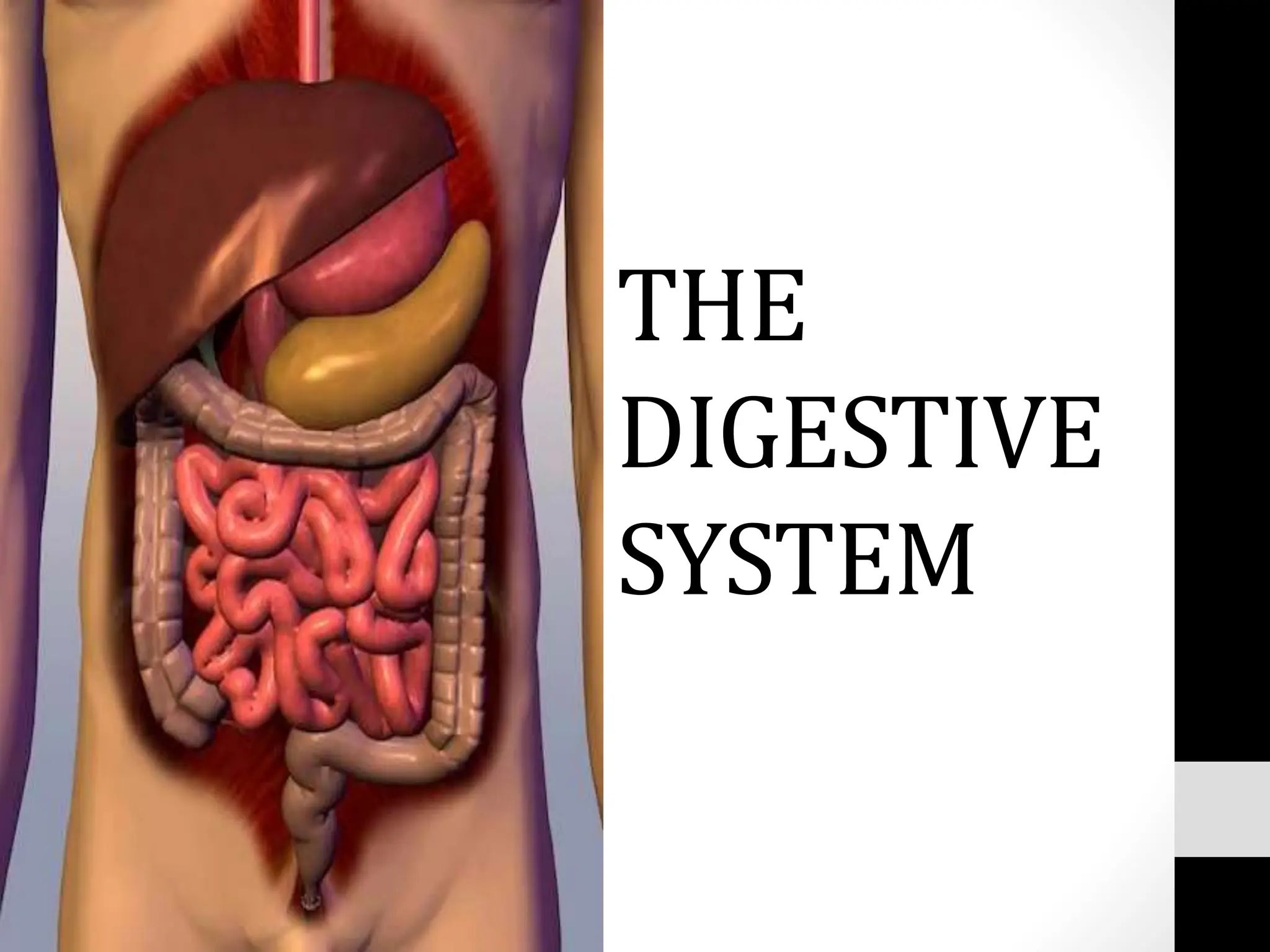
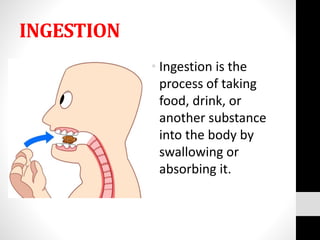
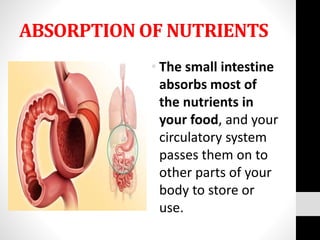
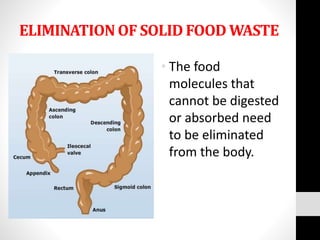
The document describes the digestive system and its functions. The digestive system processes and absorbs nutrients from food. It has four main functions: ingestion, digestion of food, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of solid waste. It describes each organ involved and its role, such as the mouth chewing food, the esophagus transporting food to the stomach for digestion, the small intestine absorbing nutrients, and the large intestine and anus eliminating solid waste.