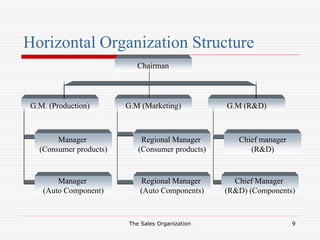
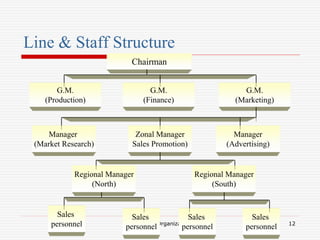
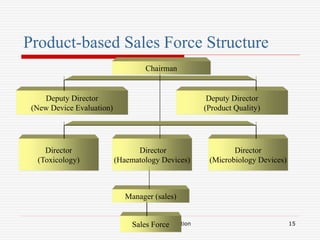
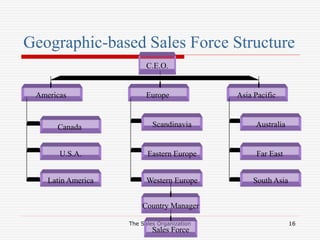
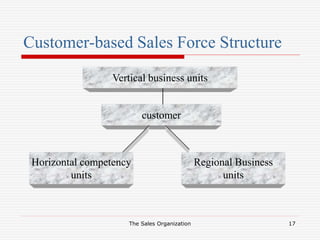
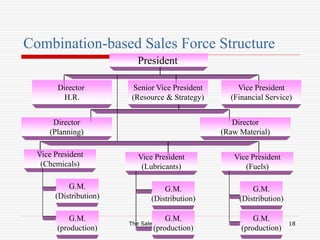
The document discusses the key aspects of designing a sales organization, including the role of the sales organization, basis for the design, types of organizational structures, sales force structures, and sales culture. Specifically, it outlines different types of organizational structures like formal vs informal and horizontal vs vertical. It also describes different sales force structures such as product-based, geographic-based, and customer-based. Finally, it discusses the importance of developing an effective sales culture.