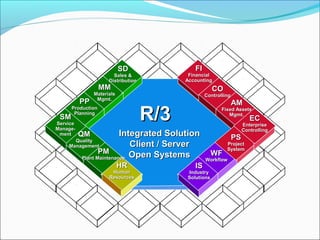
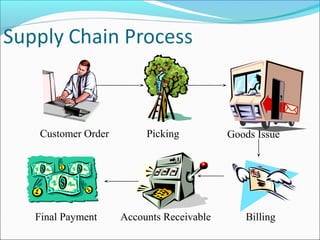
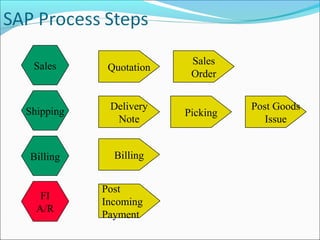
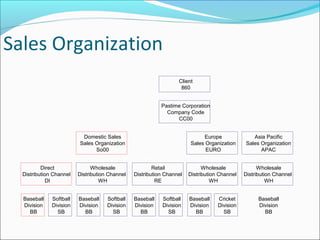
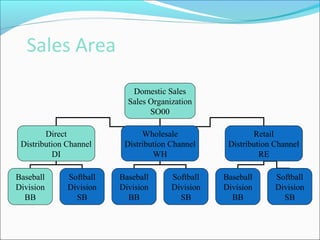
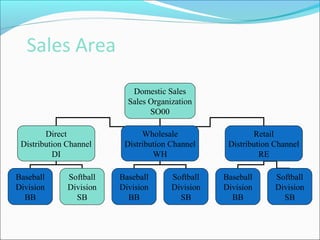
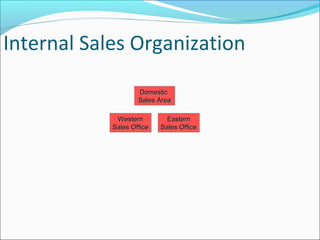
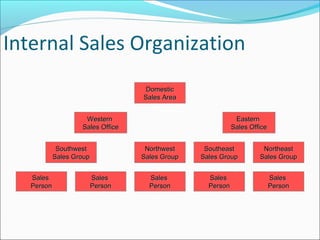
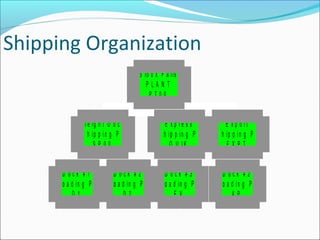
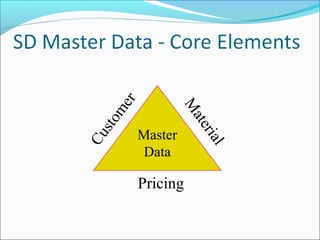
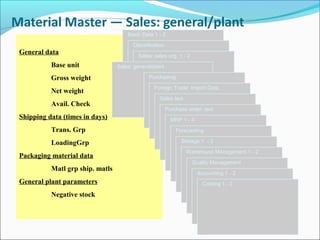
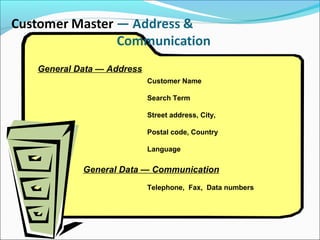
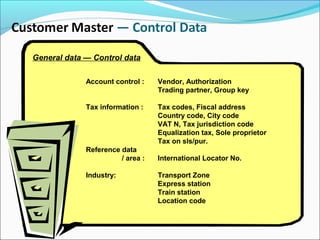
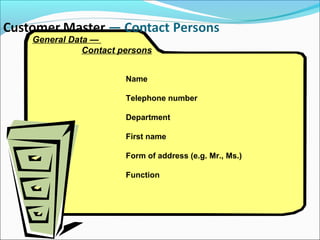
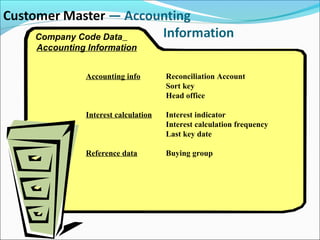
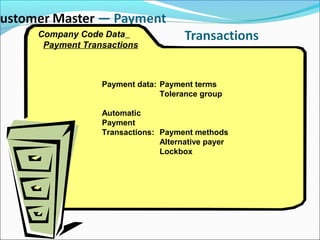
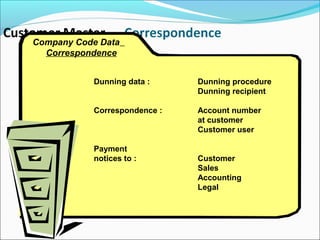
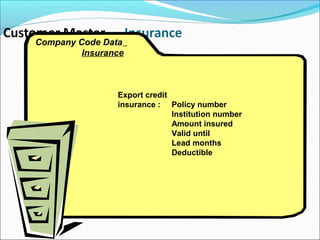
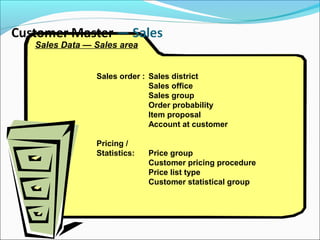
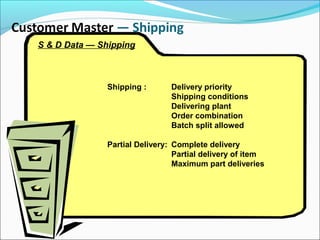
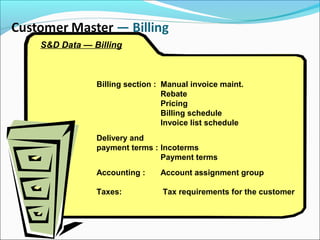
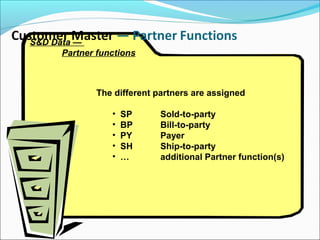
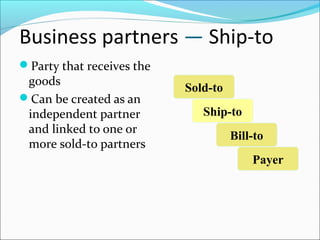
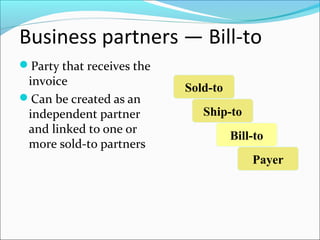
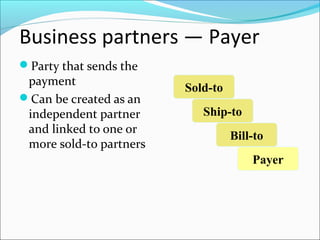
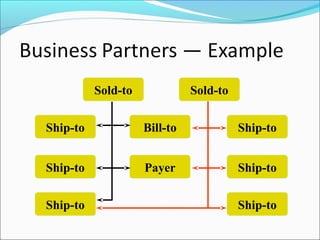
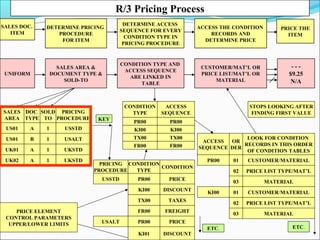
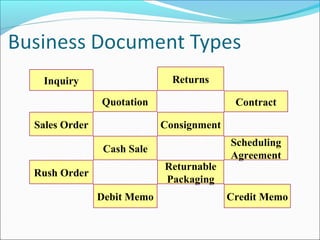
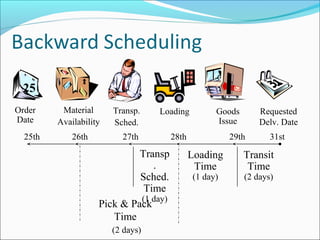
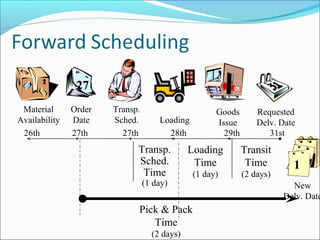
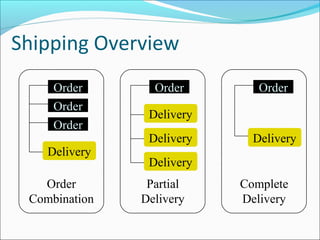
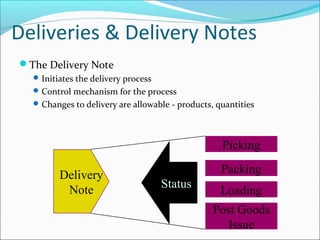
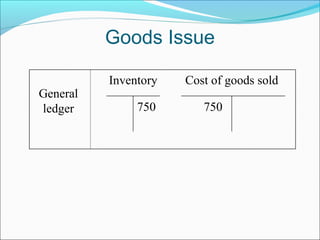
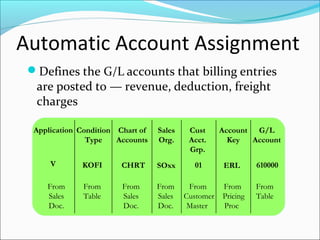
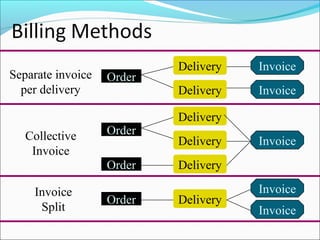
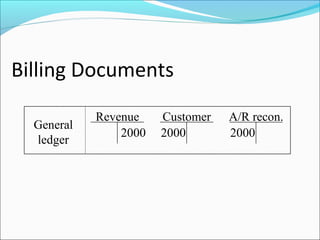
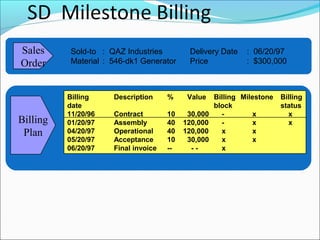
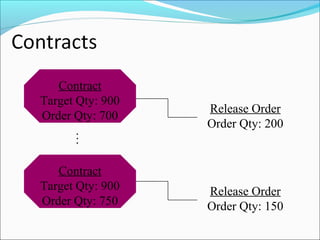
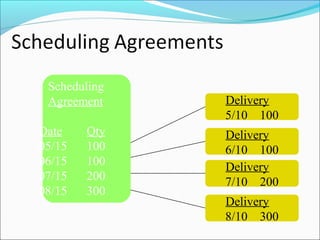
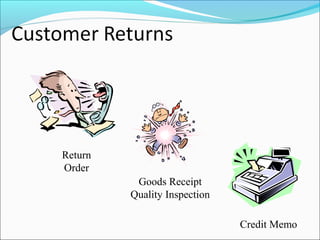
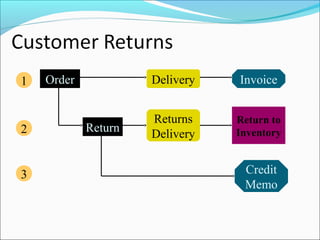
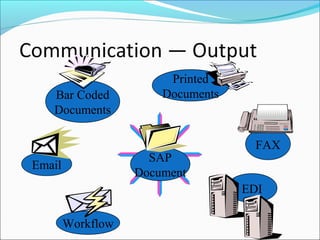
The document provides an overview of the Sales & Distribution (SD) module in SAP. It discusses the key components and functions of SD including master data, sales processes, shipping, billing, and organizational structures. Specifically, it summarizes SD as having tightly coupled data flow and flexible functionality to execute business processes in selling, shipping, and billing of products and services. It also discusses how SD utilizes master data such as customers, materials, and pricing to support these processes.