Embed presentation
Download to read offline


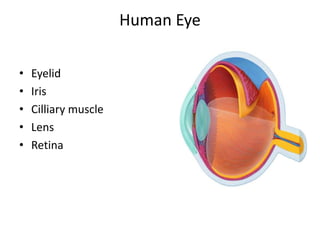



Science aims to understand natural phenomena through reasoned investigation and discovery of new principles, while engineering applies scientific knowledge to design tools, machines, and systems that manipulate nature for human benefit. The document discusses the objectives and differences between science and engineering, provides details on the human eye and how it compares to a camera, and outlines similarities and differences between how birds and aircraft fly based on aerodynamic principles despite using different mechanisms.




