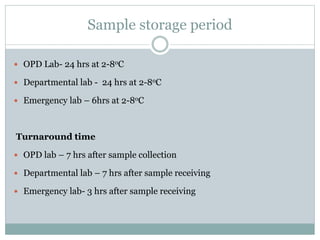
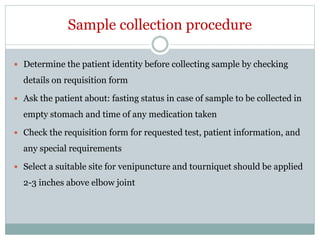
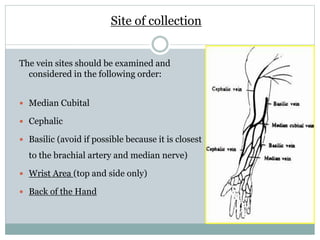
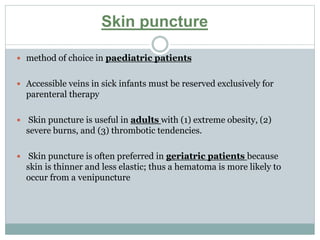
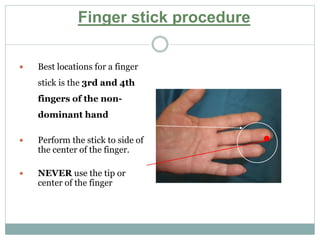
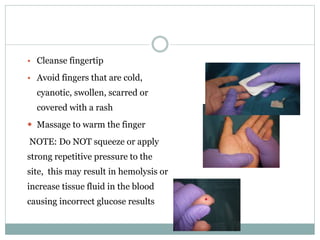
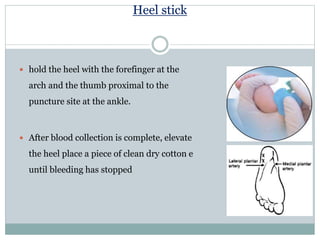
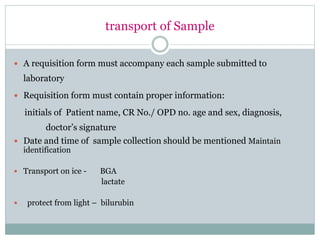
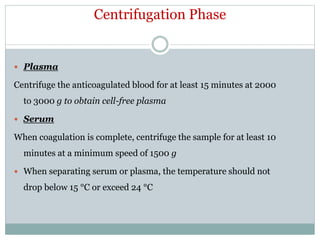
Dr. Rajju Tiwari discusses sample collection and processing procedures. Standard precautions include using personal protective equipment, proper hand hygiene, and handling all blood as potentially infectious. Phlebotomy involves making an incision in a vein with a needle to collect blood samples. Proper sample collection requires checking patient identity, sample type, and special requirements. Common sample types are blood, urine, and fluids. Centrifugation is used to separate plasma or serum from whole blood for processing. Samples must be properly labeled, transported, stored, and processed within specified timeframes for accurate testing and results.




















![Prevention of bilirubin interference
The high prevalence of hyperbilirubinaemia in patients from
intensive care, gastroenterological surgical or paediatric departments
--Blanking procedures are useful to eliminate spectral bilirubin
interferences
K4 [Fe(CN)6] effectively eliminates bilirubin interference in H2O2-
forming enzymatic methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samplecollectionprocessing-240117061909-cba52deb/85/Sample-Collection-Processing-pptxDr-Rajju-Tiwari-M-D-biochemistry-31-320.jpg)