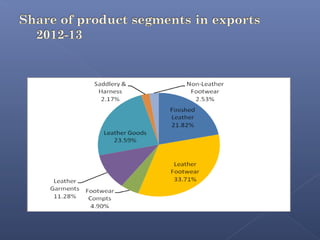
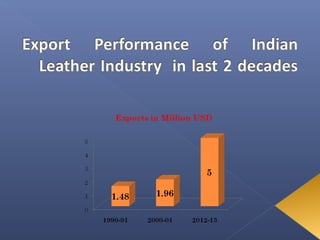
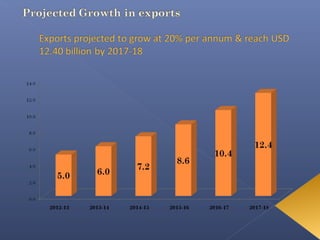
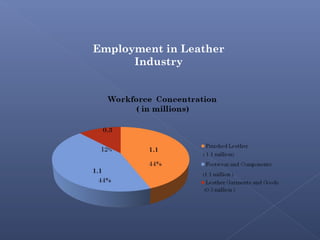
The leather industry is a major contributor to the Indian economy, generating over 2.5 million jobs. India is one of the largest producers and exporters of leather and leather products globally. It is the second largest producer of footwear and leather garments, and third largest producer of saddlery and harness items. However, the industry faces threats from environmental regulations, rising competition, and dependence on imports. To sustain long-term growth, the industry needs to invest in modern production technologies and develop the domestic market.