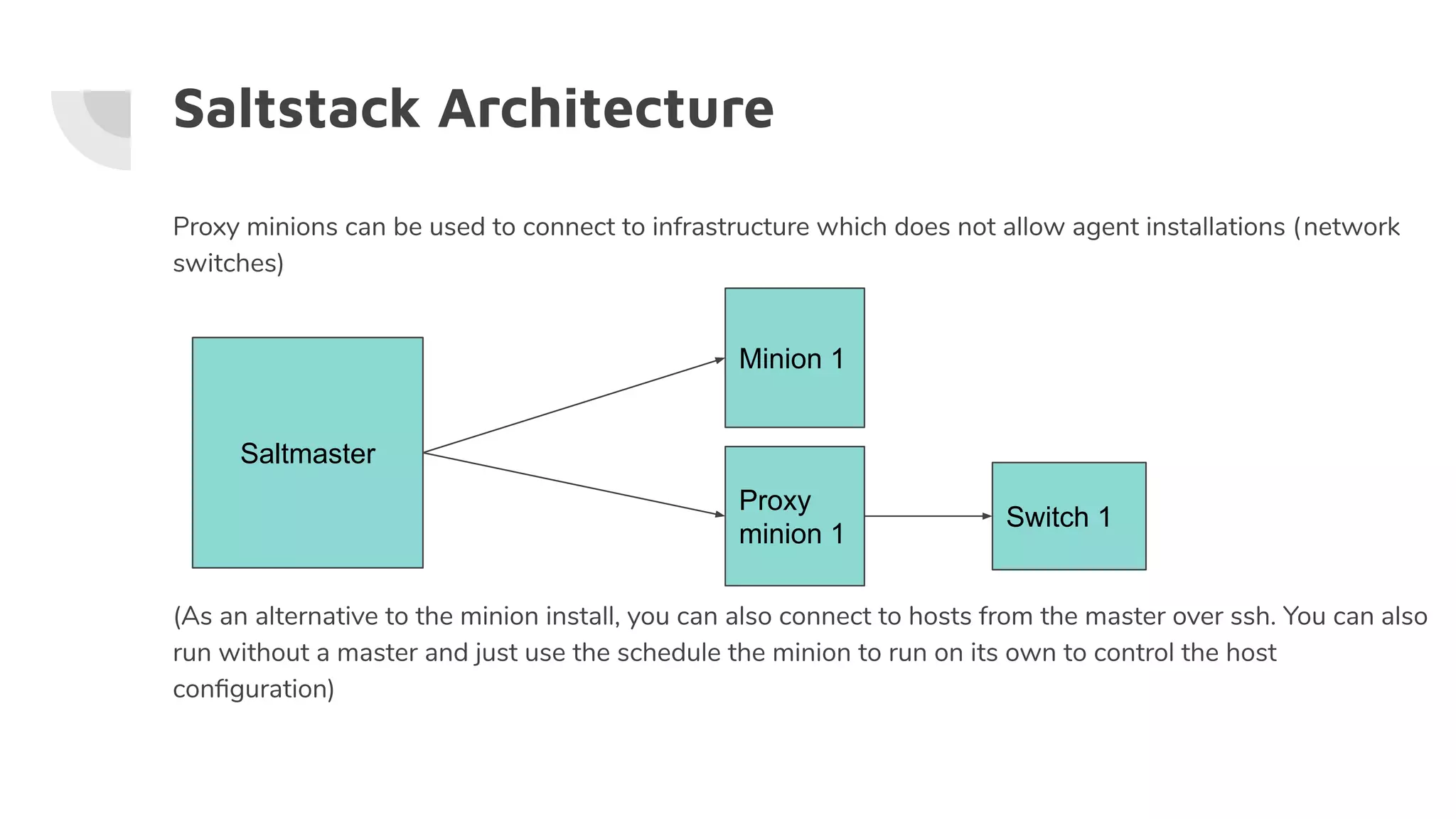
Saltcheck is a tool that leverages SaltStack's remote execution capabilities for validating various infrastructure elements, including code deployment, configuration files, and user management. It utilizes Salt's modular architecture, allowing for custom assertions and tests using YAML/Jinja rendering. Additionally, it facilitates knowledge reuse within teams by providing a consistent framework for infrastructure validation.


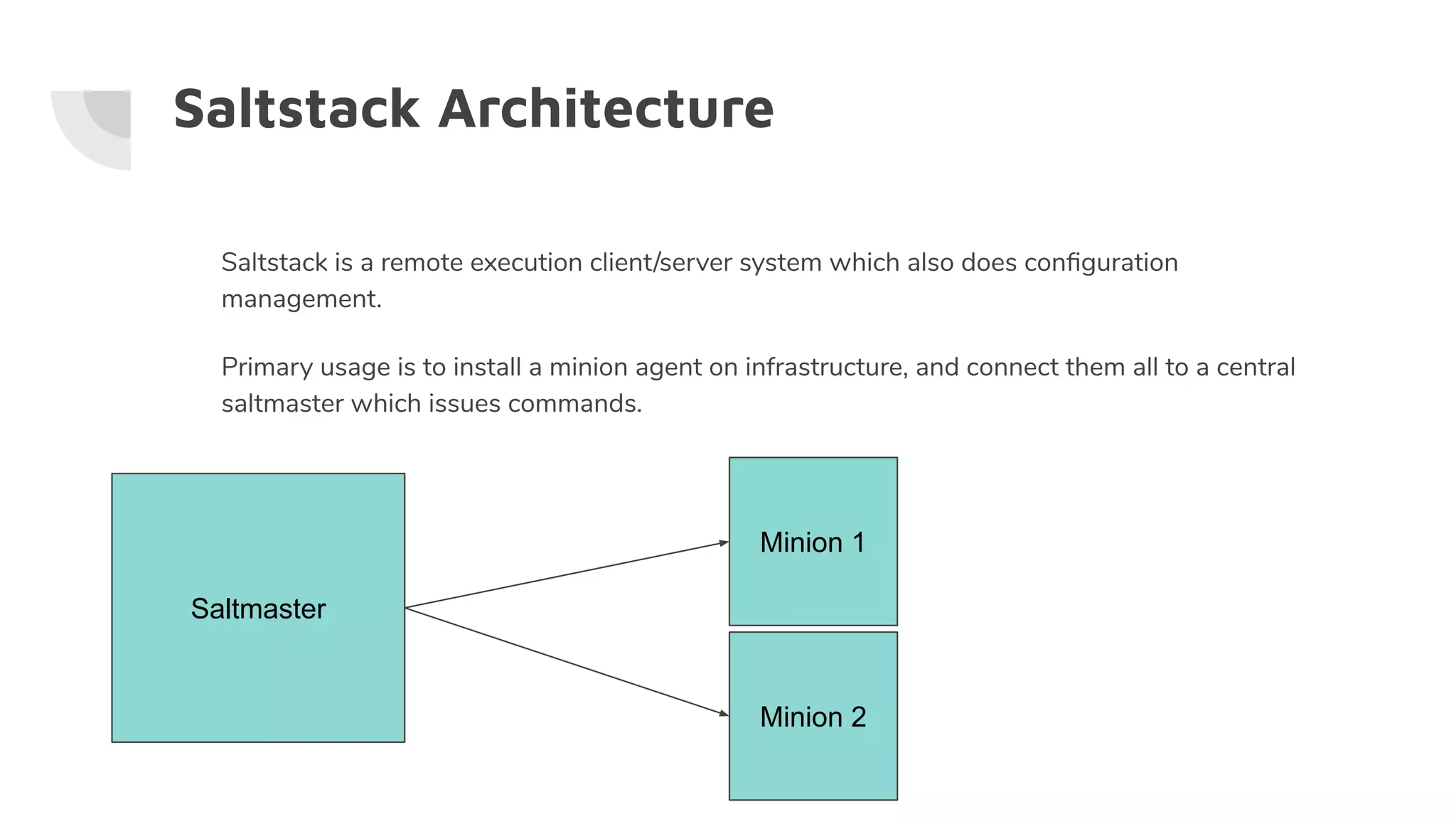

![Saltstack Architecture: yaml/jinja
/etc/http/conf/http.conf:
file.managed:
- source: salt://apache/http.conf
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
{% set motd = ['/etc/motd'] %}
{% if grains['os'] == 'Debian' %}
{% set motd = ['/etc/motd.tail', '/var/run/motd'] %}
{% endif %}
{% for motdfile in motd %}
{{ motdfile }}:
file.managed:
- source: salt://motd
{% endfor %}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltcheckmeetup-200807111003/75/Saltcheck-a-tool-in-the-salt-toolbox-7-2048.jpg)

![Saltcheck
Salt execution module: salt ‘*’ saltcheck.run_highstate_tests
package_latest:
module_and_function: pkg.upgrade_available
args:
- apache2
assertion: assertFalse
{% for package in ["apache2", "openssh"] %}
test_{{ package }}_latest:
module_and_function: pkg.upgrade_available
args:
- {{ package }}
assertion: assertFalse
{% endfor %}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltcheckmeetup-200807111003/75/Saltcheck-a-tool-in-the-salt-toolbox-9-2048.jpg)

 %}
{% set oozie_version = salt['grains.get']('ec2_tags:OOZIE_VERSION') %}
{% set prime_version = salt['grains.get']('ec2_tags:PRIME_RELEASE') %}
validate_refdata_jars:
module_and_function: hadoop.dfs_present
args:
- /refData/oozie-automation/{{ refdata_version }}_{{ prime_version
}}/oozie/workflows/refdata-config-{{ prime_version }}.jar
assertion: assertTrue
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltcheckmeetup-200807111003/75/Saltcheck-a-tool-in-the-salt-toolbox-11-2048.jpg)

.iteritems() %}
validate_user_{{ usr }}:
module_and_function: user.info
assertion_section: shell
args:
- {{ usr }}
assertion: assertEqual
expected-return: /bin/bash
check_ssh_key_{{ usr }}:
module_and_function: ssh.check_key
args:
- {{ usr }}
- {{ data.key }}
- ssh-rsa
- ''
- ''
assertion: assertEqual
expected-return: exists
{% endfor %}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltcheckmeetup-200807111003/75/Saltcheck-a-tool-in-the-salt-toolbox-13-2048.jpg)