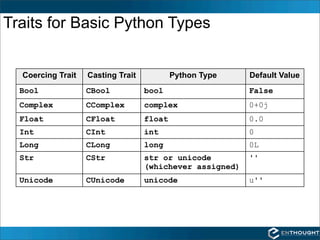
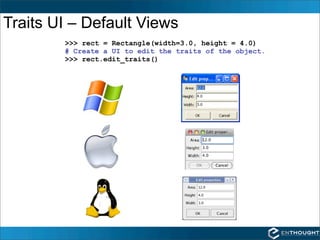
Traits provide additional functionality for Python object attributes such as initialization, validation, delegation, and notification. Traits are defined by deriving a class from HasTraits and declaring attributes as specific trait types like Float or Int. Trait values can be set and observed either statically via observer methods or dynamically by registering callback functions with on_trait_change.