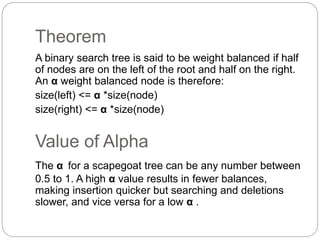
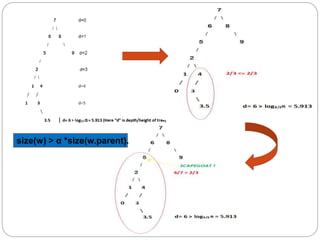
The scapegoat tree is a self-balancing binary search tree that achieves O(log n) time for search, insert, and delete operations. It works by occasionally selecting an unbalanced "scapegoat" node and rebuilding its subtree to rebalance the tree. The scapegoat is identified when a node's size is more than an alpha value times its parent's size. The subtree rooted at the scapegoat is then rebuilt by converting its inorder traversal to a new balanced binary search tree.