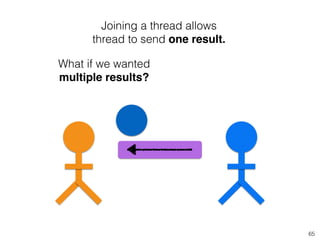
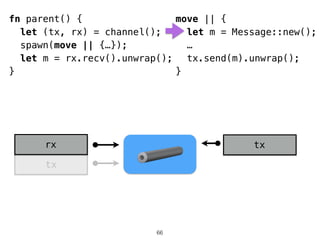
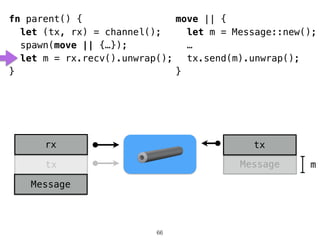
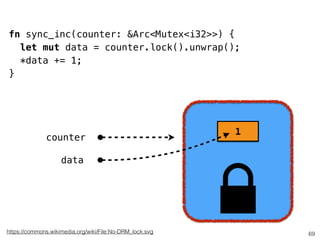
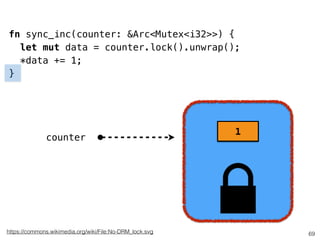
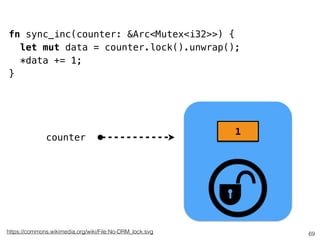
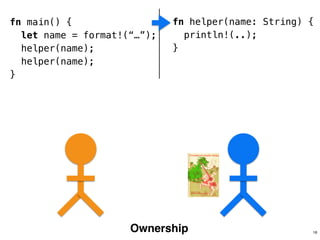
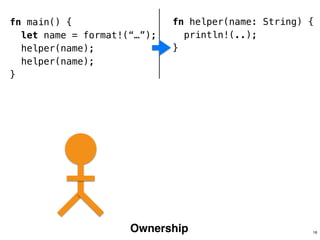
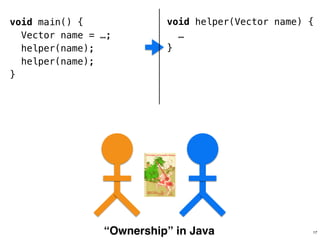
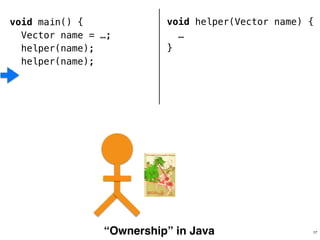
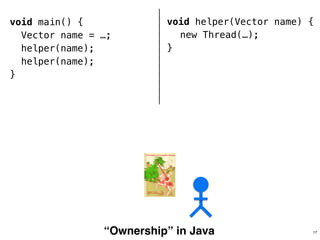
The document discusses Rust programming concepts focusing on ownership, borrowing, and safety, illustrating how to manage memory without runtime errors. It includes examples of functions that sum positive integers, handle parallel sorting, and demonstrate ownership rules through code snippets. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of an open-source community that supports learning and experimentation in systems programming.




![// sums all the positive values in `v`
fn sum_pos(v: &[i32]) -> i32 {
let mut sum = 0;
for i in v.iter().filter(|i| **i > 0) {
sum += *i;
}
sum
}
High-level coding
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-5-320.jpg)
![// sums all the positive values in `v`
fn sum_pos(v: &[i32]) -> i32 {
let mut sum = 0;
for i in v.iter().filter(|i| **i > 0) {
sum += *i;
}
sum
}
High-level coding
3
Iterators.
Closures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-6-320.jpg)

![fn foo(v: &[i32]) -> i32 {
v.iter()
.filter(|i| **i > 0)
.map(|i| *i)
.sum()
}
Higher-level coding
5
…generates the same assembly code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-8-320.jpg)



![fn parallel_qsort(vec: &mut [int]) {
if vec.len() <= 1 { return; }
let pivot = vec[random(vec.len())];
let mid = vec.partition(vec, pivot);
let (less, greater) = vec.split_at_mut(mid);
rayon::join(
|| parallel_qsort(less),
|| parallel_qsort(greater)
);
}
Parallel
7Caveat: shameless plug for third-party package of mine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-12-320.jpg)
![fn parallel_qsort(vec: &mut [int]) {
if vec.len() <= 1 { return; }
let pivot = vec[random(vec.len())];
let mid = vec.partition(vec, pivot);
let (less, greater) = vec.split_at_mut(mid);
rayon::join(
|| parallel_qsort(less),
|| parallel_qsort(greater)
);
}
Parallel
7
Sort left and right
in parallel.Caveat: shameless plug for third-party package of mine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-13-320.jpg)
![fn parallel_qsort(vec: &mut [int]) {
if vec.len() <= 1 { return; }
let pivot = vec[random(vec.len())];
let mid = vec.partition(vec, pivot);
let (less, greater) = vec.split_at_mut(mid);
rayon::join(
|| parallel_qsort(less),
|| parallel_qsort(less)
);
}
Parallel… and safe
8
Data race.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-14-320.jpg)
![fn parallel_qsort(vec: &mut [int]) {
if vec.len() <= 1 { return; }
let pivot = vec[random(vec.len())];
let mid = vec.partition(vec, pivot);
let (less, greater) = vec.split_at_mut(mid);
rayon::join(
|| parallel_qsort(less),
|| parallel_qsort(less)
);
}
Parallel… and safe
8
error: closure requires unique access to `less`
but it is already borrowed
|| parallel_qsort(less)
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Data race.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-15-320.jpg)























































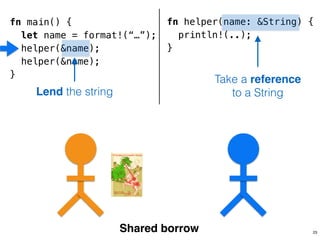
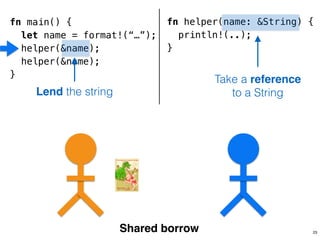















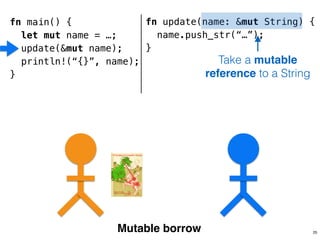







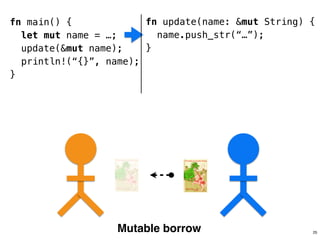
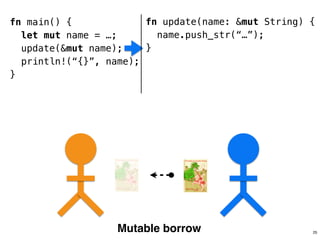






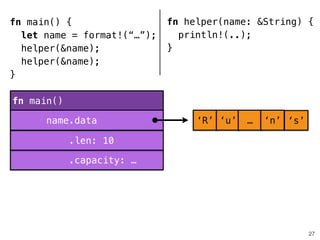
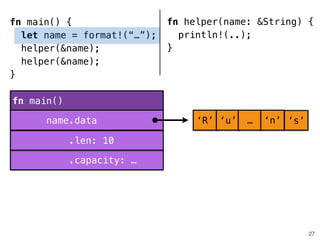


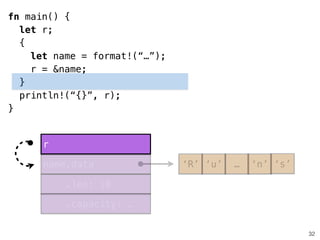
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-116-320.jpg)
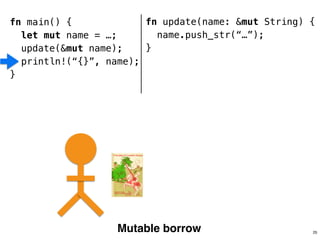
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-117-320.jpg)
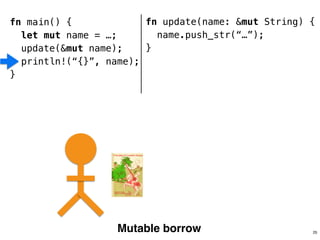
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-118-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-119-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
Subslice of a string
owned up the stack](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-120-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-121-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
helper(&name[1..]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-122-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
helper(&name[1..]);
“stacean”
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-123-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
helper(&name[1..]);
“stacean”
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-124-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
helper(&name[1..]);
“stacean”
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-125-320.jpg)
![.capacity: …
.len: 10
fn helper(name: &str) {
!
}
28
fn main()
name.data
fn helper()
name.data
fn main() {
let name = format!(“…”);
helper(&name[1..9]);
helper(&name);
}
.len: 8
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’ ‘s’
“ustacean”
helper(&name[1..]);
“stacean”
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-126-320.jpg)
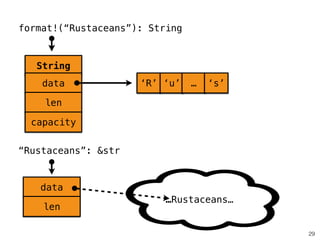
















































![34
use std::thread;
!
fn helper(name: &String) {
thread::spawn(move || {
use(name);
});
}
`name` can only be
used within this fn
Might escape
the function!
error: the type `[…]` does not fulfill the required lifetime
thread::spawn(move || {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
note: type must outlive the static lifetime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-179-320.jpg)
![34
use std::thread;
!
fn helper(name: &String) {
thread::spawn(move || {
use(name);
});
}
`name` can only be
used within this fn
error: the type `[…]` does not fulfill the required lifetime
thread::spawn(move || {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
note: type must outlive the static lifetime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-180-320.jpg)
![34
use std::thread;
!
fn helper(name: &String) {
thread::spawn(move || {
use(name);
});
}
`name` can only be
used within this fn
error: the type `[…]` does not fulfill the required lifetime
thread::spawn(move || {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
note: type must outlive the static lifetime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-181-320.jpg)
![34
use std::thread;
!
fn helper(name: &String) {
thread::spawn(move || {
use(name);
});
}
`name` can only be
used within this fn
error: the type `[…]` does not fulfill the required lifetime
thread::spawn(move || {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
note: type must outlive the static lifetime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-182-320.jpg)
![34
use std::thread;
!
fn helper(name: &String) {
thread::spawn(move || {
use(name);
});
}
`name` can only be
used within this fn
error: the type `[…]` does not fulfill the required lifetime
thread::spawn(move || {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
note: type must outlive the static lifetime
However: see crossbeam,
simple_parallel, etc on
crates.io](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-183-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-184-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-185-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-186-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-187-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-188-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity
data
len](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-189-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity
data
len](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-190-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity
data
len](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-191-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-192-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘s’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-193-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
‘s’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-194-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
‘s’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-195-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
‘s’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-196-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
‘s’
Dangling
reference!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-197-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
35
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
String
data
len
capacity
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
data
len
‘R’ ‘u’ … ‘n’
‘s’
Dangling
reference!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-198-320.jpg)

![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-200-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-201-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-202-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-203-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope
error: cannot borrow `buffer` as mutable
because it is also borrowed as immutable
buffer.push_str(“s”);
^~~~~~
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-204-320.jpg)
![Dangers of mutation
37
fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
let slice = &buffer[1..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope
error: cannot borrow `buffer` as mutable
because it is also borrowed as immutable
buffer.push_str(“s”);
^~~~~~
http://is.gd/MCPVWg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-205-320.jpg)
![fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
for i in 0 .. buffer.len() {
let slice = &buffer[i..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
buffer.push_str(“s”);
}
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-206-320.jpg)
![fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
for i in 0 .. buffer.len() {
let slice = &buffer[i..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
buffer.push_str(“s”);
}
38
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-207-320.jpg)
![fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
for i in 0 .. buffer.len() {
let slice = &buffer[i..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
buffer.push_str(“s”);
}
38
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-208-320.jpg)
![fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
for i in 0 .. buffer.len() {
let slice = &buffer[i..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
buffer.push_str(“s”);
}
38
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-209-320.jpg)
![fn main() {
let mut buffer: String = format!(“Rustacean”);
for i in 0 .. buffer.len() {
let slice = &buffer[i..];
buffer.push_str(“s”);
println!(“{:?}”, slice);
}
buffer.push_str(“s”);
}
38
Borrow “locks”
`buffer` until `slice`
goes out of scope
OK: `buffer` is not borrowed here](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-210-320.jpg)
![Exercise: borrowing
39
http://smallcultfollowing.com/20151209
Cheat sheet:
&String // type of shared reference
&mut String // type of mutable reference
&str // type of string slice
!
&name // shared borrow
&mut name // mutable borrow
&name[x..y] // slice expression
http://doc.rust-lang.org/std](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-211-320.jpg)















![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-227-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-228-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-229-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-230-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-231-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-232-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-233-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-234-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-235-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-236-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-237-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-238-320.jpg)
![43
struct Item {
name: &’static str,
price: f32,
}
Other fundamental types
f32
f64
!
!
i8
i16
i32
i64
isize
u8
u16
u32
u64
usize
&str
&[T]
!
!
floats signed unsigned slices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-239-320.jpg)












![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-252-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-253-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-254-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-255-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-256-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-257-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-258-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-259-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-260-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-261-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-262-320.jpg)
![Methods
45
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
return Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
};
}
}
Store::new(some_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-263-320.jpg)
![Return is optional
46
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-264-320.jpg)
![Return is optional
46
struct Store { .. }
!
impl Store {
fn new(name: String) -> Store {
Store {
name: name,
items: vec![],
}
}
}
No `;` on last expression:
“return this value”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-265-320.jpg)











![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-277-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-278-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-279-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-280-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:
Vec<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-281-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:
String
Vec<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-282-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-283-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-284-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-285-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-286-320.jpg)
![For Loops
48
fn main() {
let v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
for s in v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
}
http://is.gd/6kJc0O
“Gamma”
v: s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-287-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-288-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-289-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
&Vec<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-290-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
&String
&Vec<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-291-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-292-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-293-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-294-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-295-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
s:
&mut Vec<String>
&mut String](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-296-320.jpg)
![For Loops
49
fn main() {
let mut v = vec![format!(“Alpha”),
format!(“Beta”),
format!(“Gamma”)];
!
for s in &v {
println!(“{:?}”, s);
}
!
for s in &mut v {
s.push_str(“.”);
}
}
“Alpha”
“Beta”
“Gamma”
v:
s:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-297-320.jpg)





























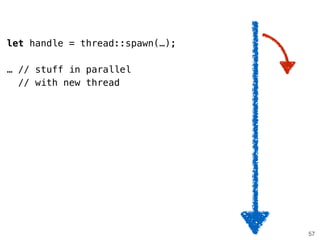
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-328-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-329-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-330-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-331-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-332-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-333-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-334-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56
Closure
takes ownership
of variables it uses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-335-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56
Closure
takes ownership
of variables it uses.
Variables used by
this closure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-336-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56
Closure
takes ownership
of variables it uses.
Variables used by
this closure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-337-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-338-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56
Handle to the
thread we spawned.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-339-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-340-320.jpg)
![Closure body can
produce a result,
here a (String, f32).
use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-341-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-342-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-343-320.jpg)
![use std::thread;
…
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-344-320.jpg)








![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-354-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-355-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-356-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-357-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-358-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-359-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-360-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-361-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-362-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-363-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-364-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-365-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-366-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-367-320.jpg)
![58
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
handles.push(
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = …;
(store.name, sum)
});
}
!
for handle in handles {
let (name, sum) =
handle.join().unwrap();
// find best price
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-368-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-369-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
Variables used by
this closure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-370-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-371-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-372-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-373-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-374-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
error: capture of moved value: `shopping_list`
let sum = store.total_price(&shopping_list);
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
…
help: perhaps you meant to use `clone()`?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-375-320.jpg)
![59
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
error: capture of moved value: `shopping_list`
let sum = store.total_price(&shopping_list);
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
…
help: perhaps you meant to use `clone()`?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-376-320.jpg)
![60
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-377-320.jpg)
![60
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-378-320.jpg)
![60
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = vec![…];
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-379-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-380-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-381-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-382-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-383-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-384-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-385-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-386-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-387-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-388-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-389-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-390-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-391-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-392-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-393-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2
data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-394-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2
data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-395-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1
arc2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-396-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];
arc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-397-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-398-320.jpg)
![61
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let arc2 = arc1.clone();
let data = &arc1[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-399-320.jpg)
![Arc => Immutable
62
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let data = &mut arc1[0];
http://is.gd/nP3Pvb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-400-320.jpg)
![Arc => Immutable
62
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let data = &mut arc1[0];
http://is.gd/nP3Pvb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-401-320.jpg)
![Arc => Immutable
62
use std::sync::Arc;
let shopping_list: Vec<ShoppingList> = …;
let arc1 = Arc::new(shopping_list);
let data = &mut arc1[0];
<anon>:6:21: 6:24 error: cannot borrow immutable borrowed
content as mutable
<anon>:6 let data = &mut arc[0];
^~~
http://is.gd/nP3Pvb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-402-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-403-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-404-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-405-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-406-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-407-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-408-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-409-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-410-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-411-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-412-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-413-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-414-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-415-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-416-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-417-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-418-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-419-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-420-320.jpg)
![63
use std::thread;
…
let shopping_list = Arc::new(vec![…]);
let mut handles = vec![];
for store in stores {
let shopping_list = shopping_list.clone();
let handle =
thread::spawn(move || {
let sum = store.total_price(shopping_list);
(store.name, sum)
});
handles.push(handle);
}
// exercise (in a bit): join the handles!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rustmozlandotutorialthreaded-151209223810-lva1-app6892/85/Rust-Mozlando-Tutorial-421-320.jpg)