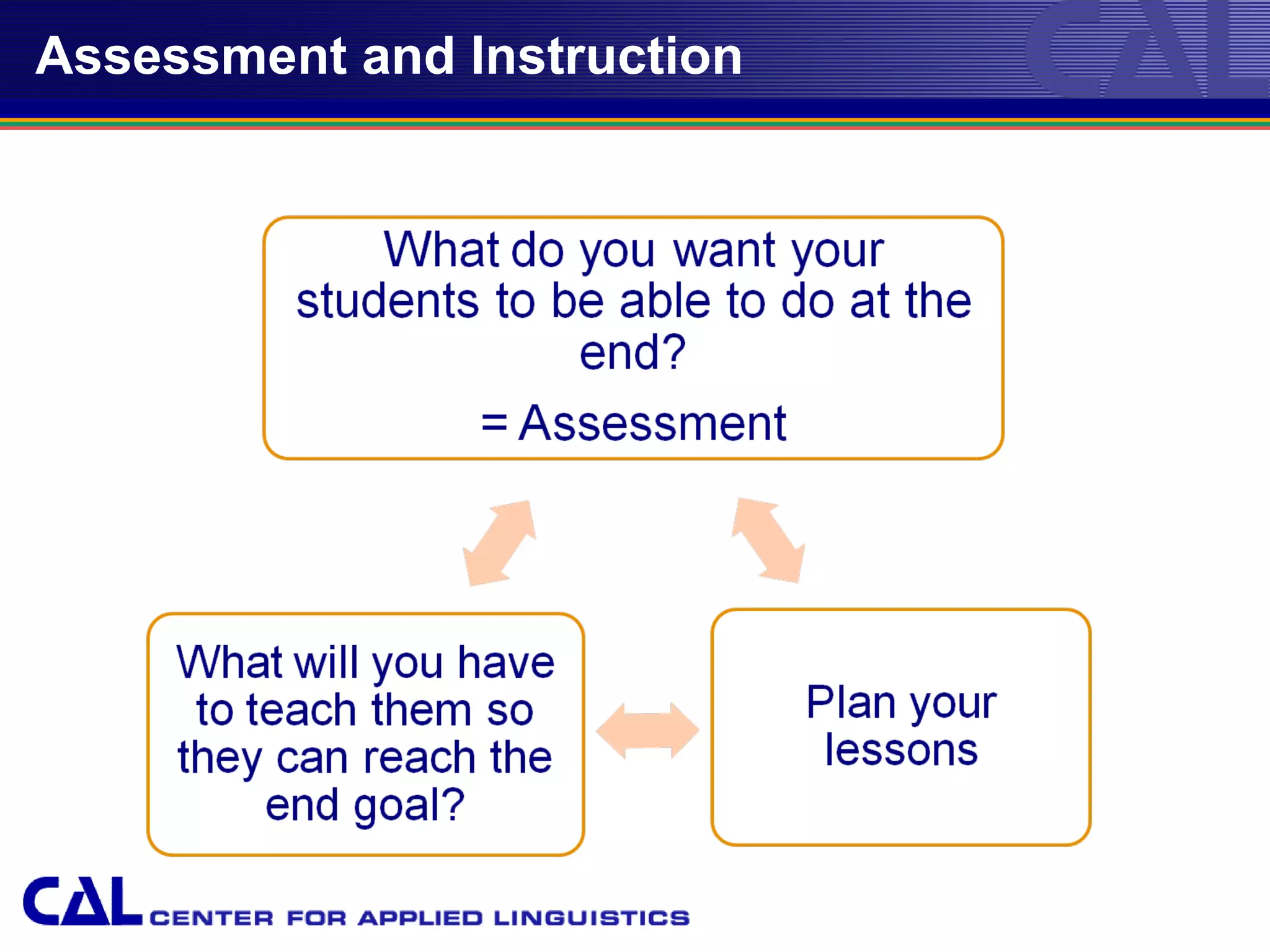
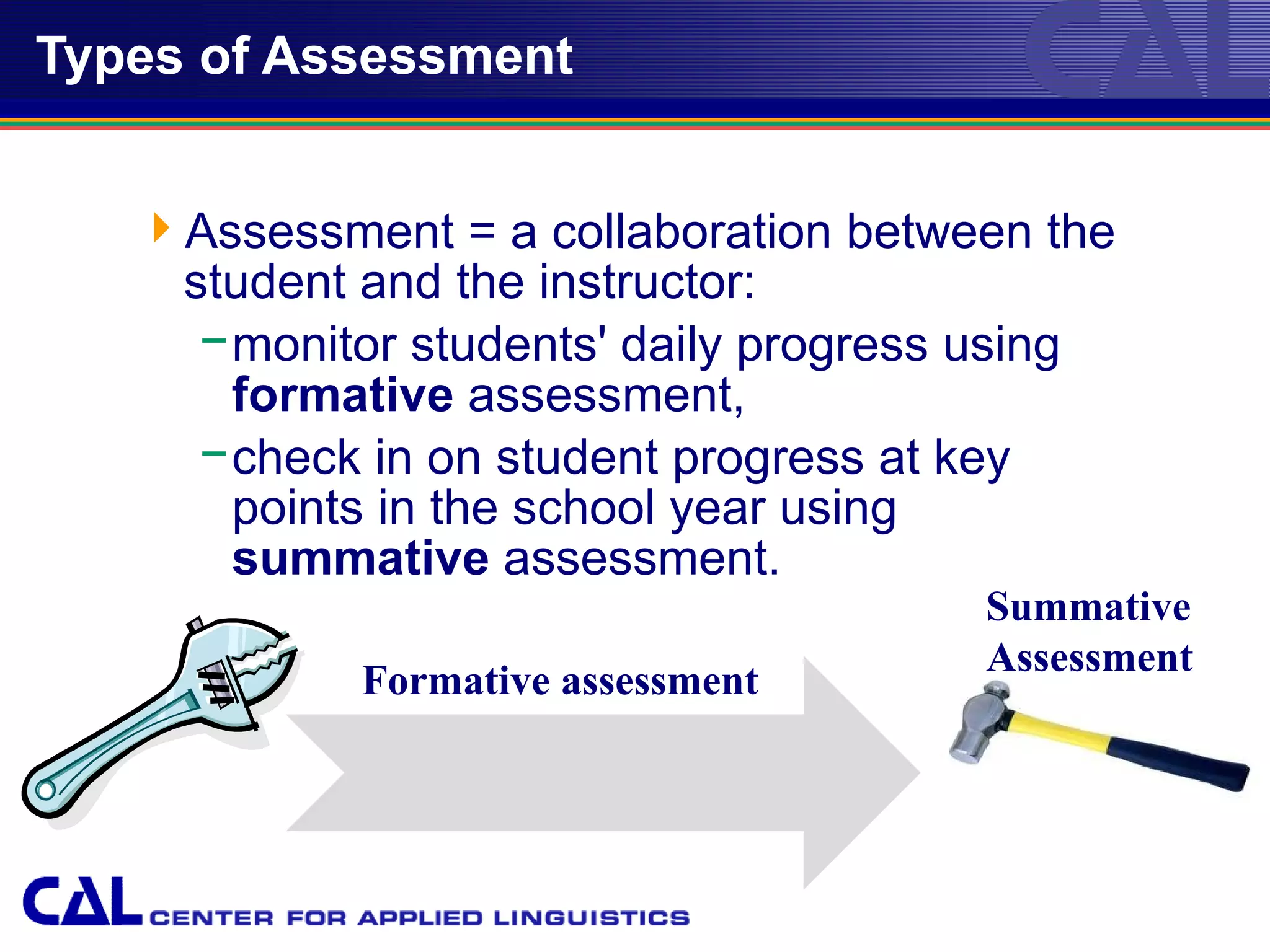
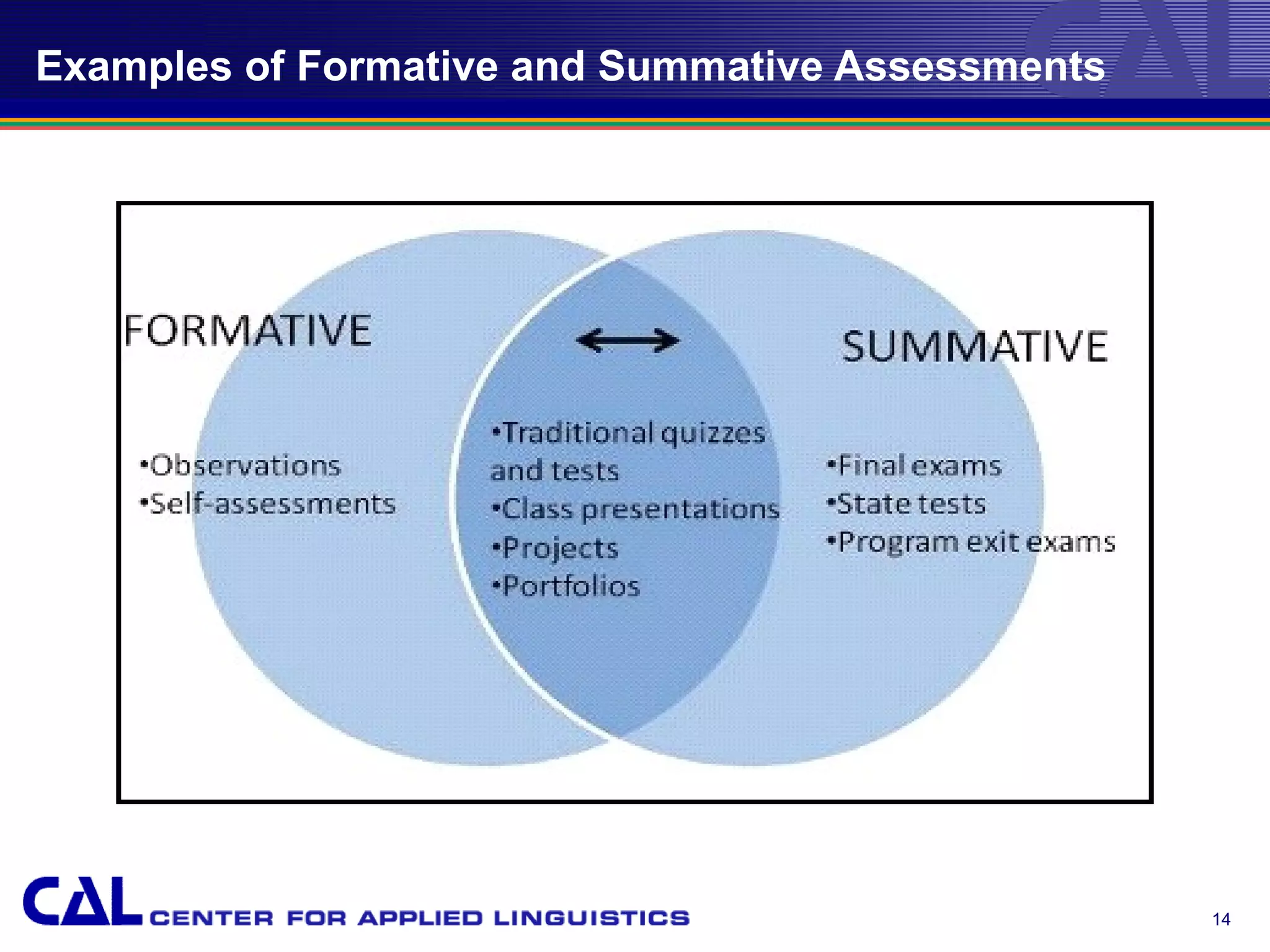
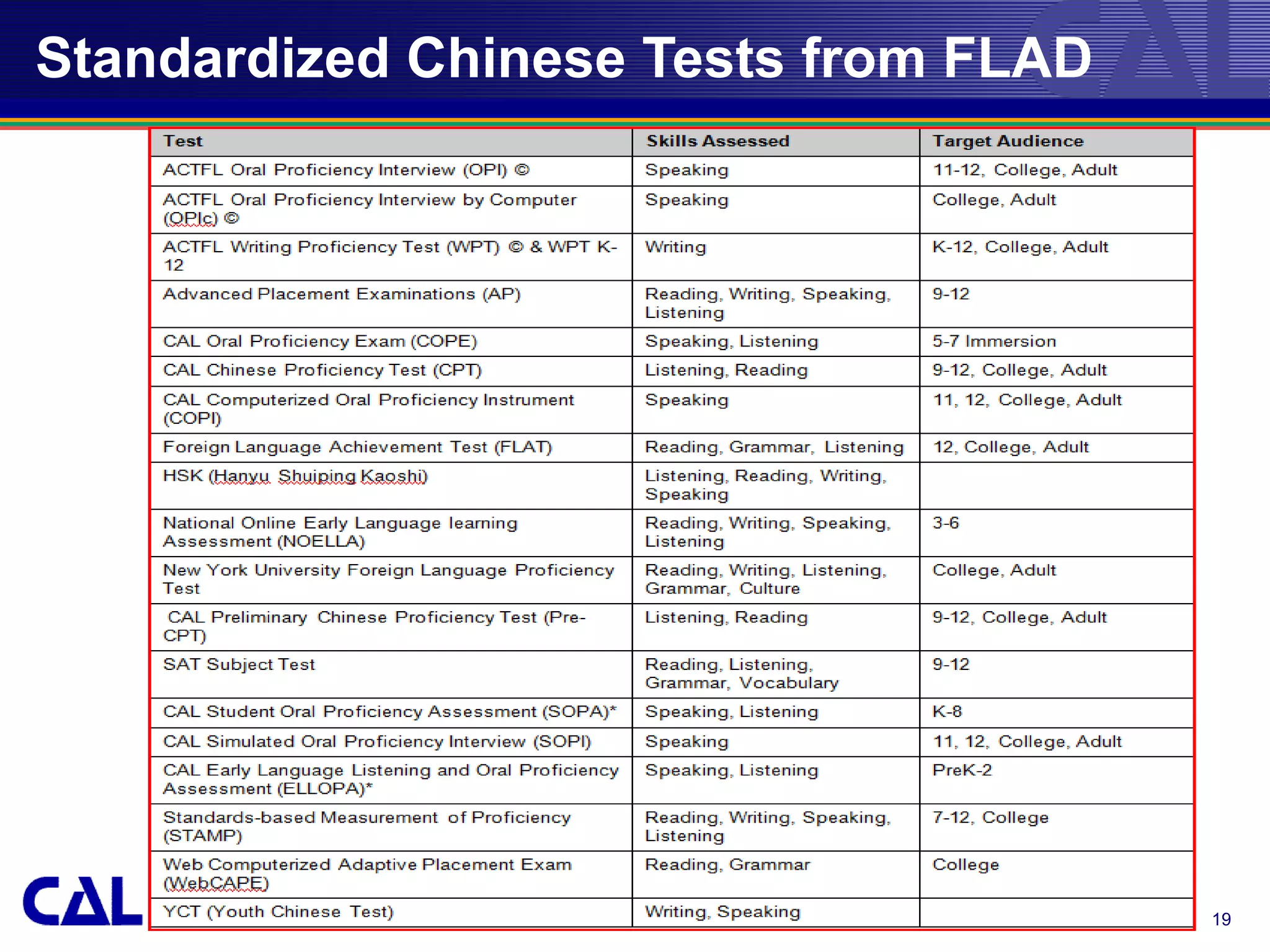
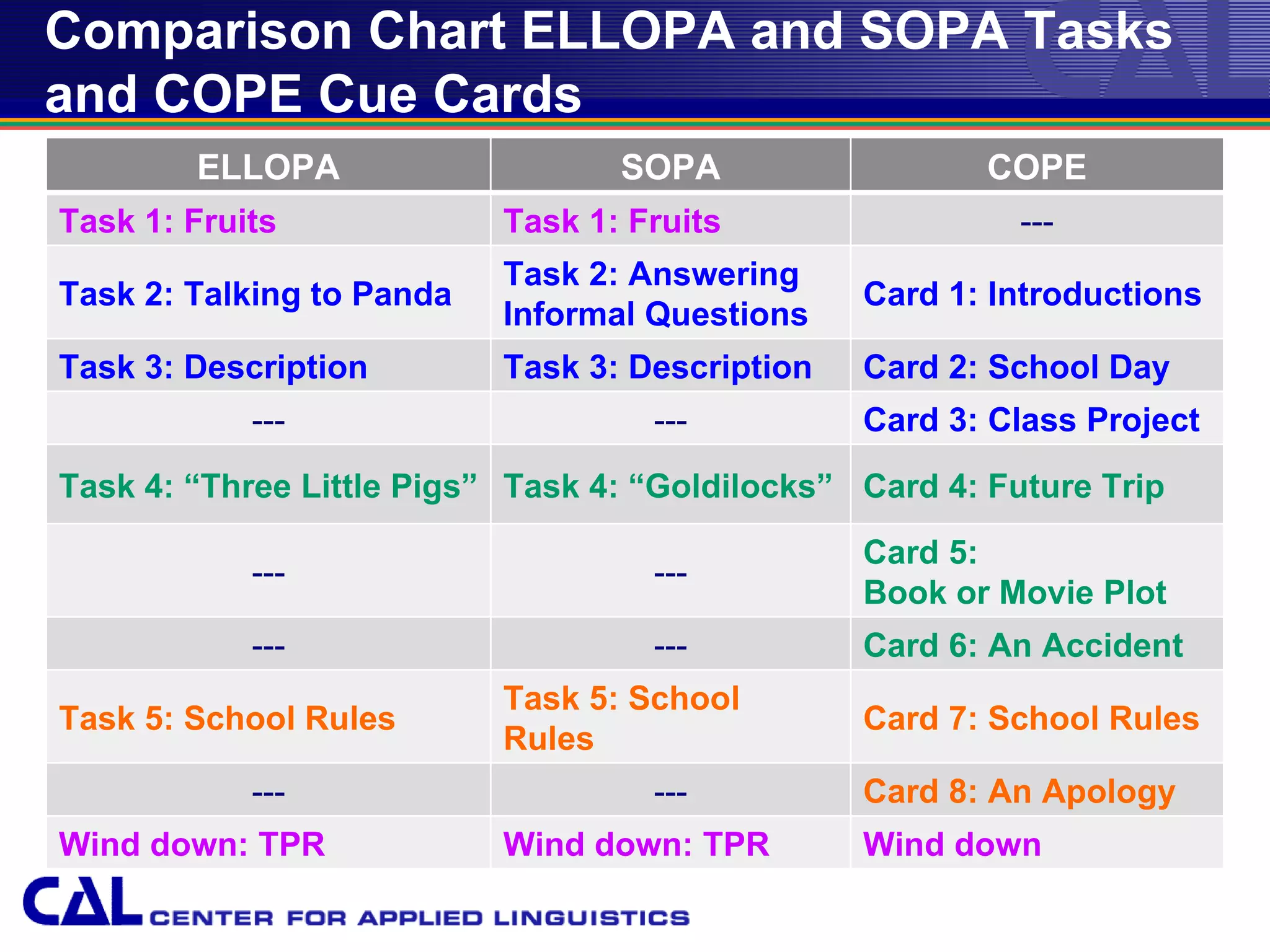
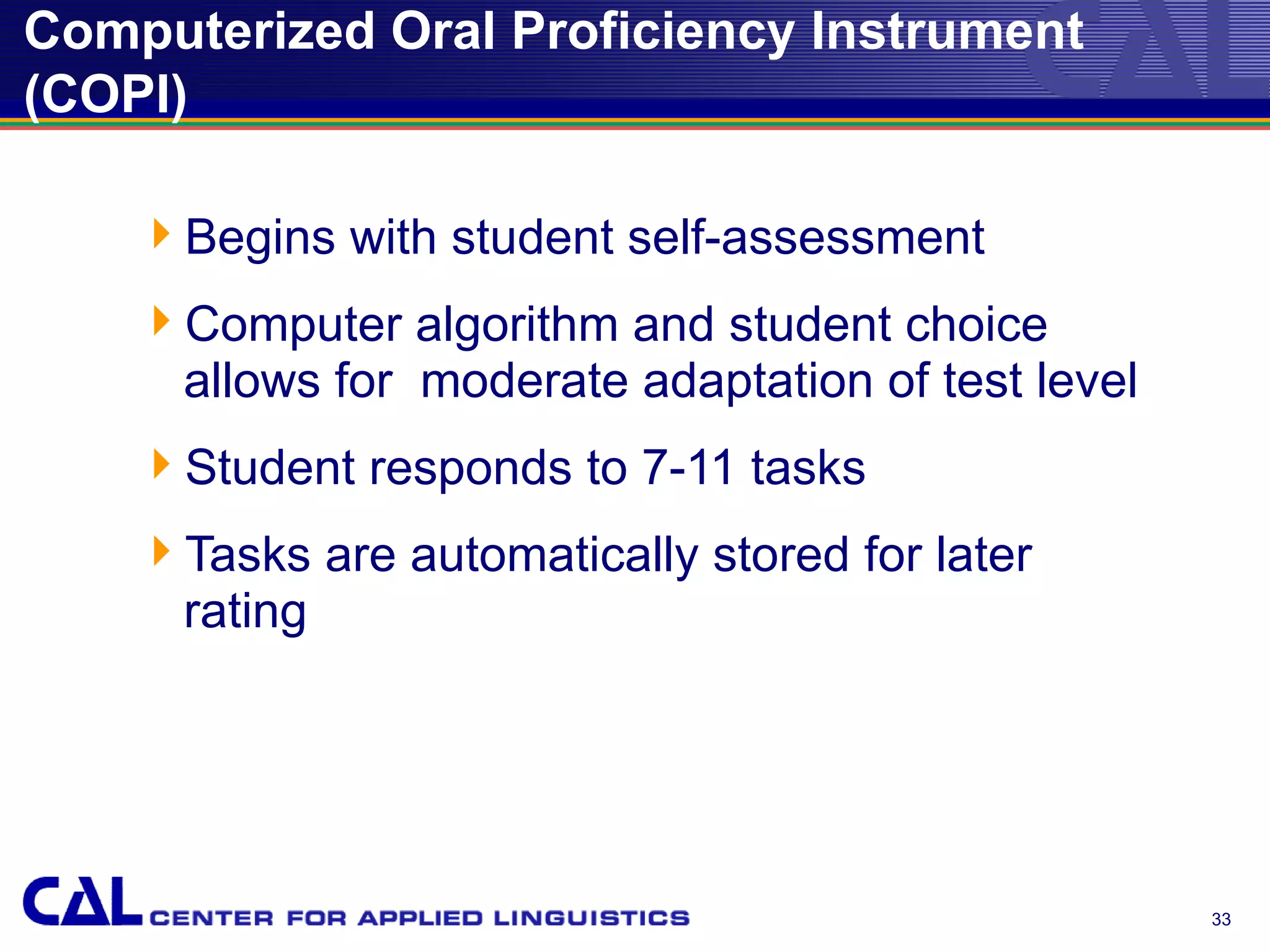
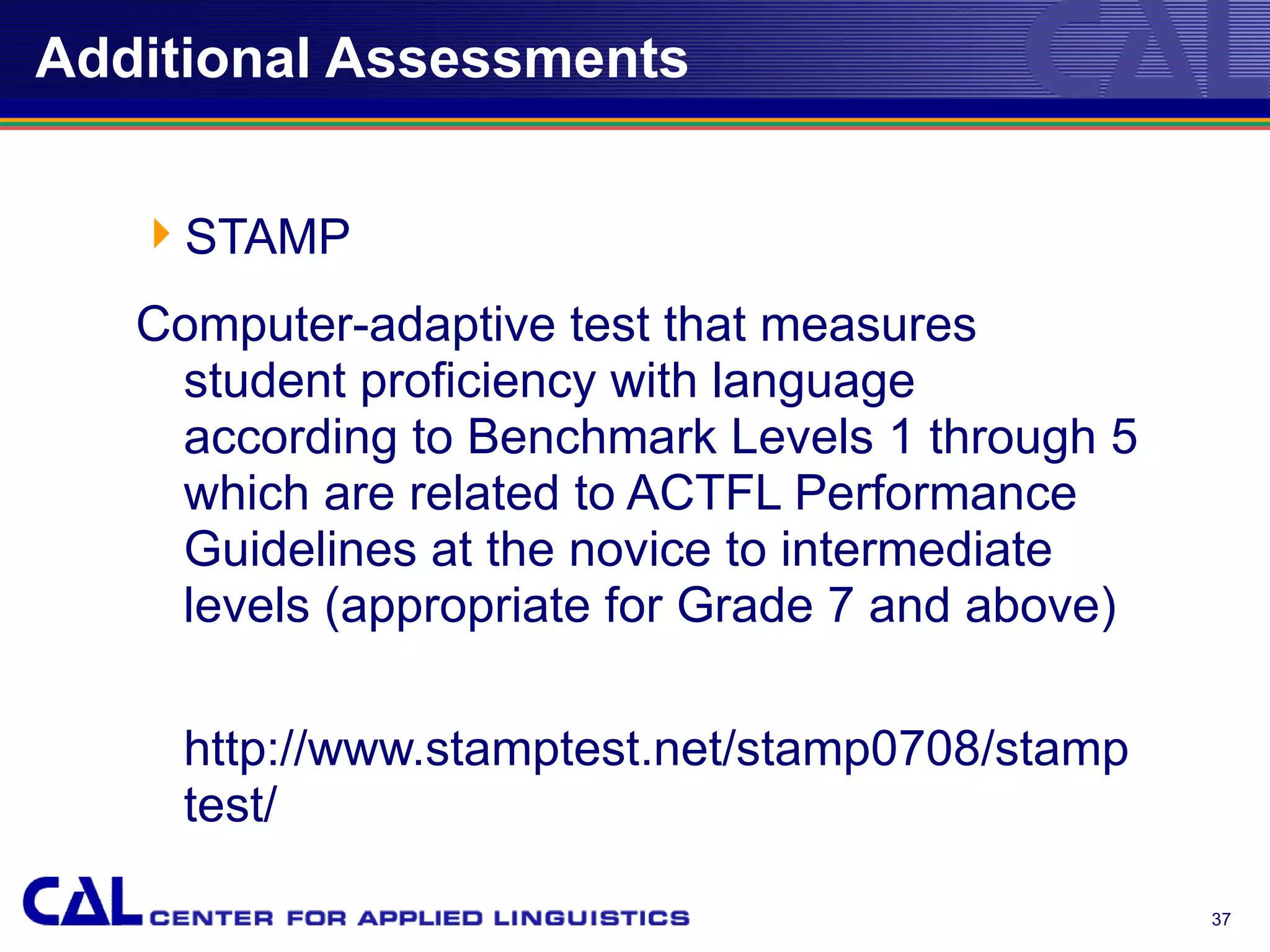
This document provides an overview of trends and best practices in Chinese language assessment for K-16 education. It introduces the Center for Applied Linguistics and its mission to improve language understanding through research. Various types of language assessments are defined, including formative and summative assessments. Innovative assessment resources for K-16 students from CAL are described, such as the Foreign Language Assessment Directory, Understanding Assessment guide, and K-8 assessments like ELLOPA, SOPA, and COPE. Additional resources for 9-16 students including the Computerized Oral Proficiency Instrument and rater training materials are also covered.