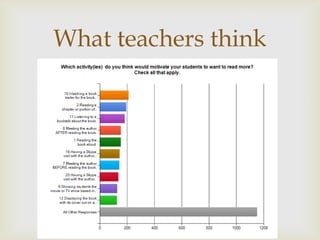
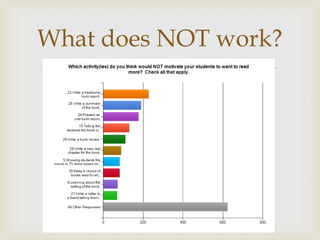
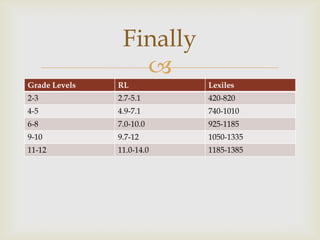
The document outlines strategies for enhancing reading engagement among students, emphasizing the importance of reading aloud, selecting appropriate literature, and building reading communities. It discusses the benefits of read-alouds in developing skills, community building, and exposing students to various genres. Additionally, it provides recommendations for fostering a love of reading through teacher-student interactions, resources, and community involvement.