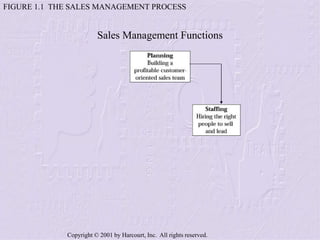
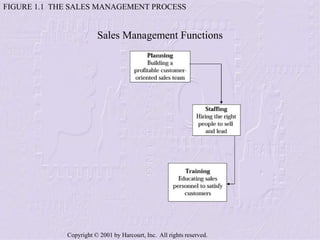
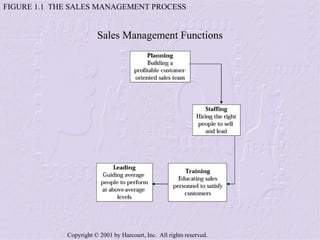
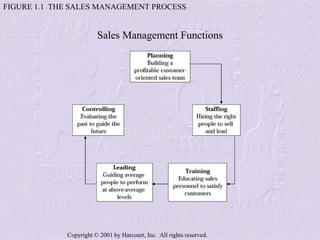
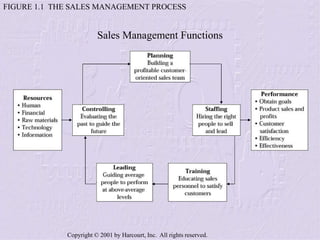
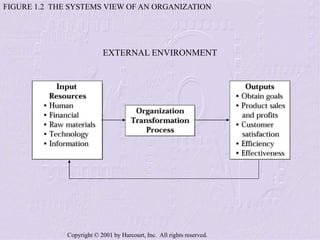
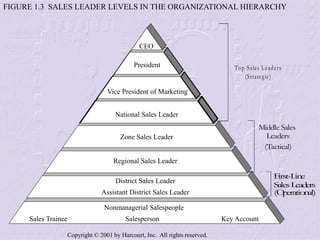
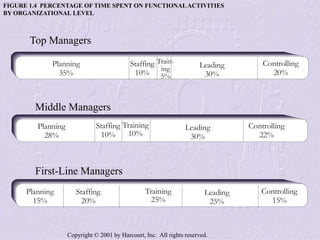
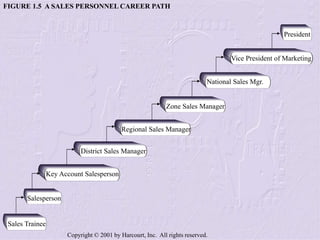
The document provides an overview of sales management, detailing the roles, skills, and responsibilities of sales managers. It outlines key functions such as planning, staffing, training, leading, and controlling, and discusses the challenges faced by new managers transitioning from sales roles. Additionally, the text emphasizes the importance of skilled sales managers in achieving organizational goals.