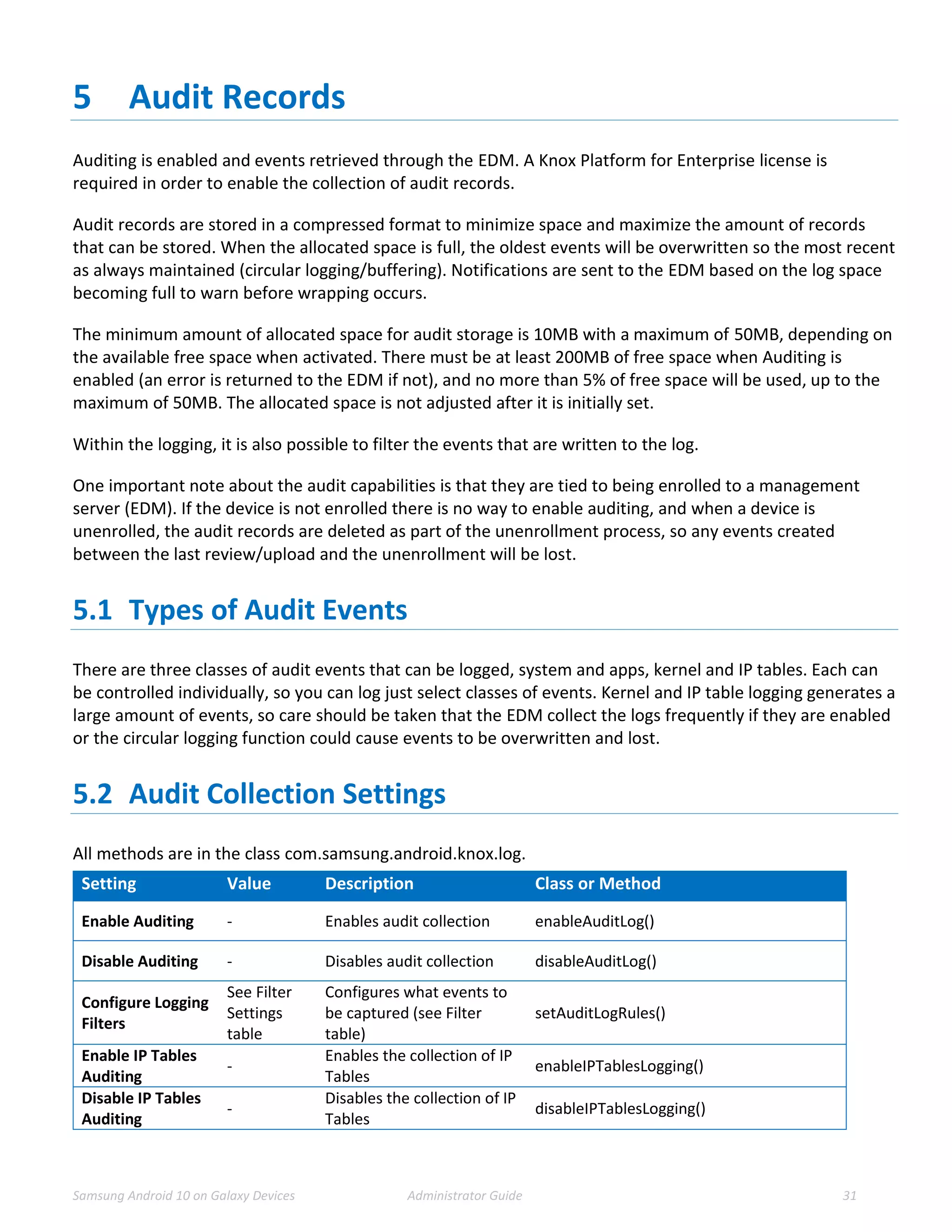
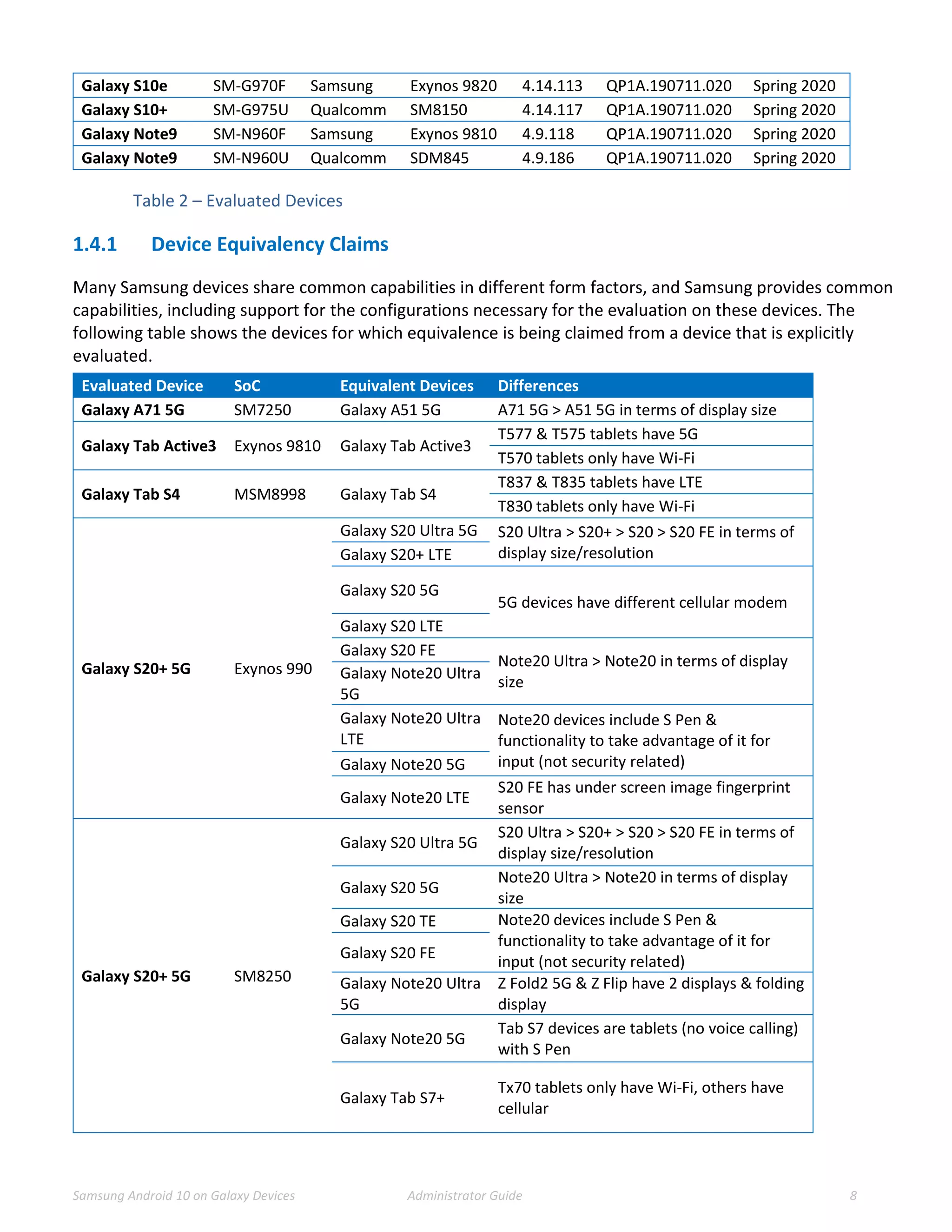
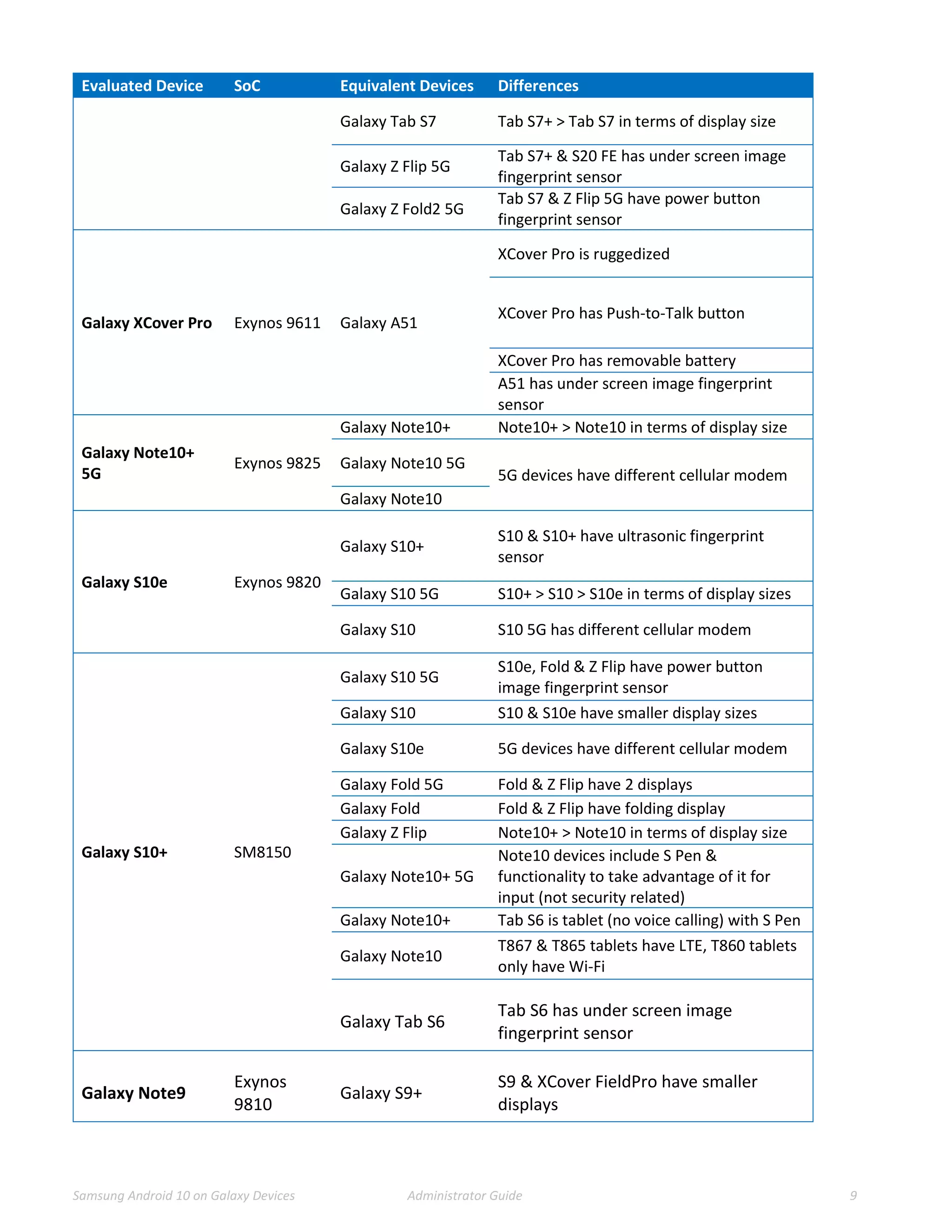
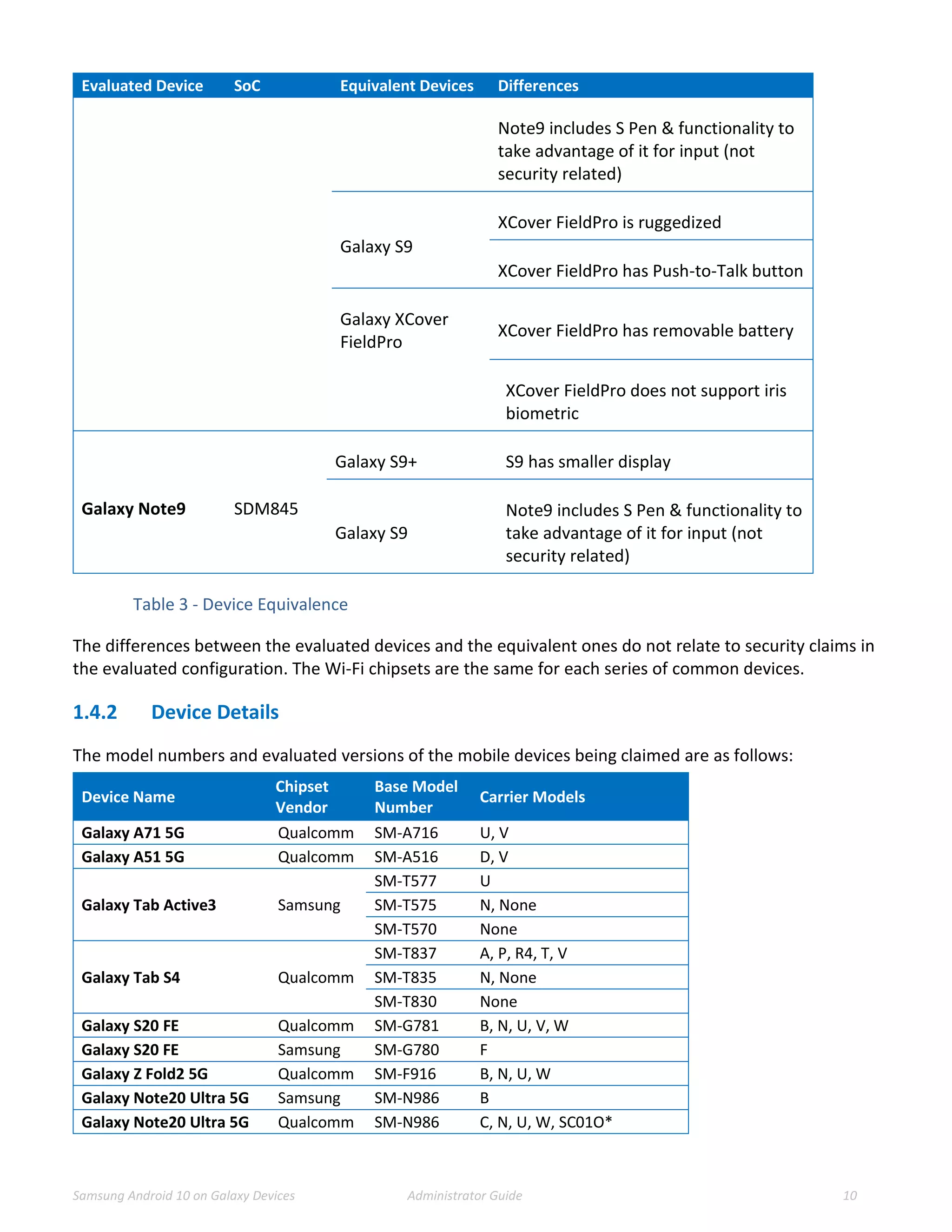
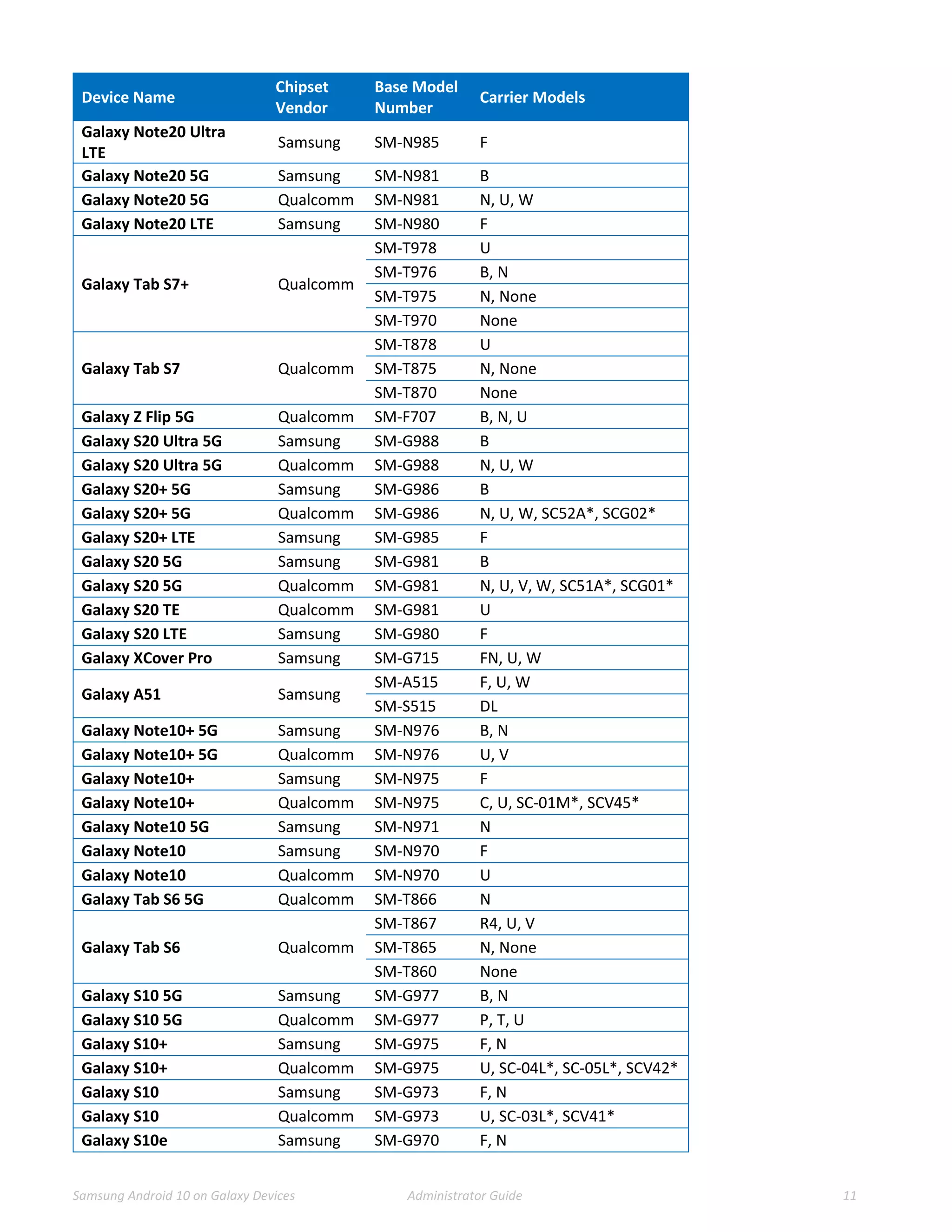
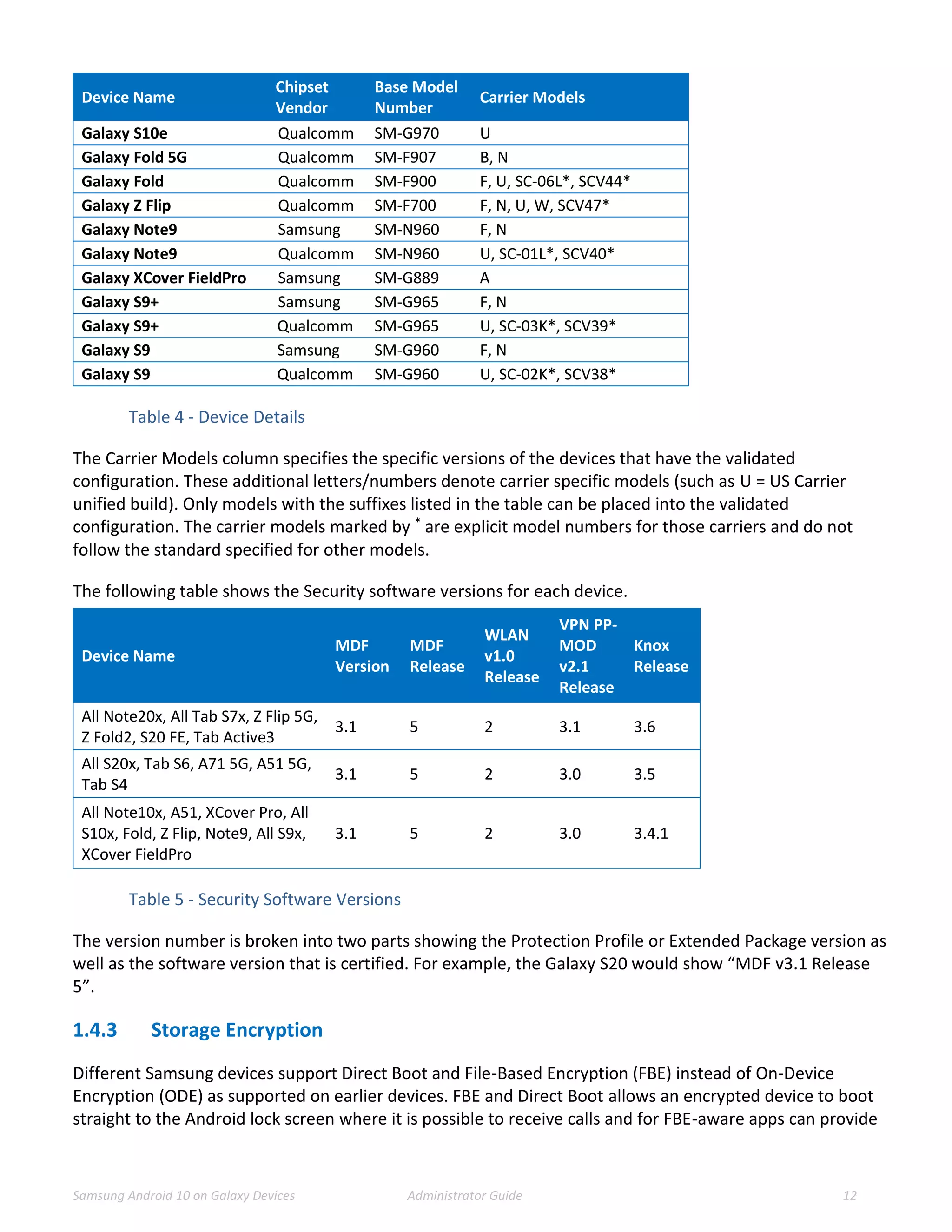
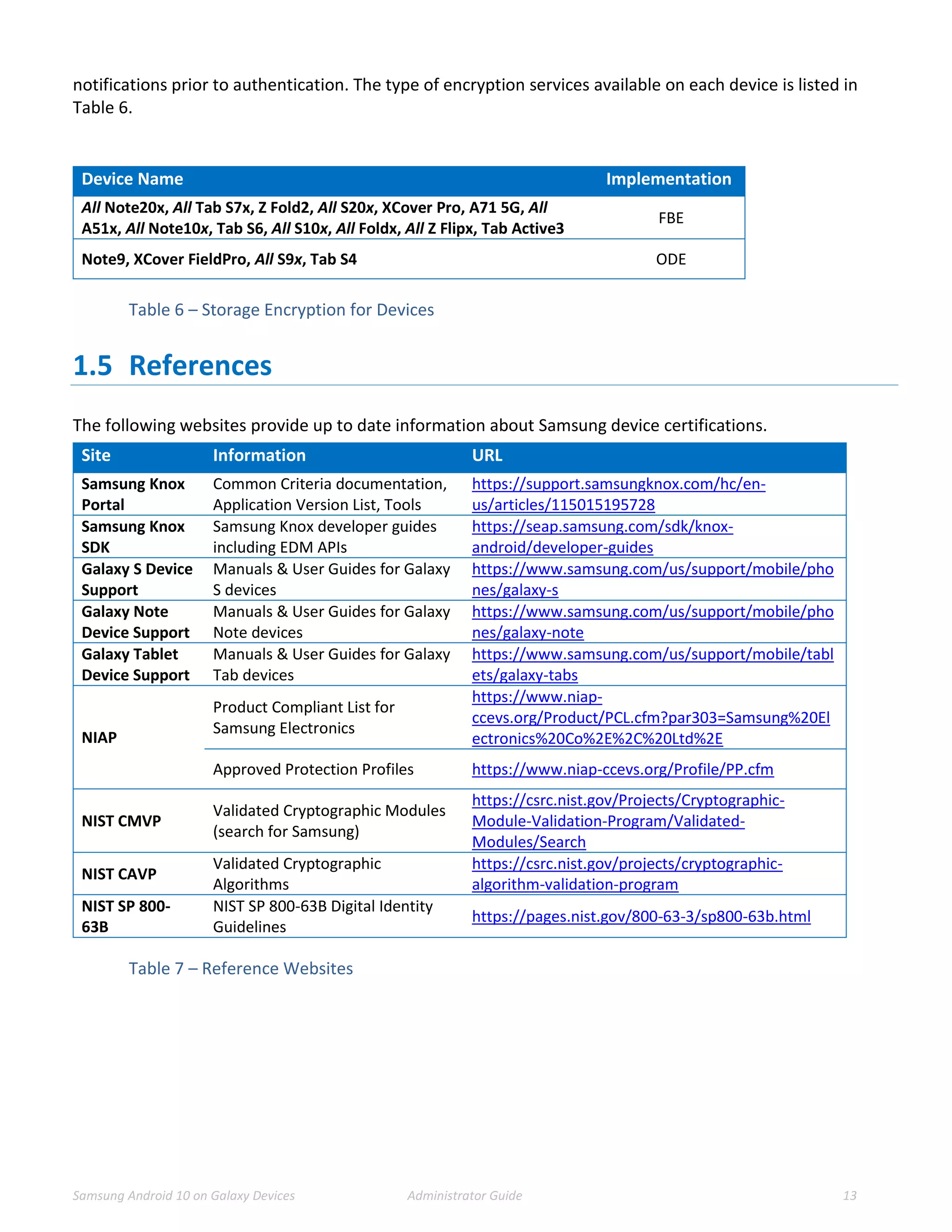
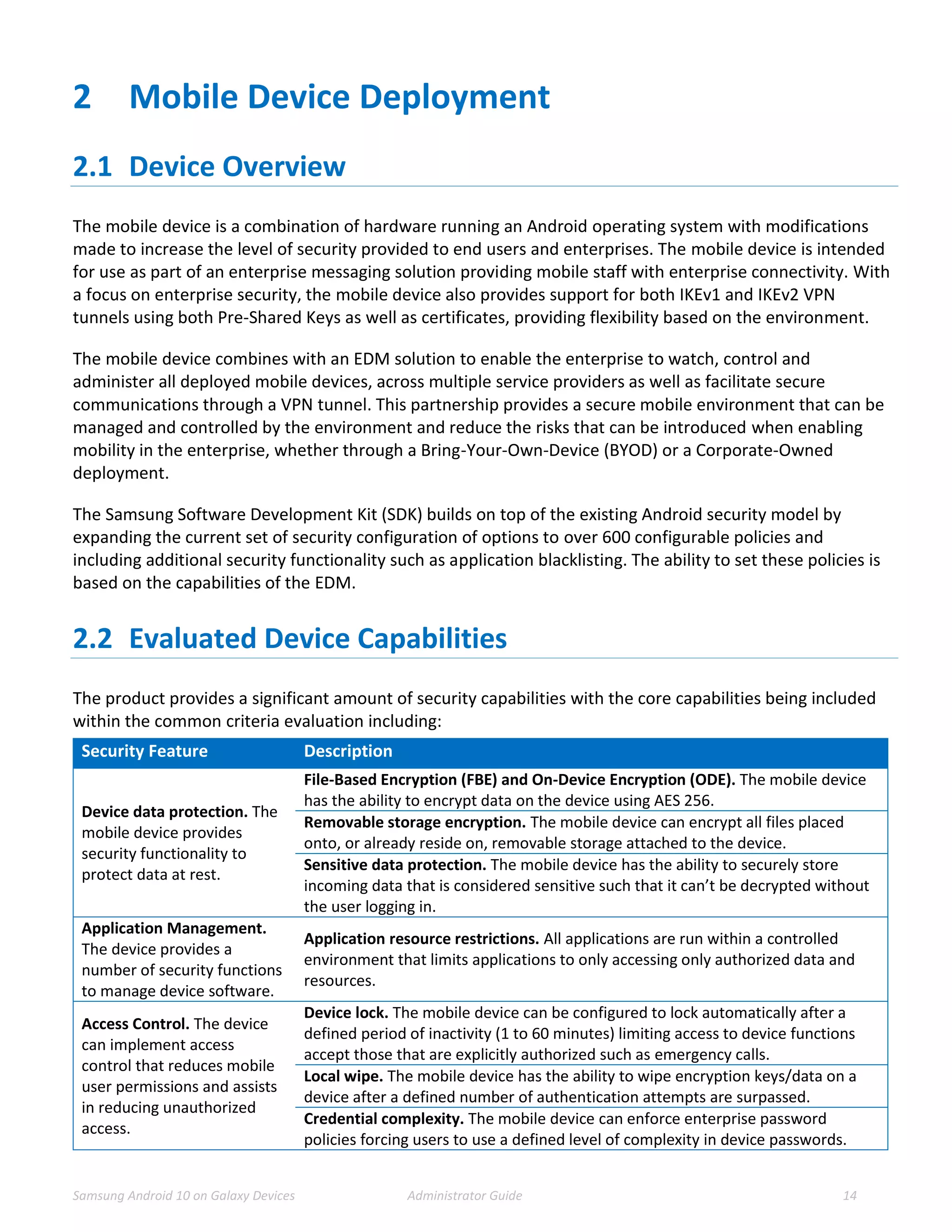
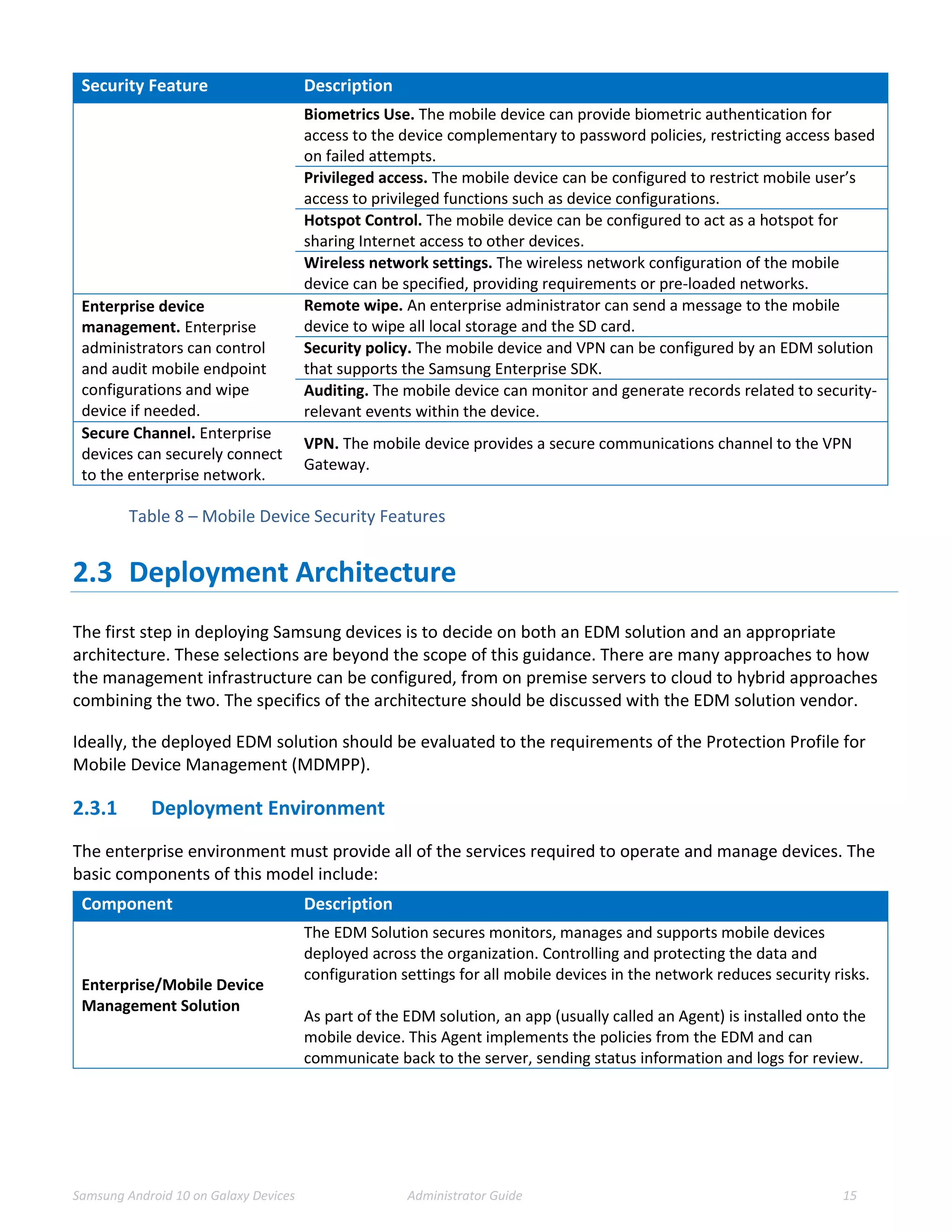
This document provides guidance for administrators on deploying and configuring Samsung devices to meet the requirements of the Common Criteria evaluation. It covers the evaluated devices and their equivalents, how to enable the Common Criteria mode, recommended security settings and VPN configurations. It also discusses device delivery, updates, and operational security practices like data wiping.












![Samsung Android 10 on Galaxy Devices Administrator Guide 25
3.4.3.1 Samsung VPN Client Configuration for Knox VPN Profile
Using Knox Generic APIs requires installation of the Samsung Proxy APK on the device, which translates
configuration received through these APIs onto the underlying Samsung VPN client. The use of other Proxy
APKs could be used to support non-Samsung VPN clients (that is not covered here).
Note: Using the Samsung VPN APK will configure the Knox VPN Profile to point to the evaluated VPN client.
Provided the profile configuration string has been created as per the next section, the API flow for creating
and starting a VPN connection will be createVpnProfile() -> addPackagesToVpn() -> activateVpnProfile() API.
The API flow for removing a VPN profile will be activateVpnProfile() (De-activate it) -> removeVpnProfile()
API.
Note: When adding packages to a VPN profile, use User0 for the whole device and User10 or User100
(depending on the device) for the Work Profile.
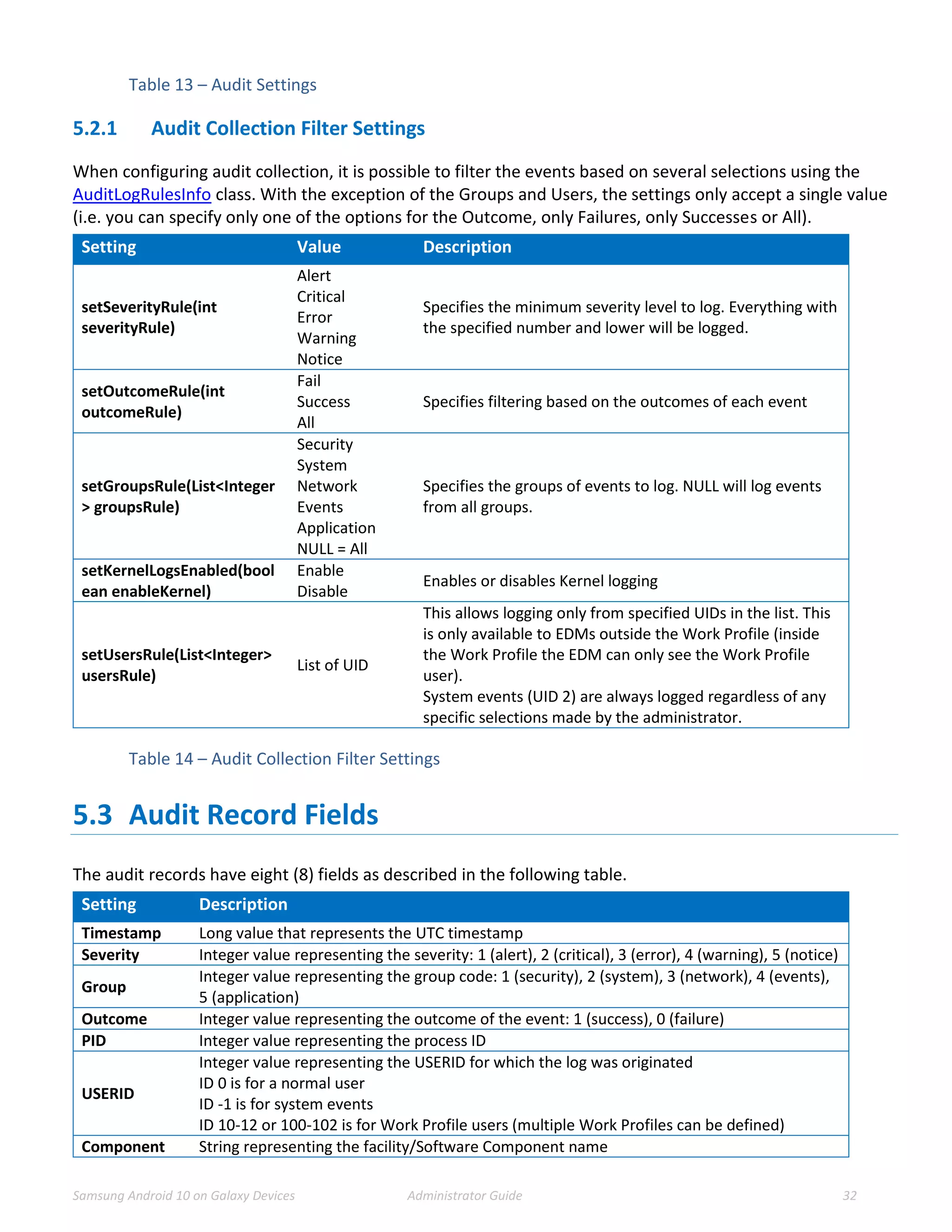
3.4.3.2 JSON Configuration String
This is an example JSON file for the Knox VPN Client Profile.
{
"KNOX_VPN_PARAMETERS": {
"profile_attribute": {
"profileName": "ss1",
"host": "",
"isUserAuthEnabled": true,
"vpn_type": "ipsec",
"vpn_route_type": 1
},
"knox": {
"connectionType": "keepon",
"chaining_enabled": "-1",
"uidpid_search_enabled": "0"
},
"vendor": {
"basic": {
"autoretry": "1",
"username": "sampleu",
"password": “samplepw",
"authentication_type": "type",
"host": "111.111.111.111"
},
"ipsec_xauth_psk": {
"identifier": "test@sta.com",
"pre_shared_key": "example",
"dns_search_domains": [],
"dns_servers": [
"8.8.8.8"
],
"frwd_routes": [
"10.0.0.0/8"
]
},
"ipsec_xauth_rsa": {
"user_cert_alias": "",
"ca_cert_alias": "",
"server_cert_alias": "",
"dns_search_domains": [],
"dns_servers": [
"8.8.8.8"
],
"frwd_routes": [
"10.0.0.0/8"
]
},
"ipsec_ike2_psk": {
"identifier": "test@sta.com",
"pre_shared_key": "example",
"dns_search_domains": [],
"dns_servers": [
"8.8.8.8"
],
"frwd_routes": [
"10.0.0.0/8"
]
},
"ipsec_ike2_rsa": {
"user_cert_alias": "",
"ca_cert_alias": "",
"server_cert_alias": "",
"dns_search_domains": [],
"dns_servers": [
"8.8.8.8"
],
"frwd_routes": [
"10.0.0.0/8"
],
"ocsp_url": ""
}
}
}
}
Example Xauth-PSK JSON (Other configurations in gray)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samsungmdfadminguidev6-211228084552/75/Samsung-mdf-admin-guide-v6-3-25-2048.jpg)