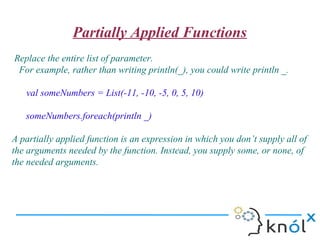
Functions in Scala allow dividing programs into smaller, manageable pieces that perform specific tasks. Some key features of functions in Scala include local functions defined inside other functions, first-class functions that can be passed as arguments, partially applied functions, closures that close over variables from outer scopes, and repeated/variable length parameters indicated with an asterisk. Tail recursion makes recursive functions more efficient by ensuring the recursive call is the last operation.



![Functions Declaration And Definition
def functionName ([list of parameters]) : [return type]
def functionName ([list of parameters]) : [return type] = {
function body
return [expr]
}
def addInt( a:Int, b:Int ) = {
var sum = 0
sum = a + b
sum
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalafunctions-130304032401-phpapp01/85/Scala-functions-5-320.jpg)
![Calling Functions
Following is the standard way to call a
method:
object Test {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
println( "Returned Value : " + addInt(5,7) )
}
def addInt( a:Int, b:Int ) : a+b
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalafunctions-130304032401-phpapp01/85/Scala-functions-6-320.jpg)