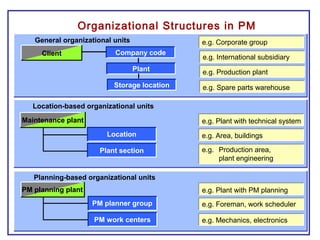
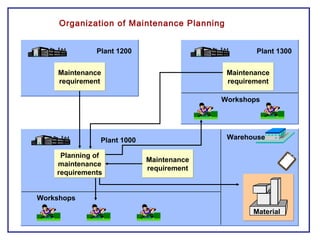
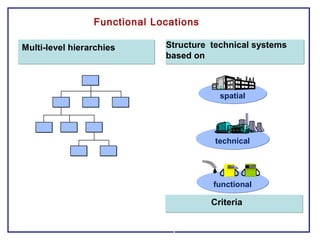
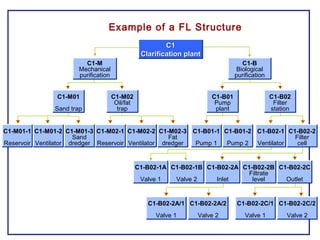
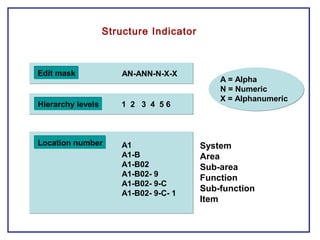
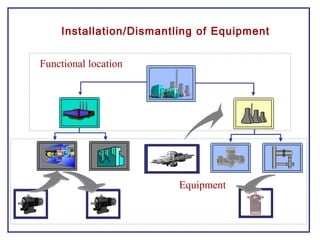
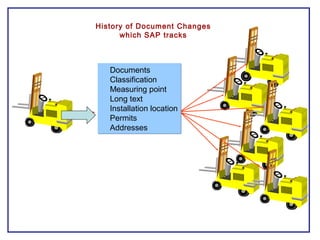
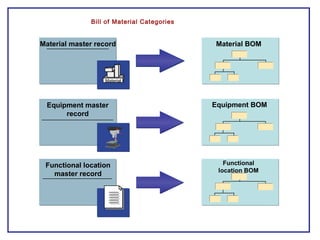
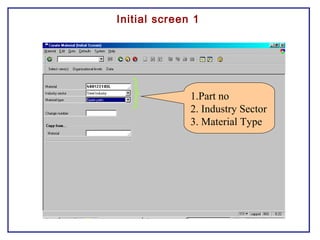
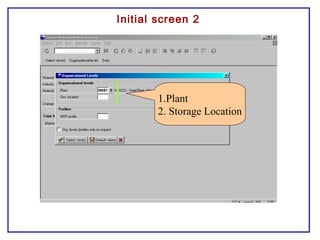
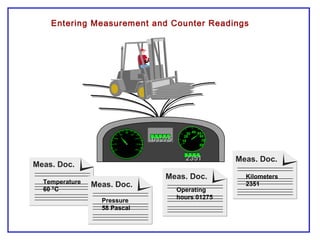
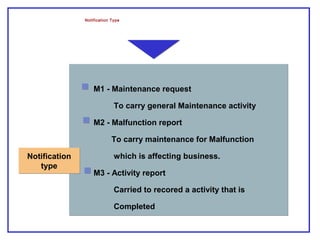
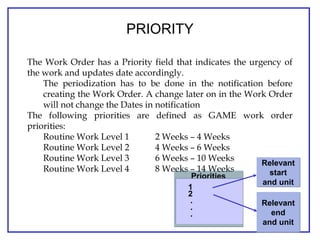
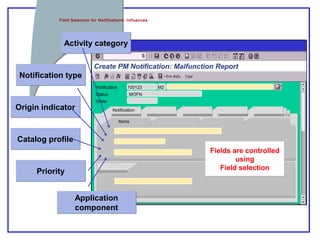
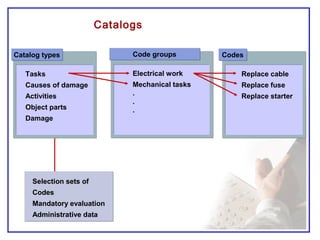
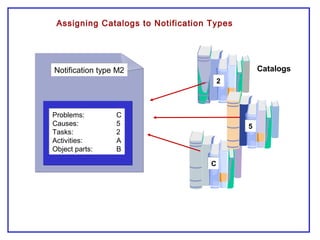
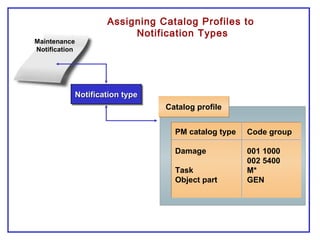
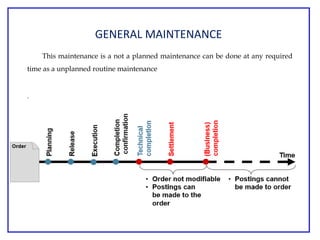
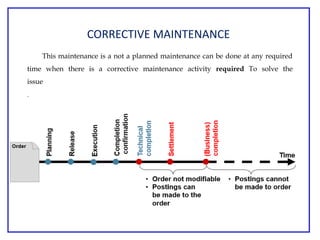
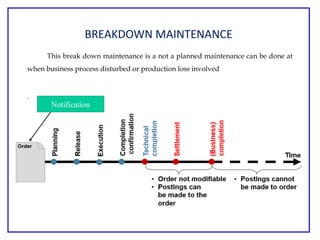
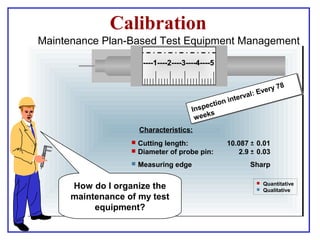
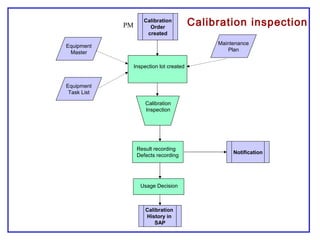
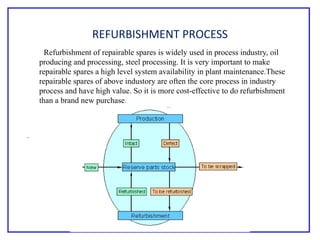
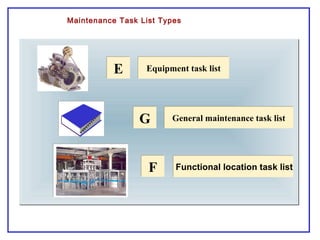
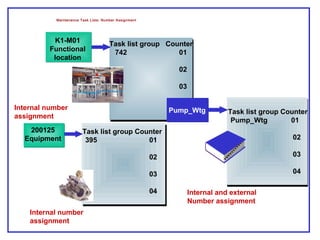
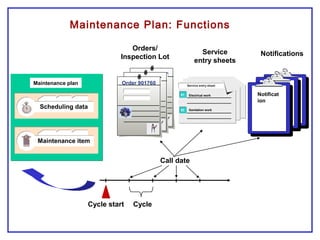
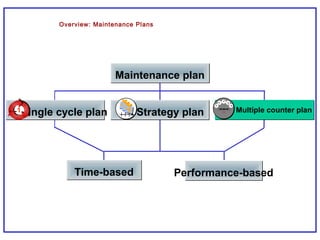
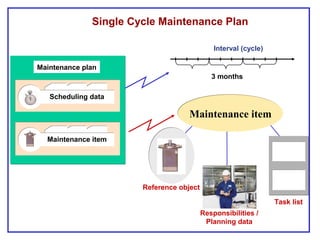
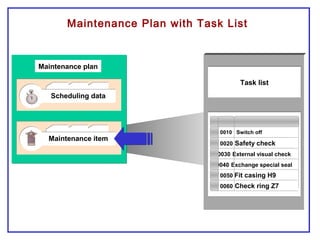
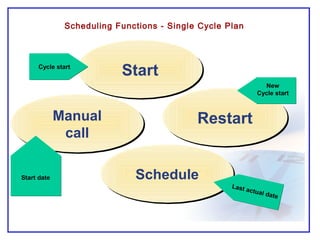
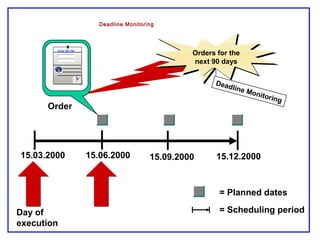
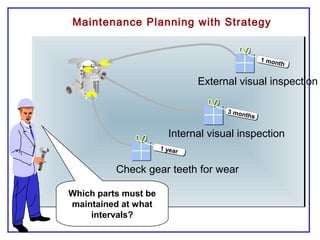
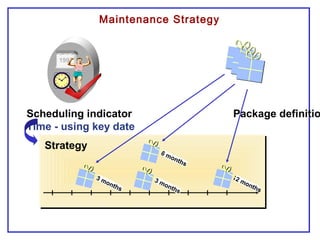
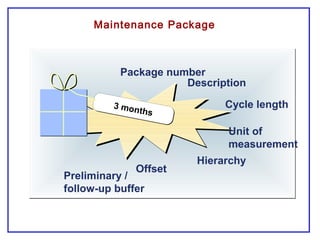
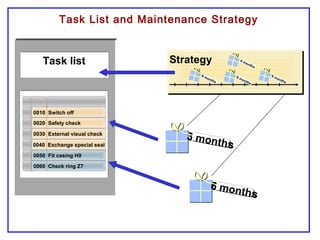
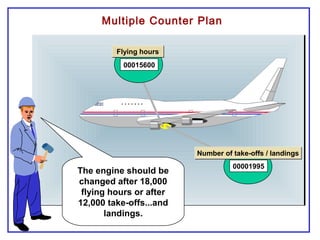
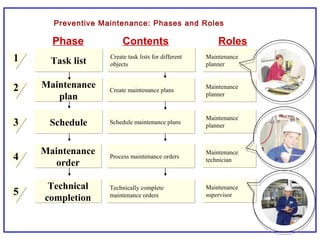
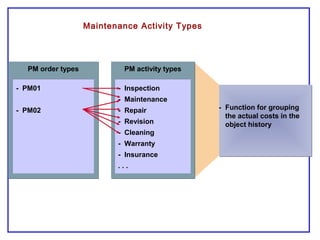
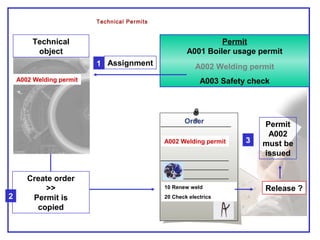
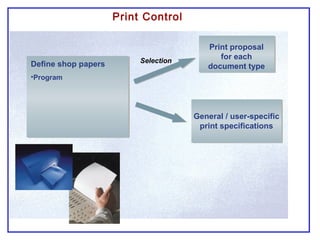
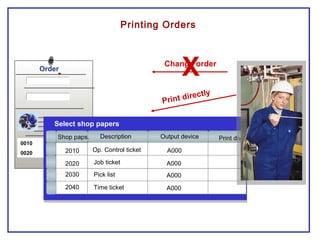
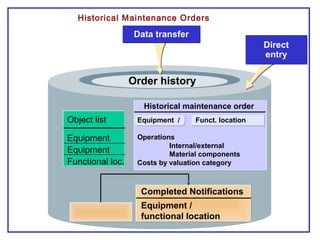
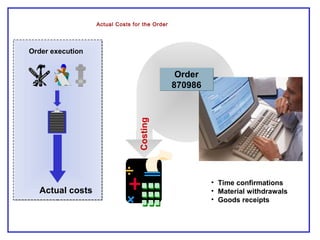
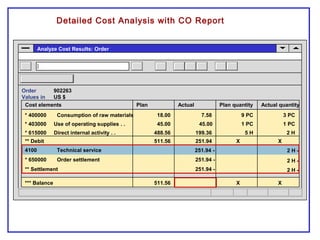
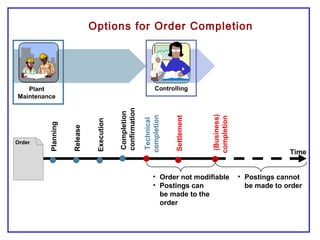
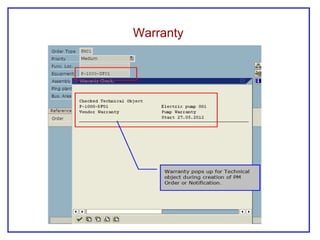
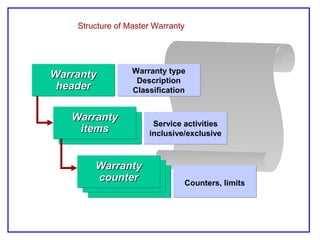
The document outlines the Plant Maintenance (PM) module of SAP R/3, focusing on key organizational structures, master data requirements, maintenance scenarios, and workflows relevant to maintenance planning. It describes essential components like work centers, functional locations, and maintenance orders while detailing various maintenance types and strategies within the system. Effective management of master data is emphasized as crucial for generating valuable reports for analysis and operational efficiency.