home
91 days after
discharge
13 additional
patients still at
home
90.9% - 50% paid
91.2% - 100% paid
2 Increase proportion of people
dying outside hospital
43% deaths outside hospital
(2010-2012)
(461 deaths outside hospital out of 1082 total
deaths [EOLC Profiles])
Payment baseline 43% (12 month period)
43% deaths
outside hospital
(464 deaths outside
hospital out of 1085 total
deaths)
3 more deaths
outside hospital
43% - 100% paid
44% deaths outside
hospital (480 deaths
outside hospital out of 1088
total deaths)
19 more deaths
outside hospital
43% - 50% paid
44% - 100% paid
46% deaths outside
hospital (503 deaths
outside hospital out of 1091
total deaths)
42 more deaths
outside hospital
45% - 50% paid
46% - 100% paid
3 Emergency admissions for
over 75s to reduce to the
London average
(all emergency admissions excl maternity,
sickle dental and MH)
38 admissions per 1,000 population
over 75 per month (Apr 2011 – Jan
2014)
335 admissions per month [HES] for 8855
population [ONS 2013]
Payment baseline 335
Performance to be based on 12 month
average
Reduce admissions
by 5 per month to
330 admissions
335 - 50% paid
330 – 100% paid
Reduce admissions
by 15 per month to
320 admissions
Payment scale:
335 (no payment) –
320 (100% paid)
Reduce admissions
by 30 per month to
305 admissions
Payment scale:
335 (no payment) –
305 (100% paid)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-150204064347-conversion-gate02/75/Scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-54-2048.jpg)
![One Hackney Performance Metrics – Payment Basis
l
METRIC MEASURE/PAYMENT BASELINE TARGET
March 2015
TARGET
September 2015
TARGET
March 2016
4 Emergency admissions all ages to
remain lower than London average
(all emergency admissions excl maternity, sickle
dental and MH)
6.1 admissions per 1,000 population per
month (Apr 2011 – Jan 2014)
1735 admissions per month [HES] for 282,000
population [ONS 2013]
Payment baseline – London average
No increase in
admission rate
compared with
London total
Below London 12
month average – 100%
paid
No increase in
admission rate
compared with
London total
Below London 12
month average –
100% paid
No increase in
admission rate
compared with
London total
Below London 12
month average – 100%
paid
5 Reduce emergency bed days 3000 bed days per month for over 75s
(Apr 2012 – March 2013)
Payment baseline 3000 bed days per month for
over 75s
Performance based on 12 month average
Reduce bed days
by 15 to 2,985 per
month in over 75s
3000 - 50% paid
2985 – 100% paid
Reduce bed days
by 75 to 2,925
per month in over
75s
Payment scale:
3000 (no payment) –
2925 (100% paid)
Reduce bed days
by 150 to 2,850
per month in over
75s
Payment scale:
3000 (no payment) –
2850 (100% paid)
6 Reduce excess bed day costs £220k per month (Apr 2012 – March
2013)
Payment baseline £220k per month
Performance based on 12 month average
Reduction of £5k
per month to
£215k
£220k - 50% paid
£215k – 100% paid
Reduction of
£20k per month
to £200k
Payment scale:
220k (no payment) –
£200k (100% paid)
Reduction of £40k
per month to
£180k
Payment scale:
220k (no payment) –
£180k (100% paid)
7 Reduce % of admissions readmitted
within 30 days
19% of admissions readmitted within 30
days (Apr 2012 – November 2013)
Payment baseline 19% (rounded)
Performance based on 12 month period
19%
19% or below - 100%
paid
17%
Payment scale:
19% (no payment) –
17% (100% paid)
15%
Payment scale:
19% (no payment) –
15% (100% paid)
NB. One Hackney informed that baseline values being verified for more recent performance to ensure that targets still relevant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-150204064347-conversion-gate02/75/Scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-55-2048.jpg)




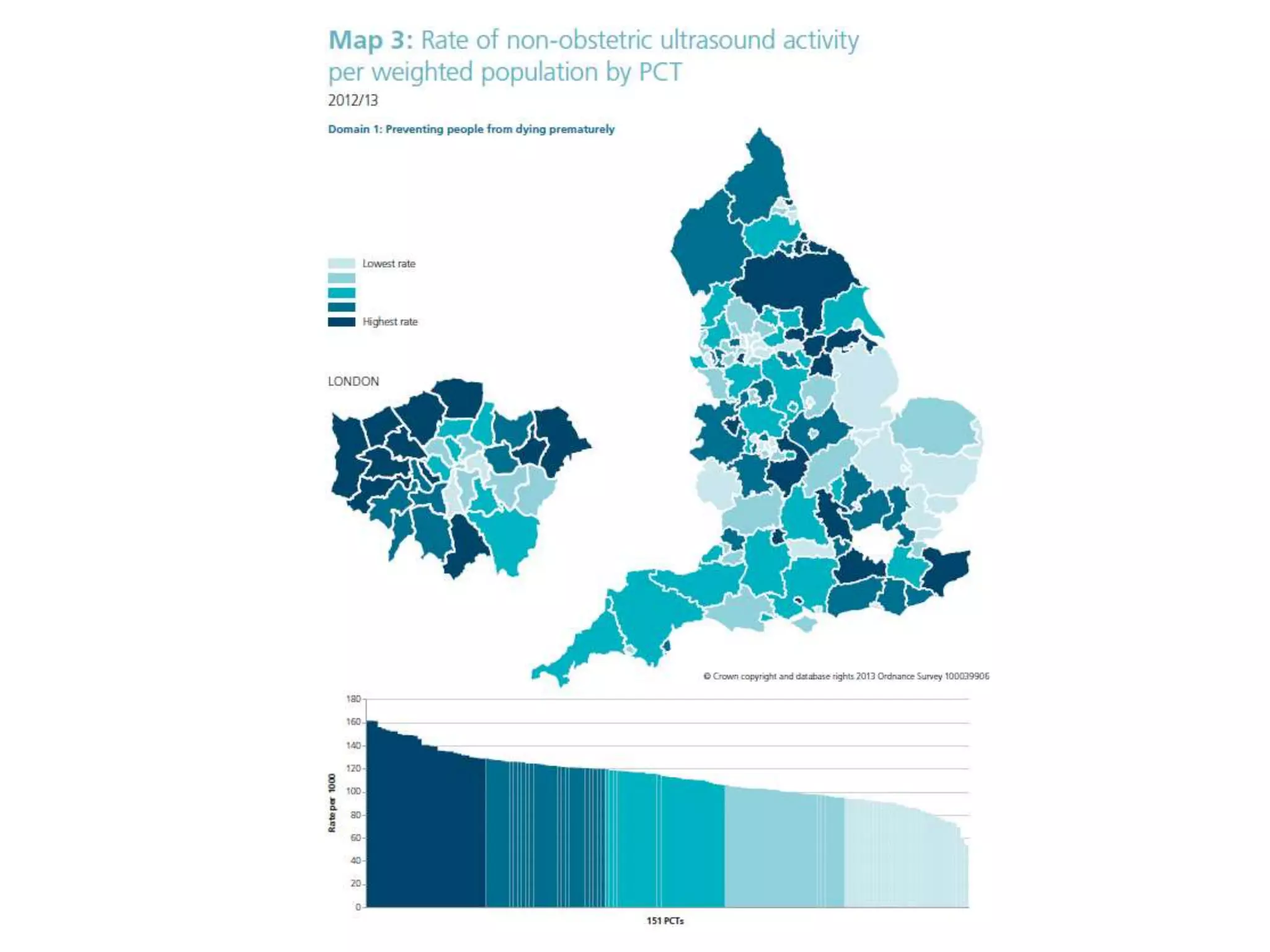













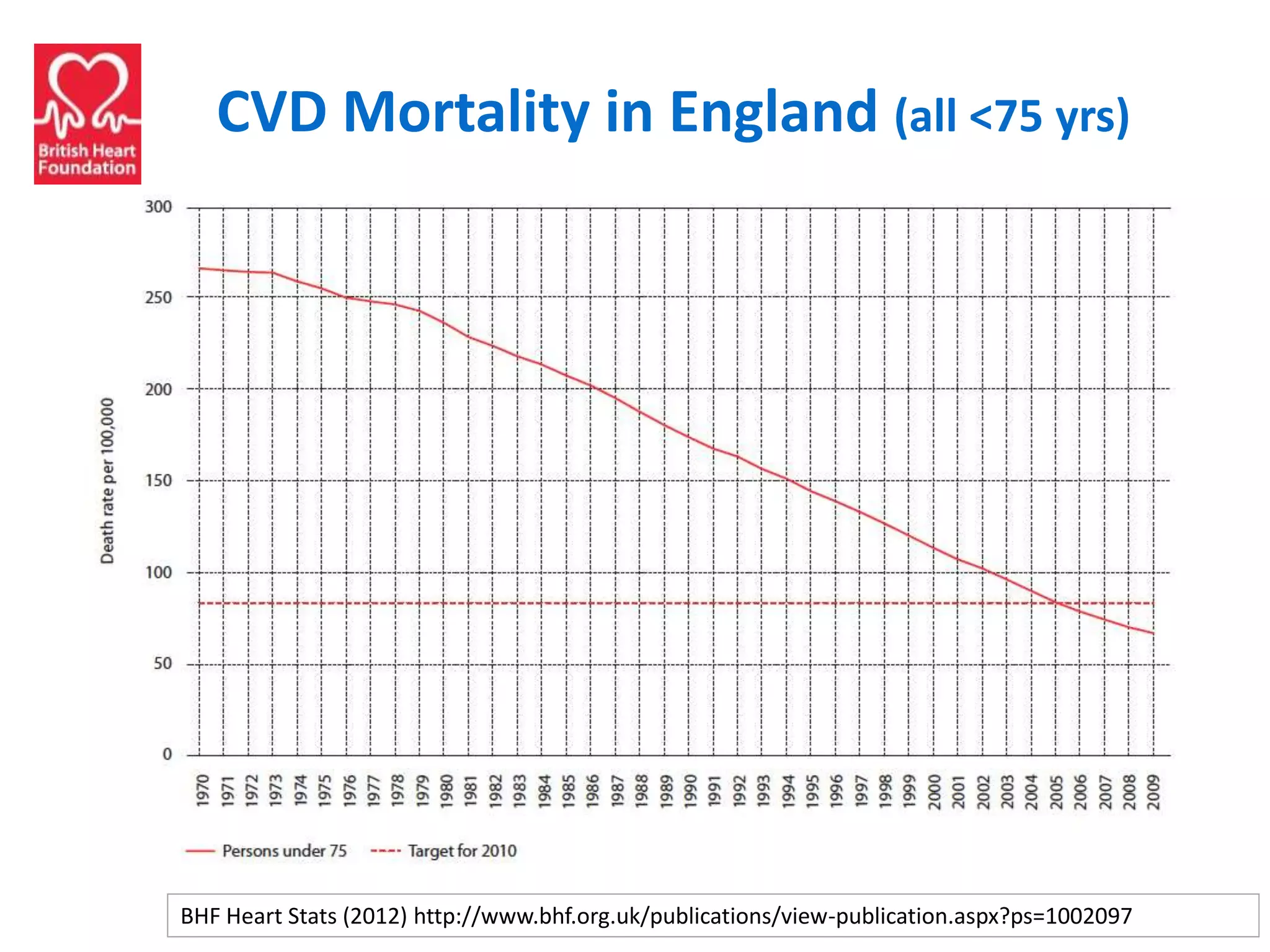
![Source: www.statistics.gov.uk/ statbase/Product.asp?vlnk=6725
Causes of Death (England, <75 yrs)
(Source: ‘Living Well for Longer’ [ONS data], 2013)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-150204064347-conversion-gate02/75/Scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-102-2048.jpg)
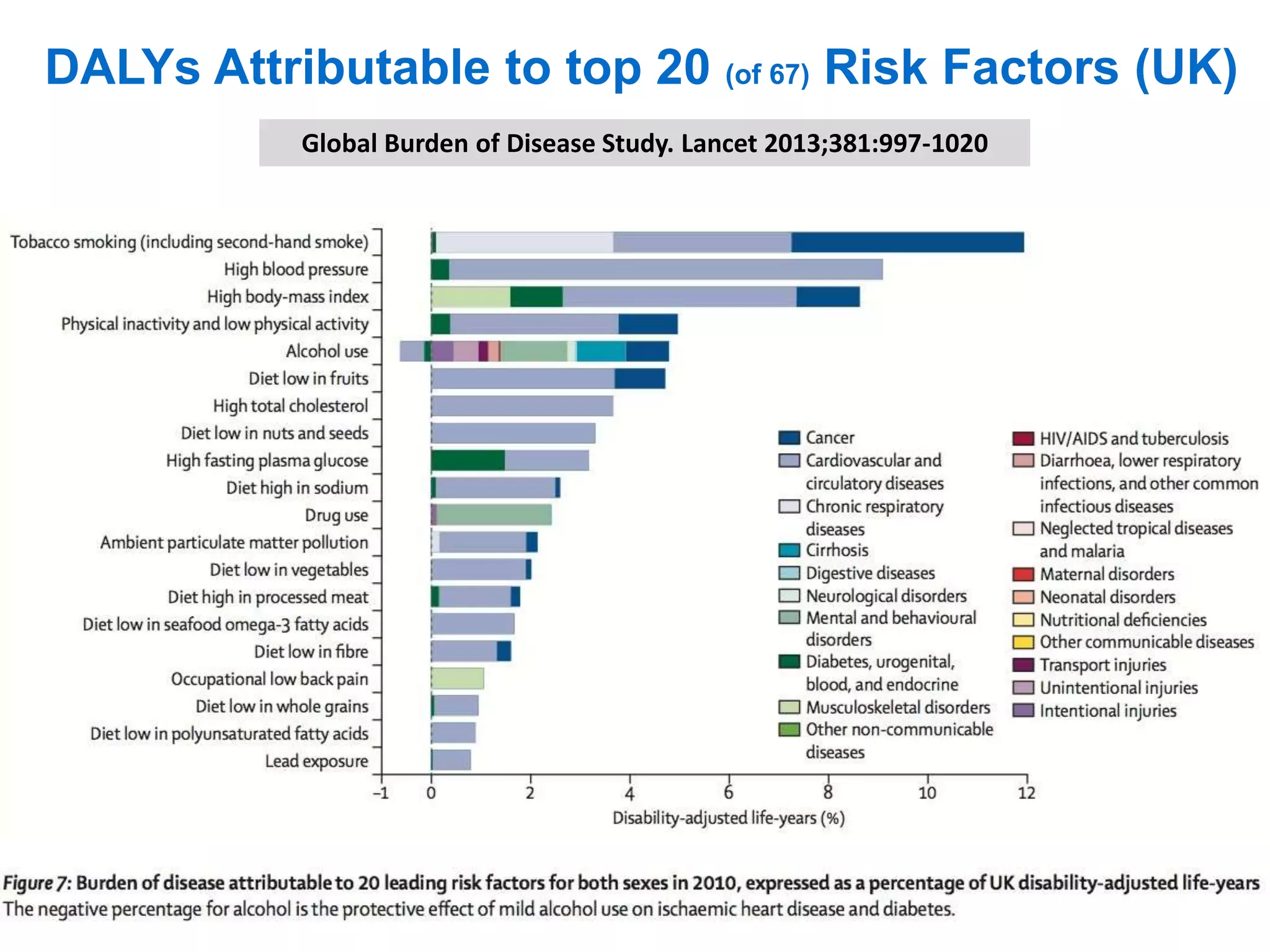
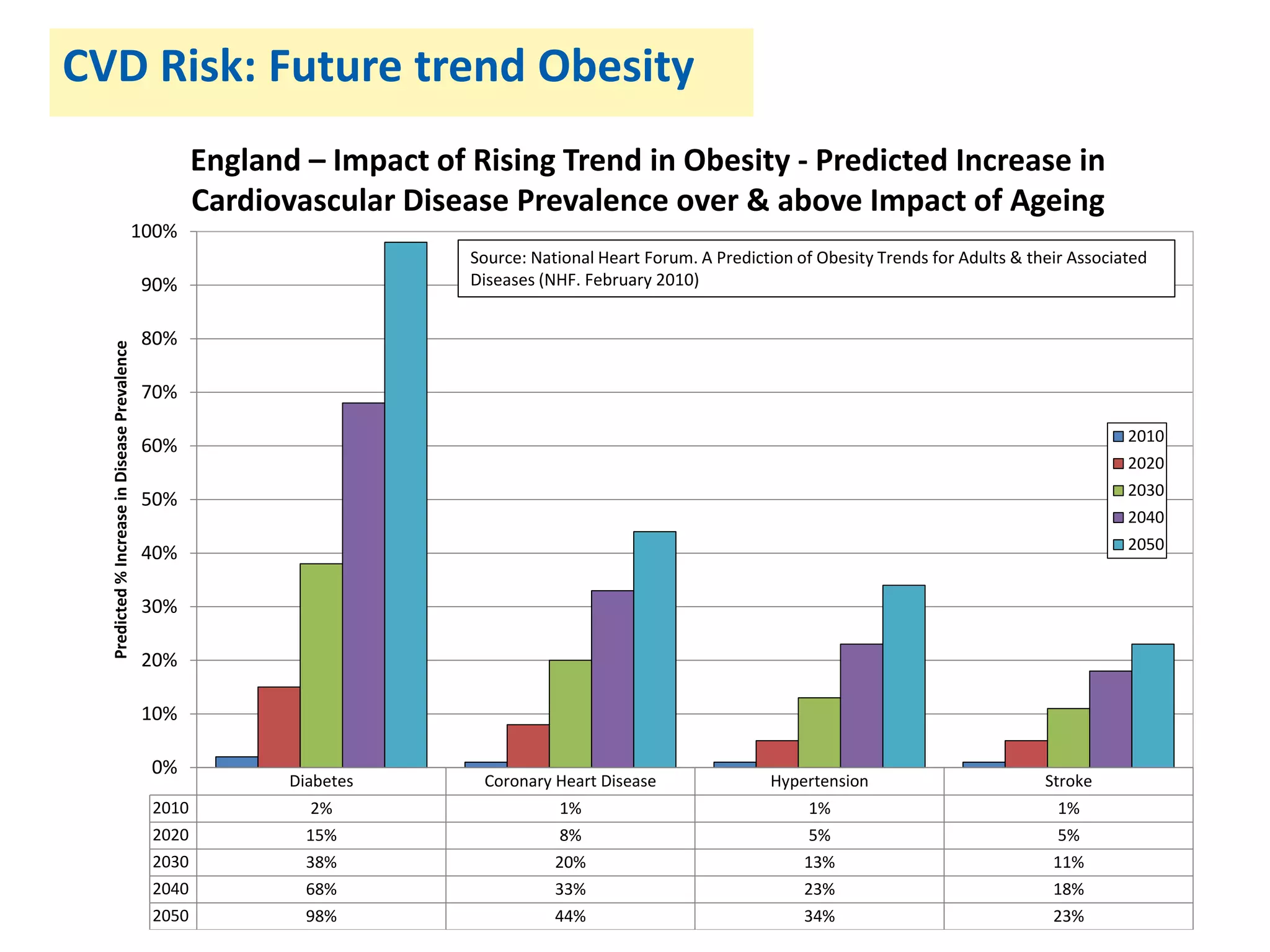
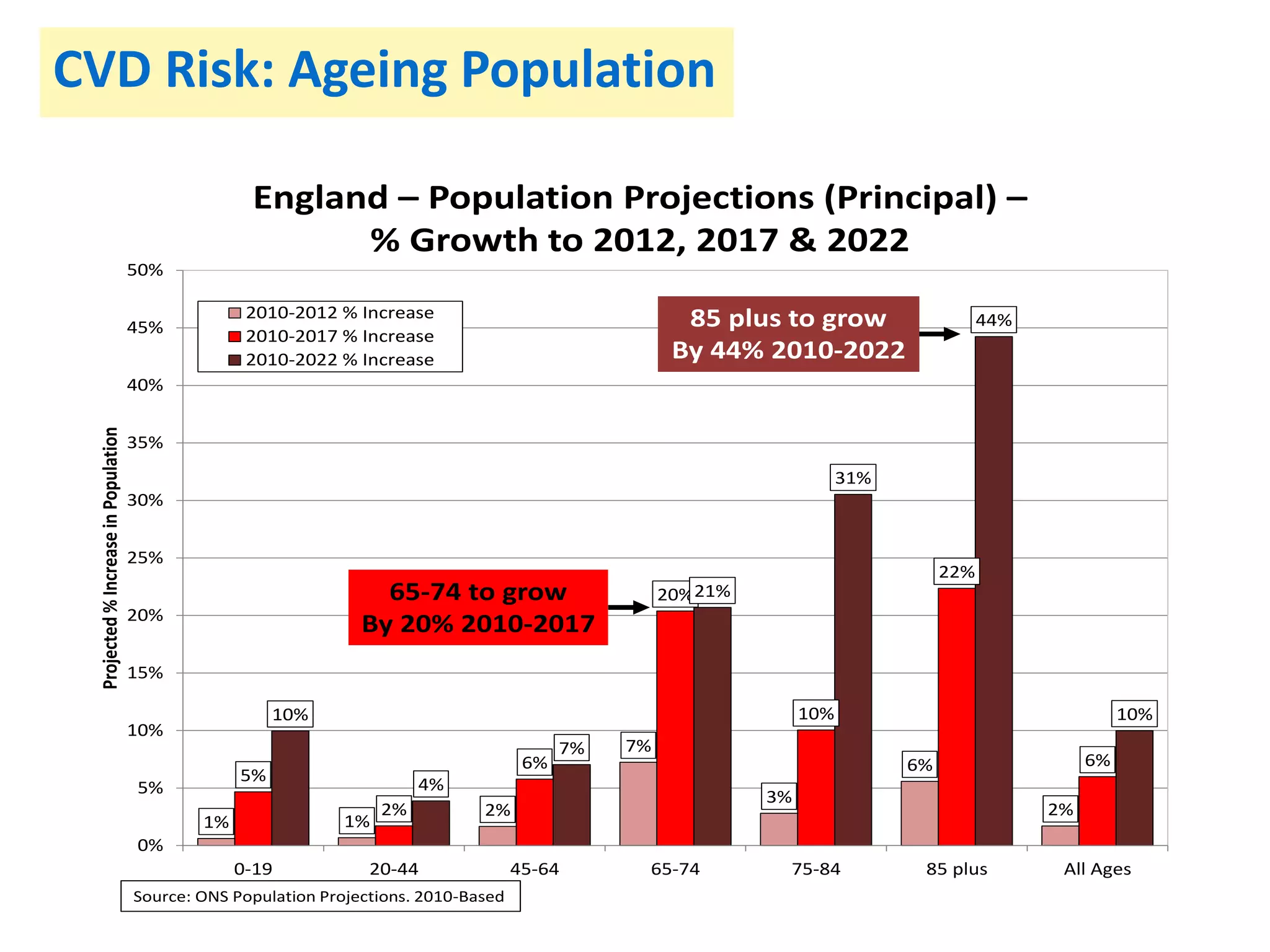












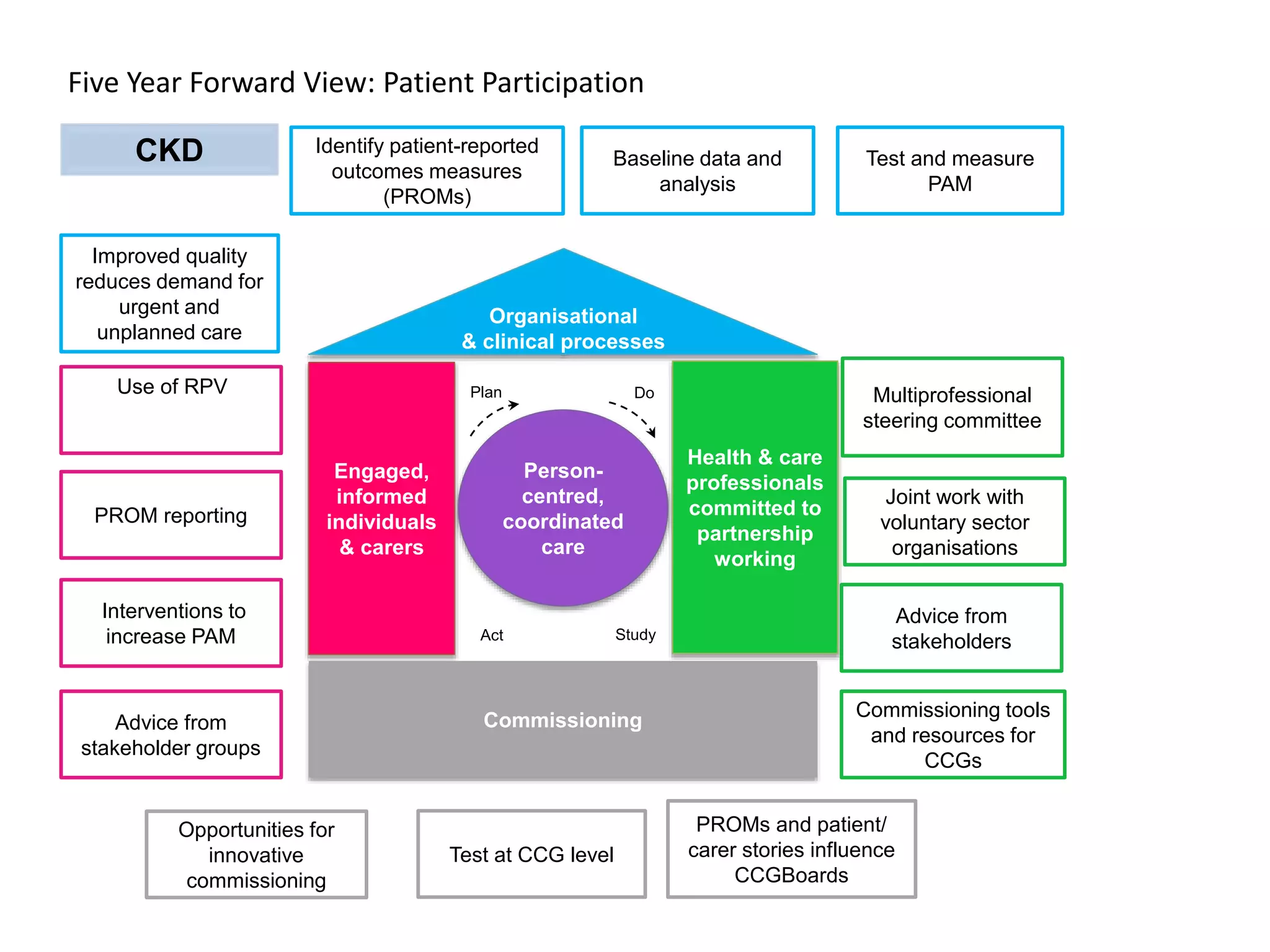









![• More people at high risk of developing diabetes will receive lifestyle
interventions to support them to lower their risk; and
• The incidence of Type 2 diabetes will reduce over the longer term;
and
• The incidence of heart, stroke, kidney, eye and foot problems (and
mortality) related to diabetes will reduce over the longer term.
Key success measures:
• [5-7%] weight reduction in participants of the programme
• Risk reduction in participants of the programme
• Reduction in the incidence of Type 2 diabetes and associated
diseases (heart attacks, strokes, etc)
Benefits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-150204064347-conversion-gate02/75/Scn-cvd-network-meeting-jan-2015-157-2048.jpg)