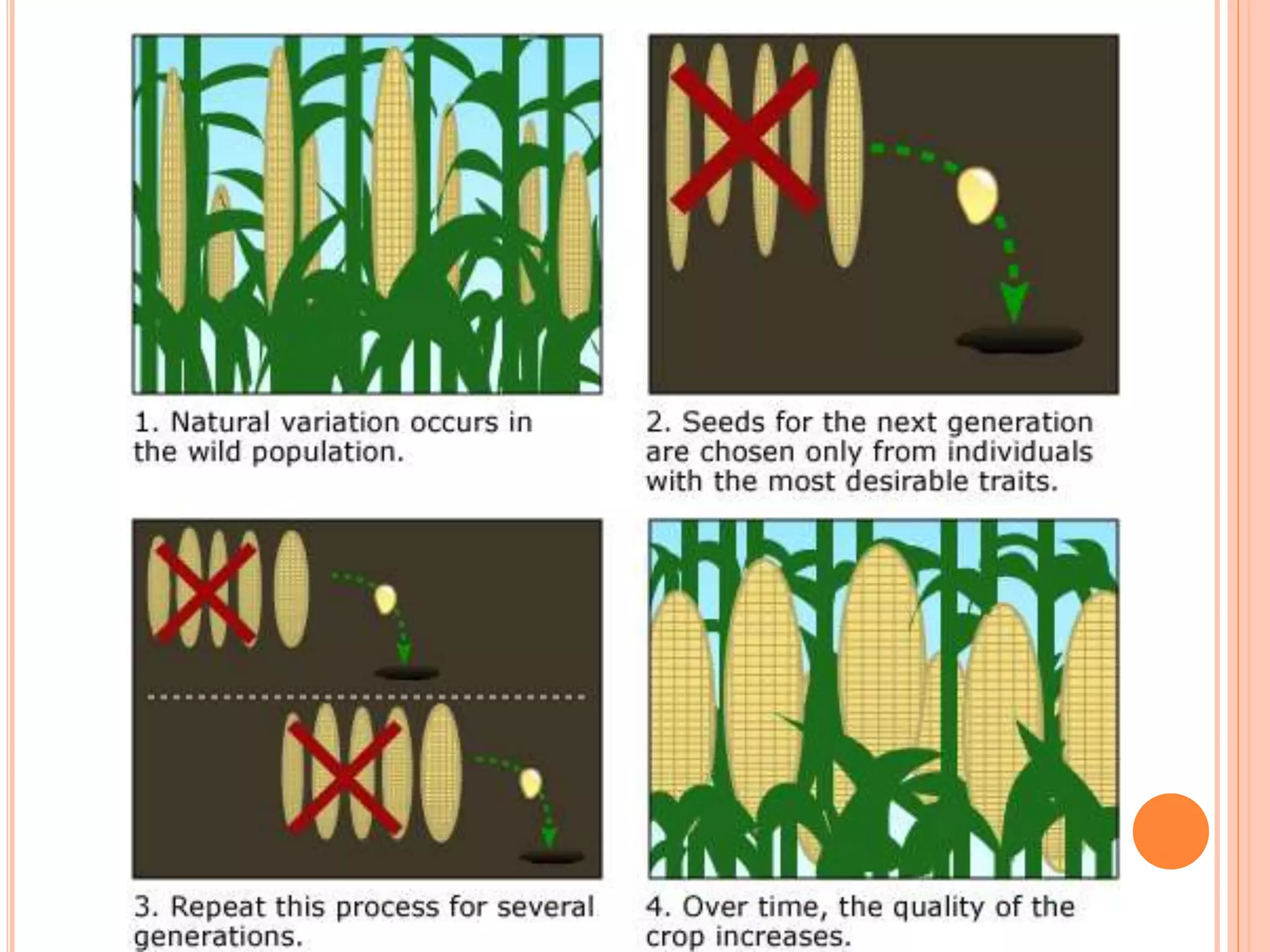
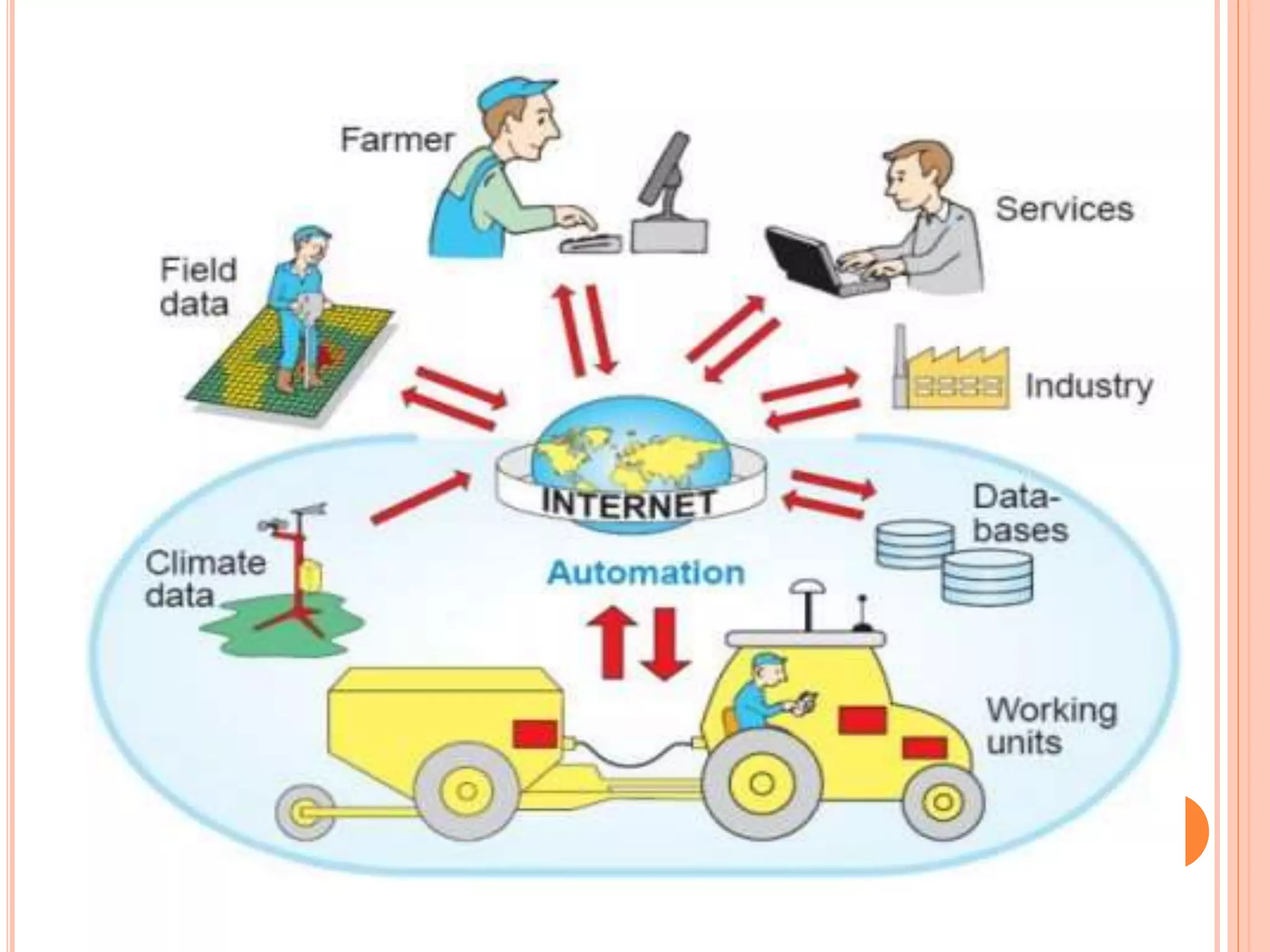
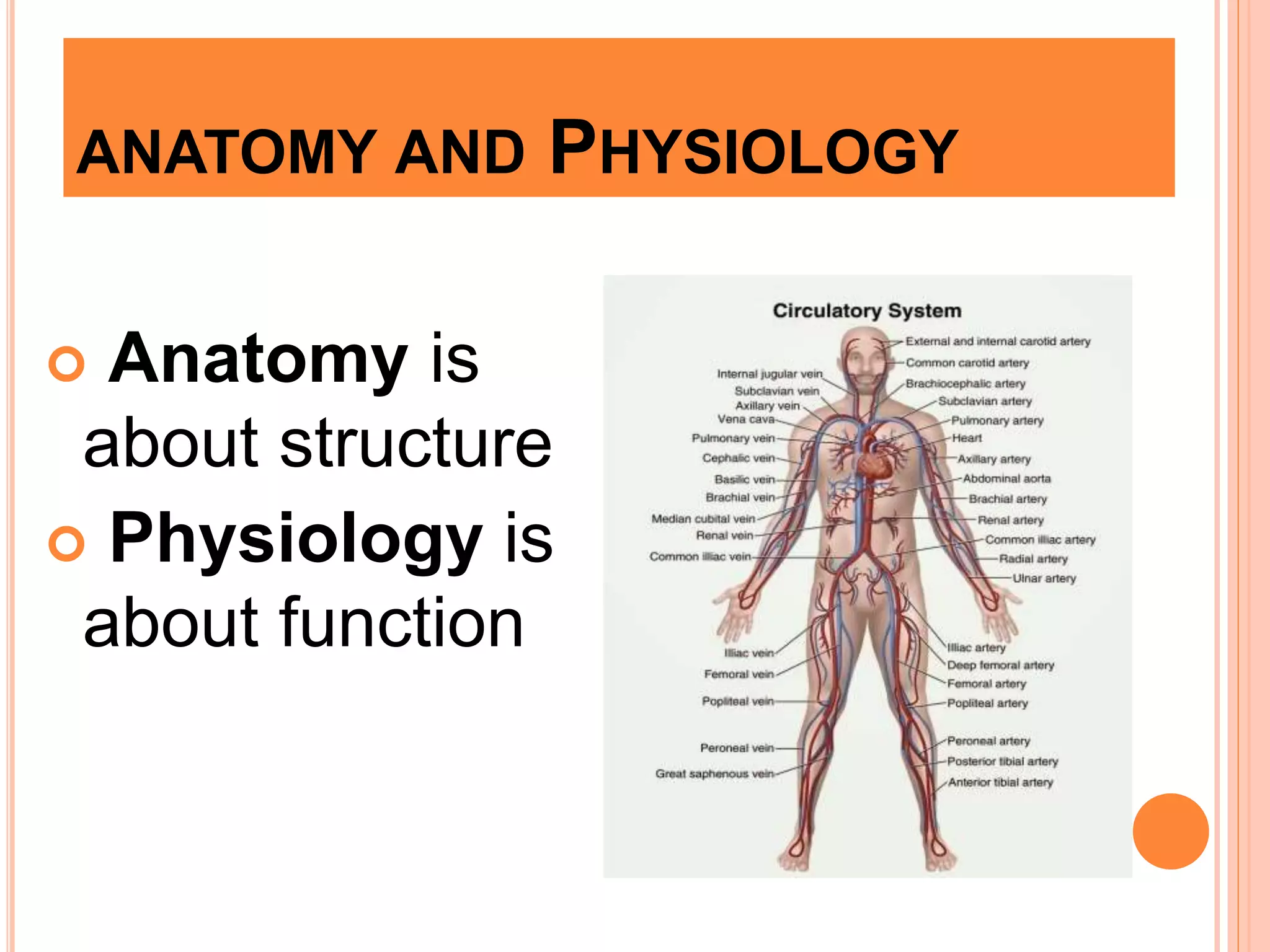
This document provides an introduction to science and technology. It describes how science seeks to gain knowledge through observation and experimentation, while technology applies scientific knowledge for practical purposes. The document also discusses the major branches of science, including physical, biological and social sciences. It provides examples of pure sciences that expand knowledge versus applied sciences that create solutions. Finally, it outlines some key impacts of science and technology on society, both positive through innovations, and potential negatives like pollution.










































![INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY [ICT] (USES)
Sending
messages
Internet
Satellite
communication
TV’s and radios](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1inroductiontoscienceandtechnology-211005075124/75/Lesson-1-inroduction-to-science-and-technology-54-2048.jpg)