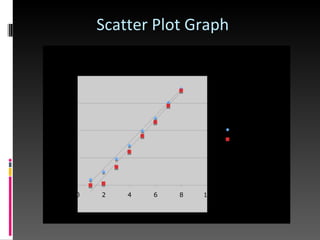
The document summarizes the steps taken by four students to plot the trajectory of missiles launched from Earth and North Korea toward the moon using a scatter plot graph. They found the point of intersection between the trajectories and calculated that it would occur 232,405 kilometers from Earth, which is less than the distance from Earth to the moon's surface. They then calculated additional trajectory details like the average speed of the missiles.