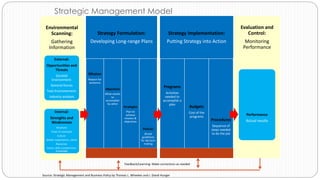
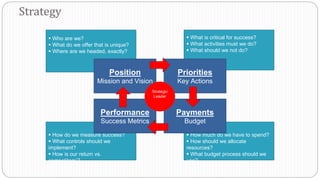
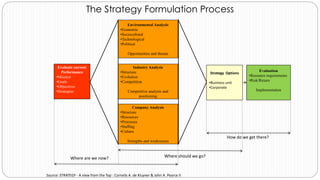
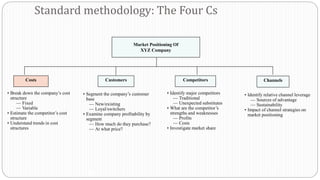
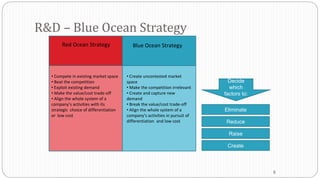
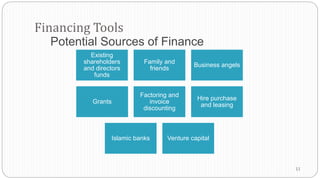
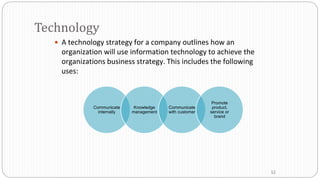
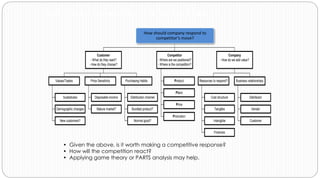
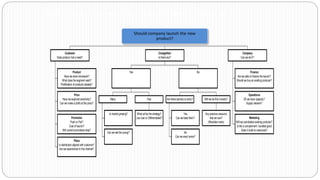
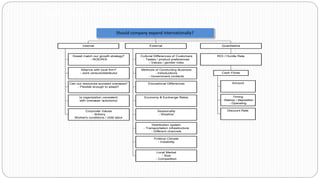
The document provides an overview of the strategic management model and process. It includes the following key elements:
1) Strategy formulation which involves developing long-range plans including the mission, objectives, strategies, policies, and environmental scanning.
2) Strategy implementation which involves putting the strategy into action through programs, budgets, procedures, and evaluating internal strengths and weaknesses.
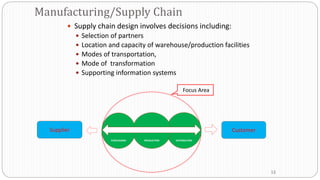
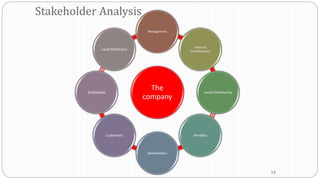
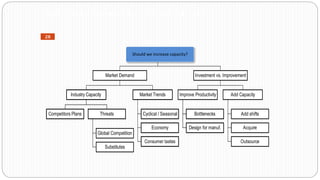
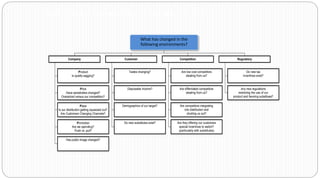
3) Environmental scanning which involves gathering external opportunities and threats as well as internal strengths and weaknesses.
4) Evaluation and control which involves monitoring performance against the mission, goals, and objectives and providing feedback to make corrections.