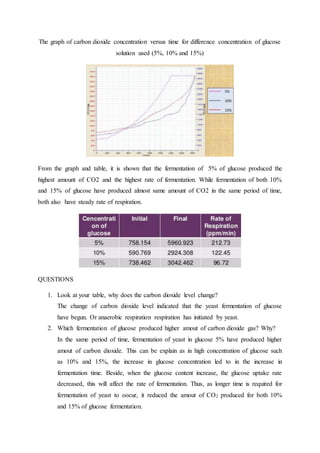
The document describes an experiment using a data logger to measure carbon dioxide production during yeast fermentation of glucose solutions at different concentrations. Yeast were mixed with 5%, 10%, and 15% glucose solutions and a carbon dioxide sensor logged measurements every 10 seconds over 10 minutes. Higher carbon dioxide production and faster fermentation rates occurred with the 5% solution compared to 10% and 15%. Data loggers offer accurate, automated data collection without human error. They have advantages for remote or continuous monitoring but also limitations like sensor calibration and missing unexpected events.