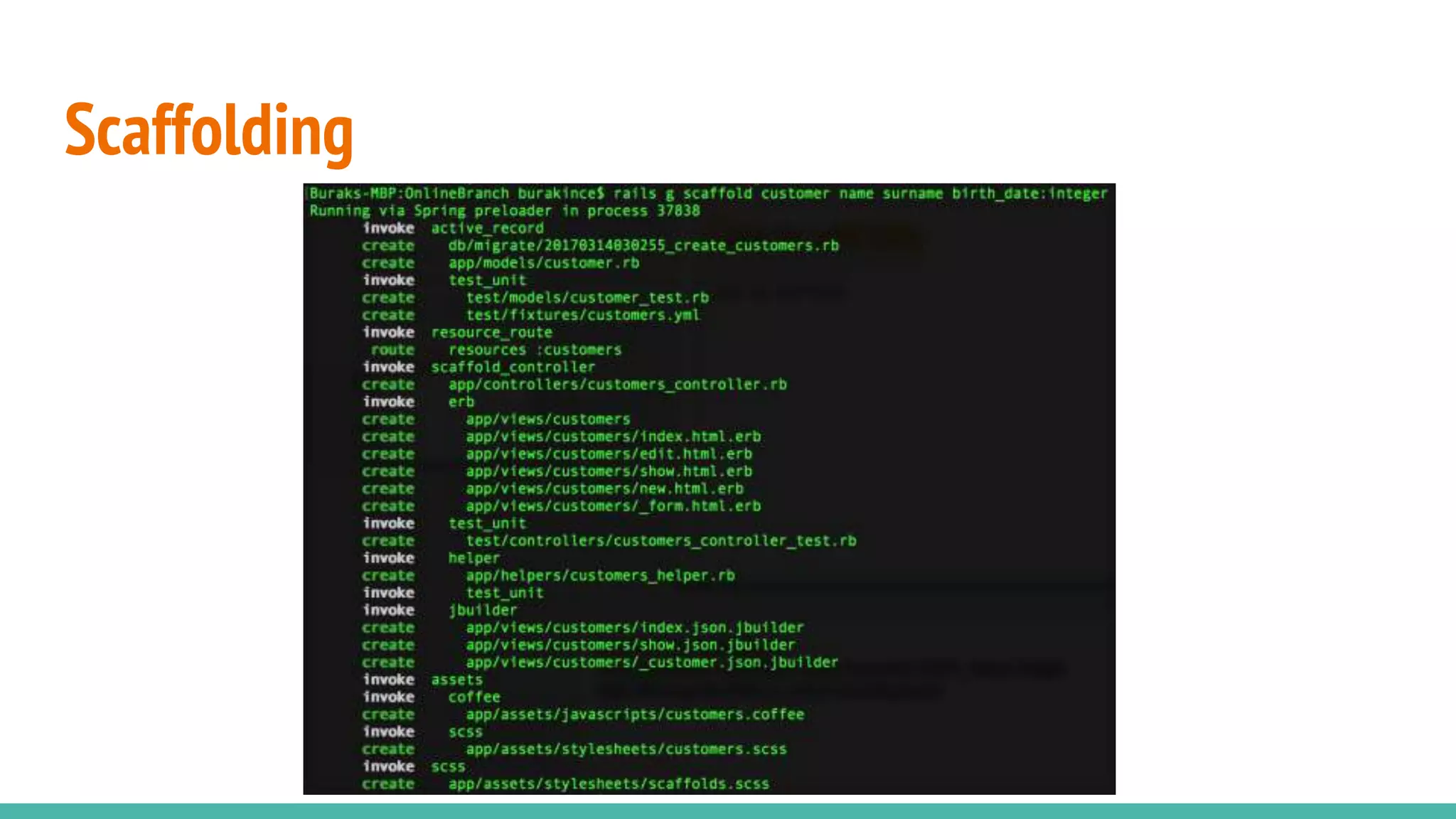
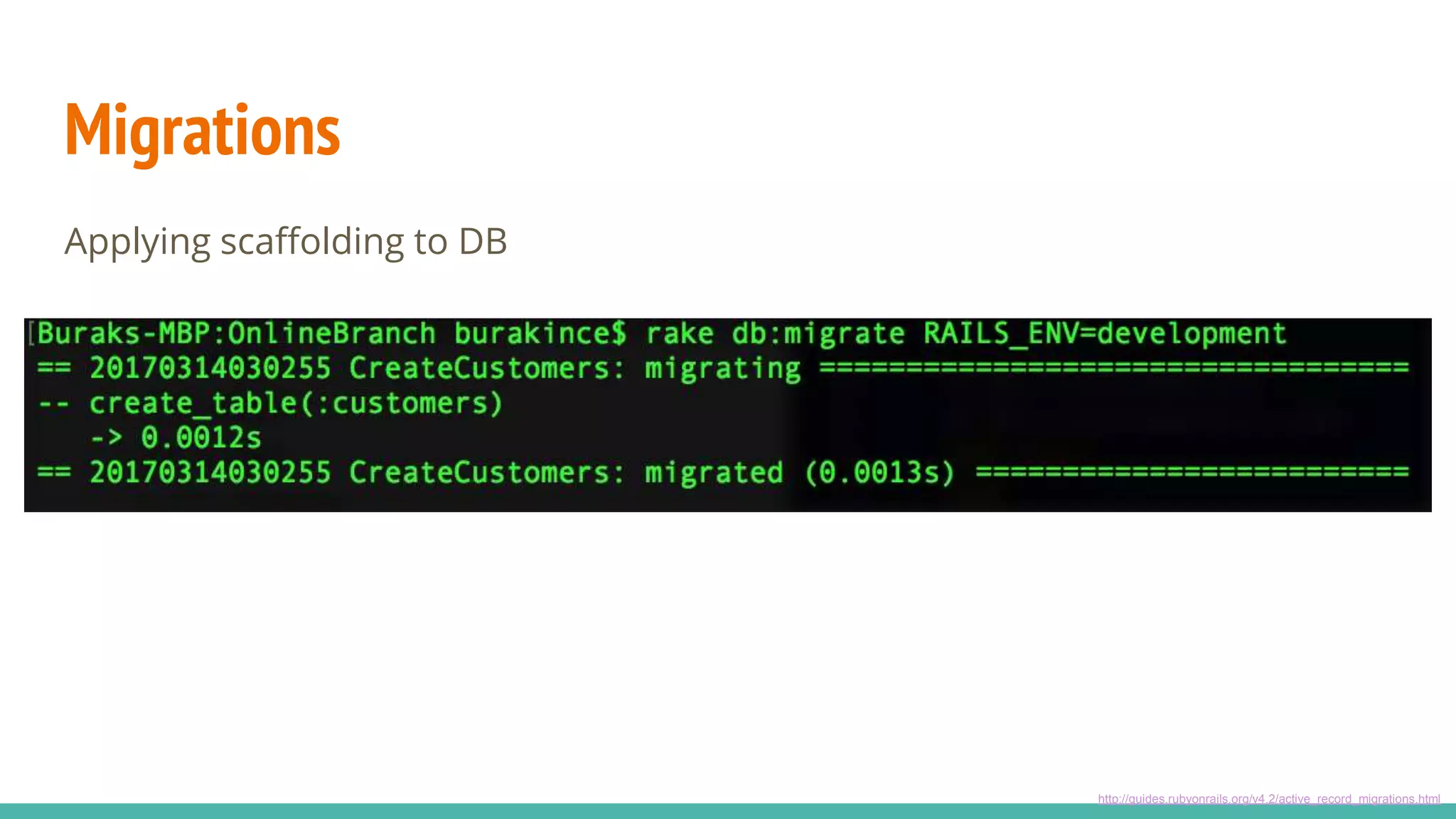
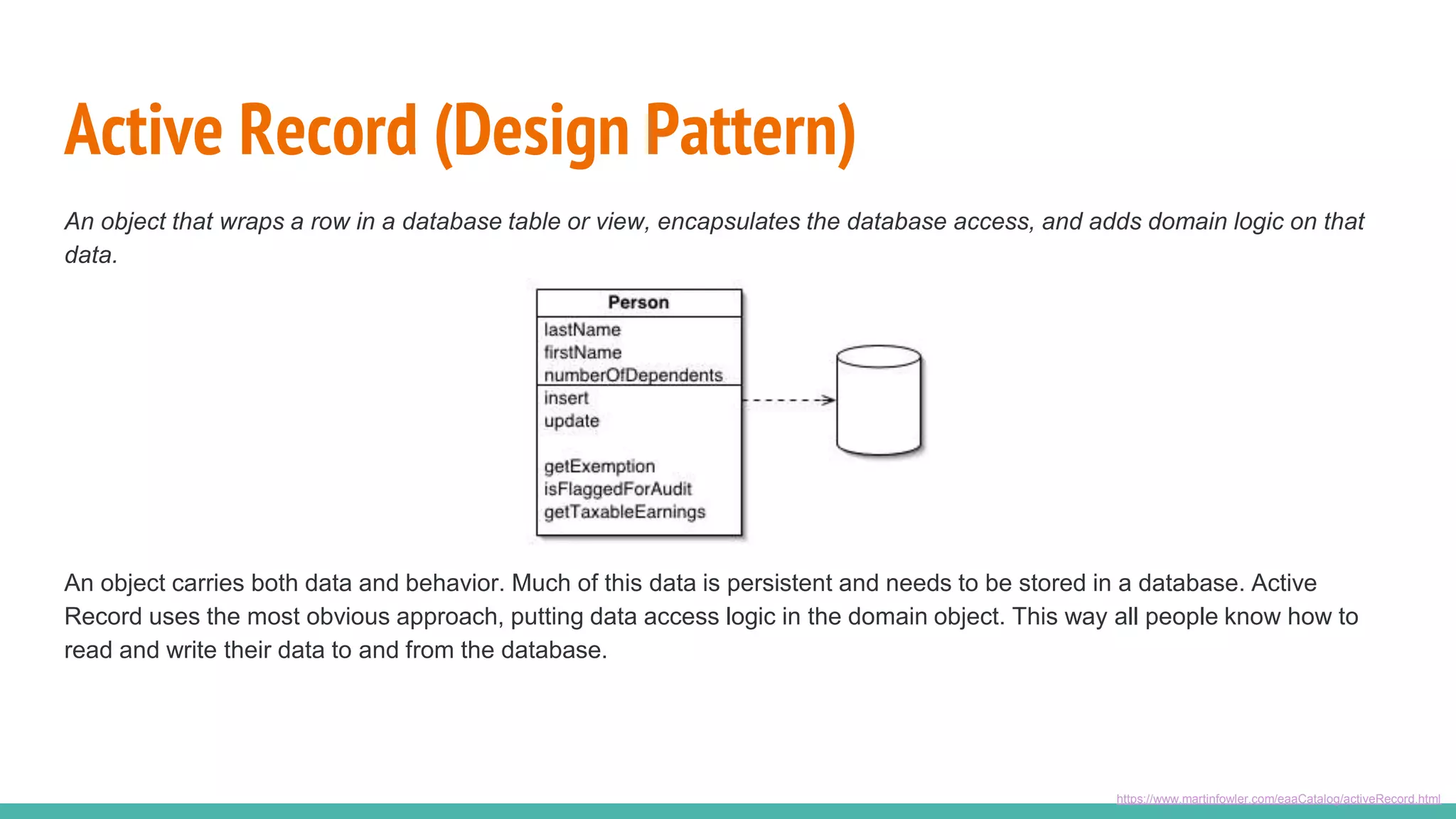
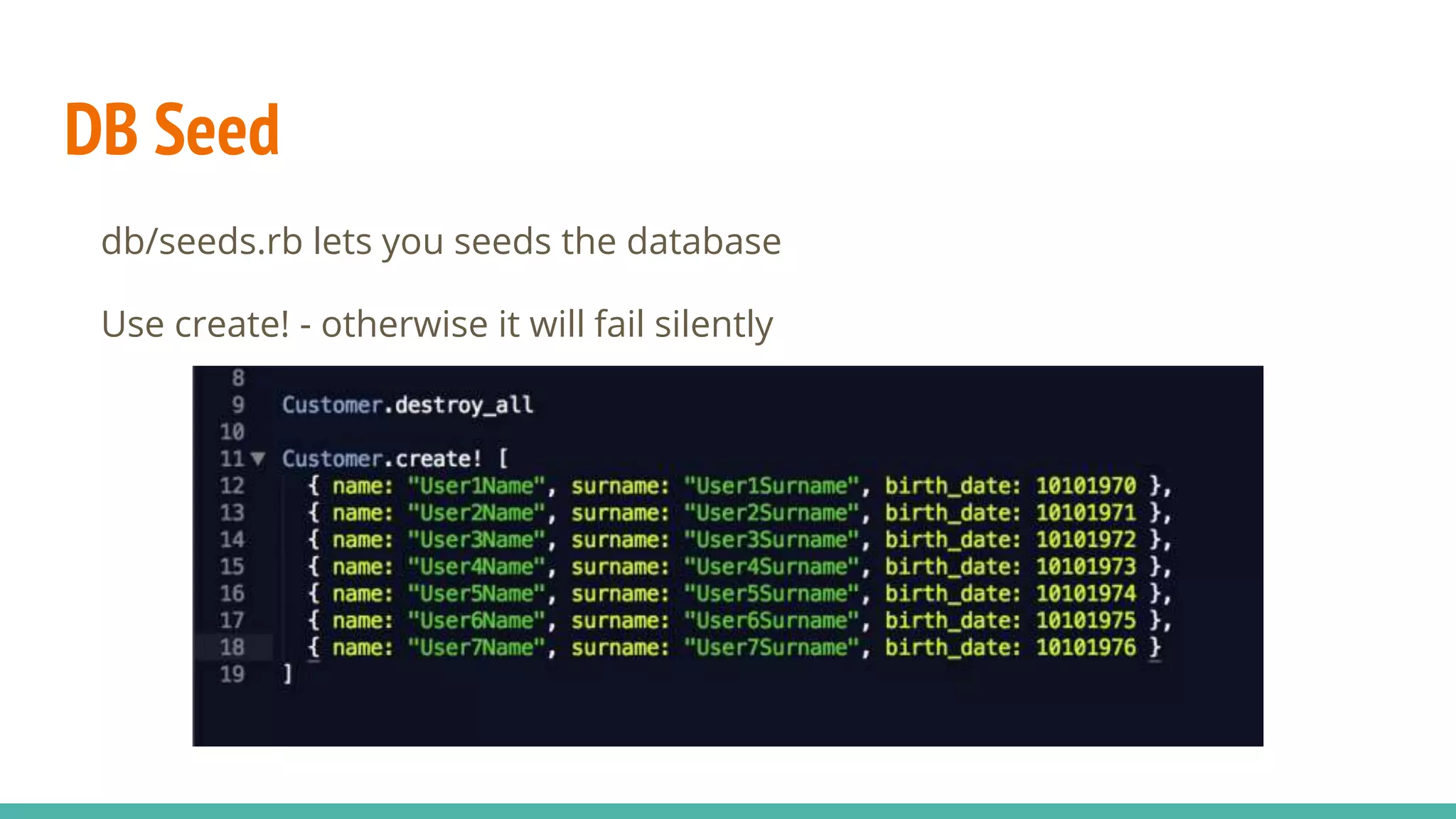
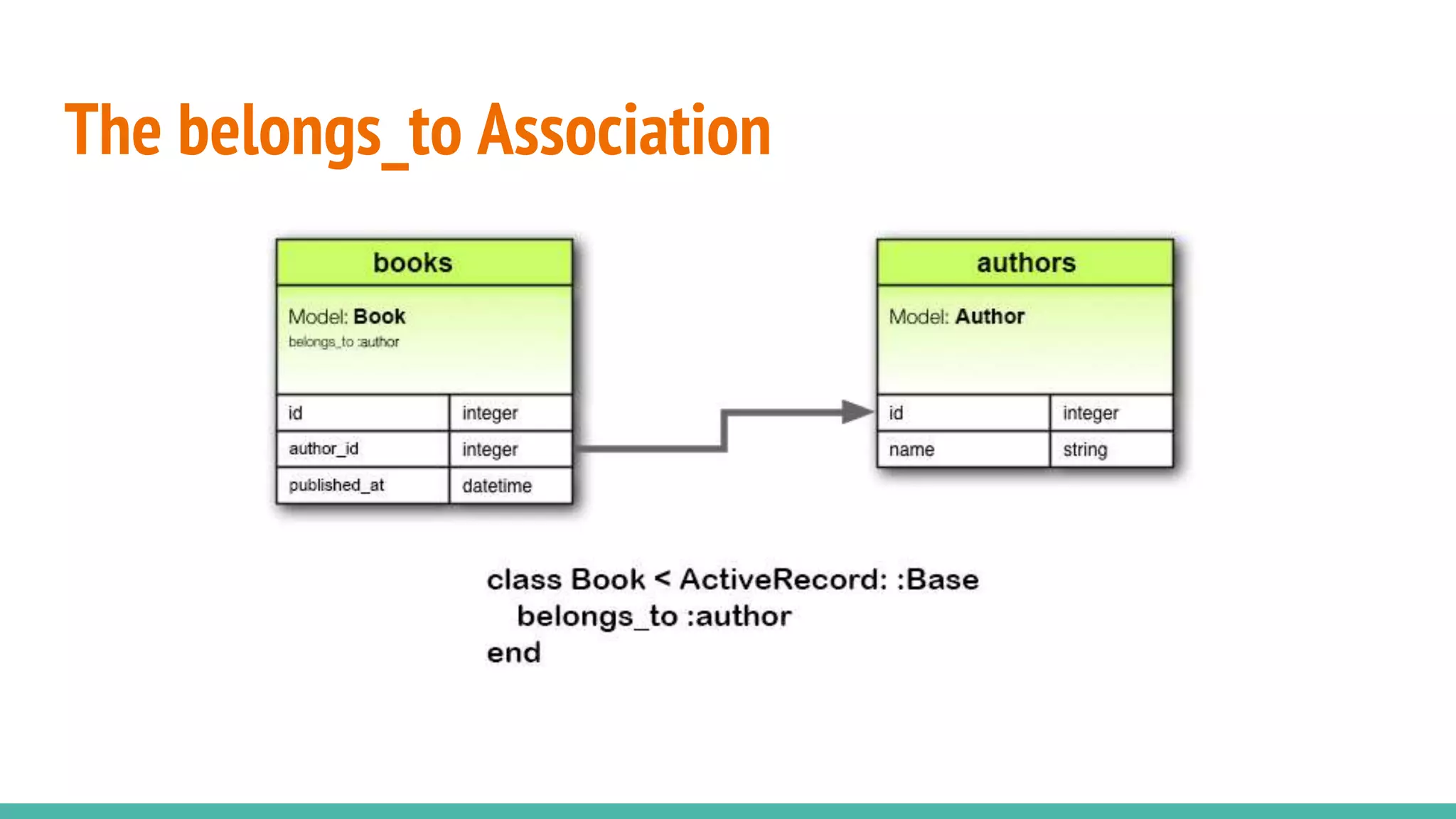
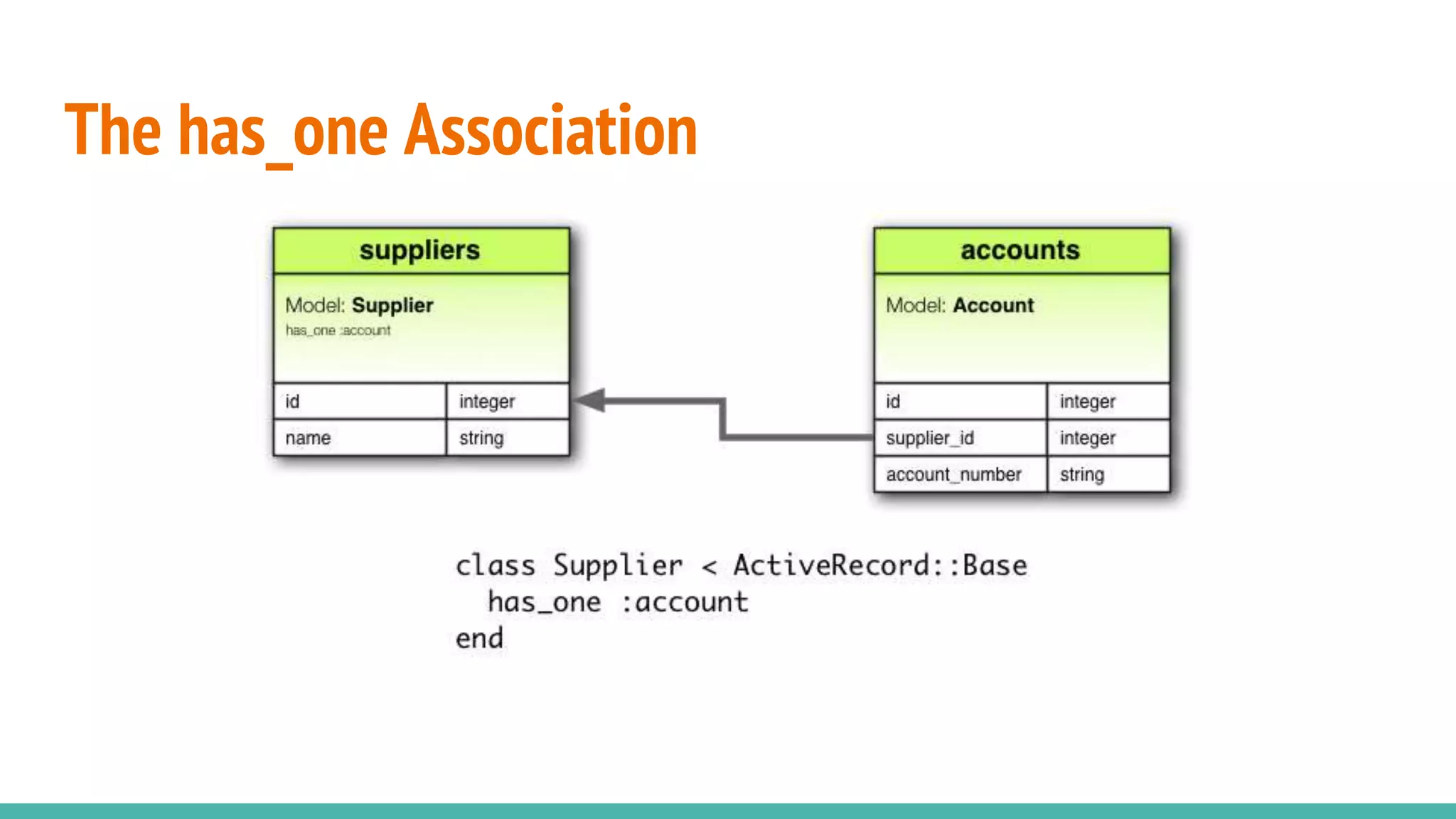
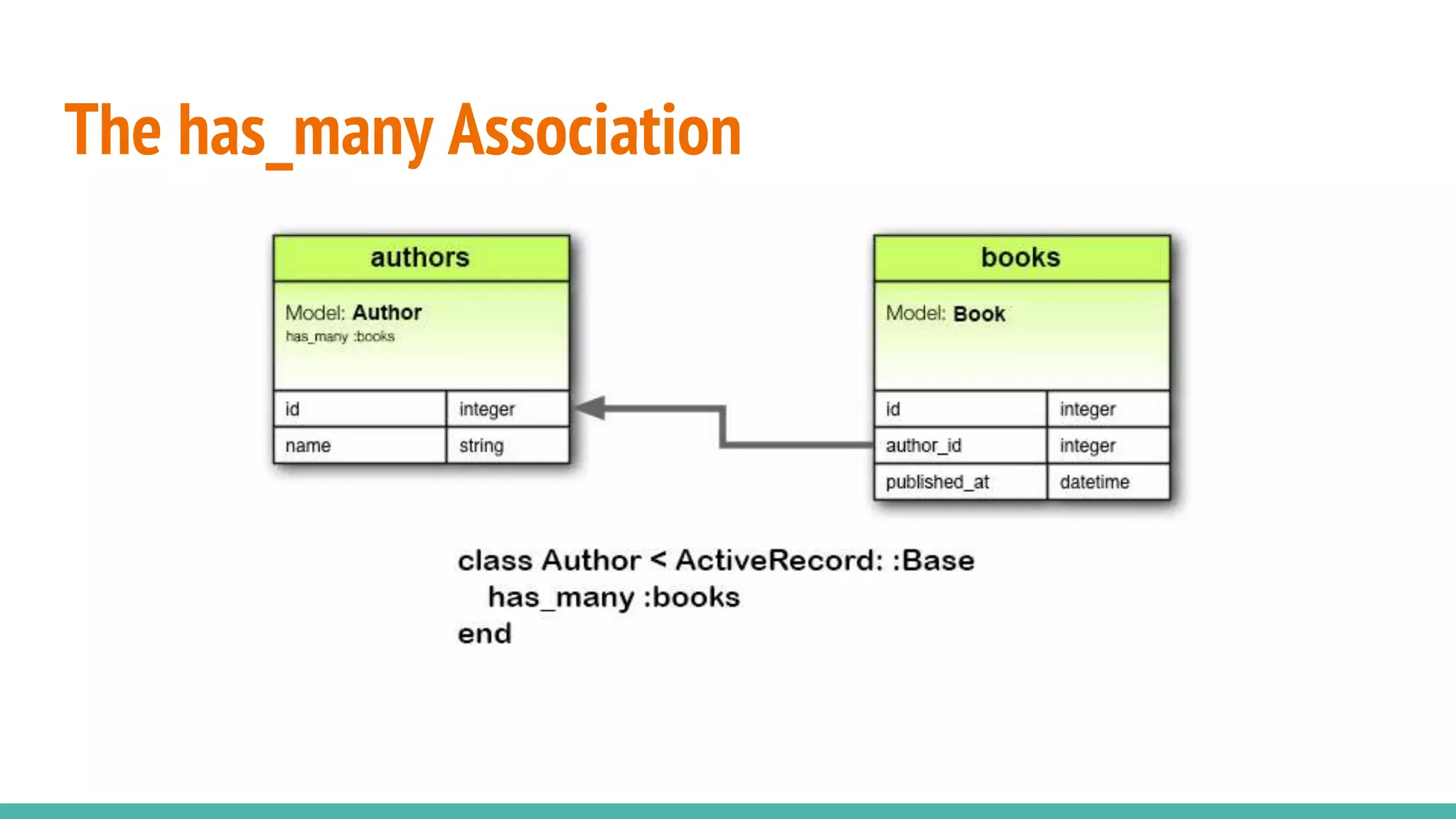
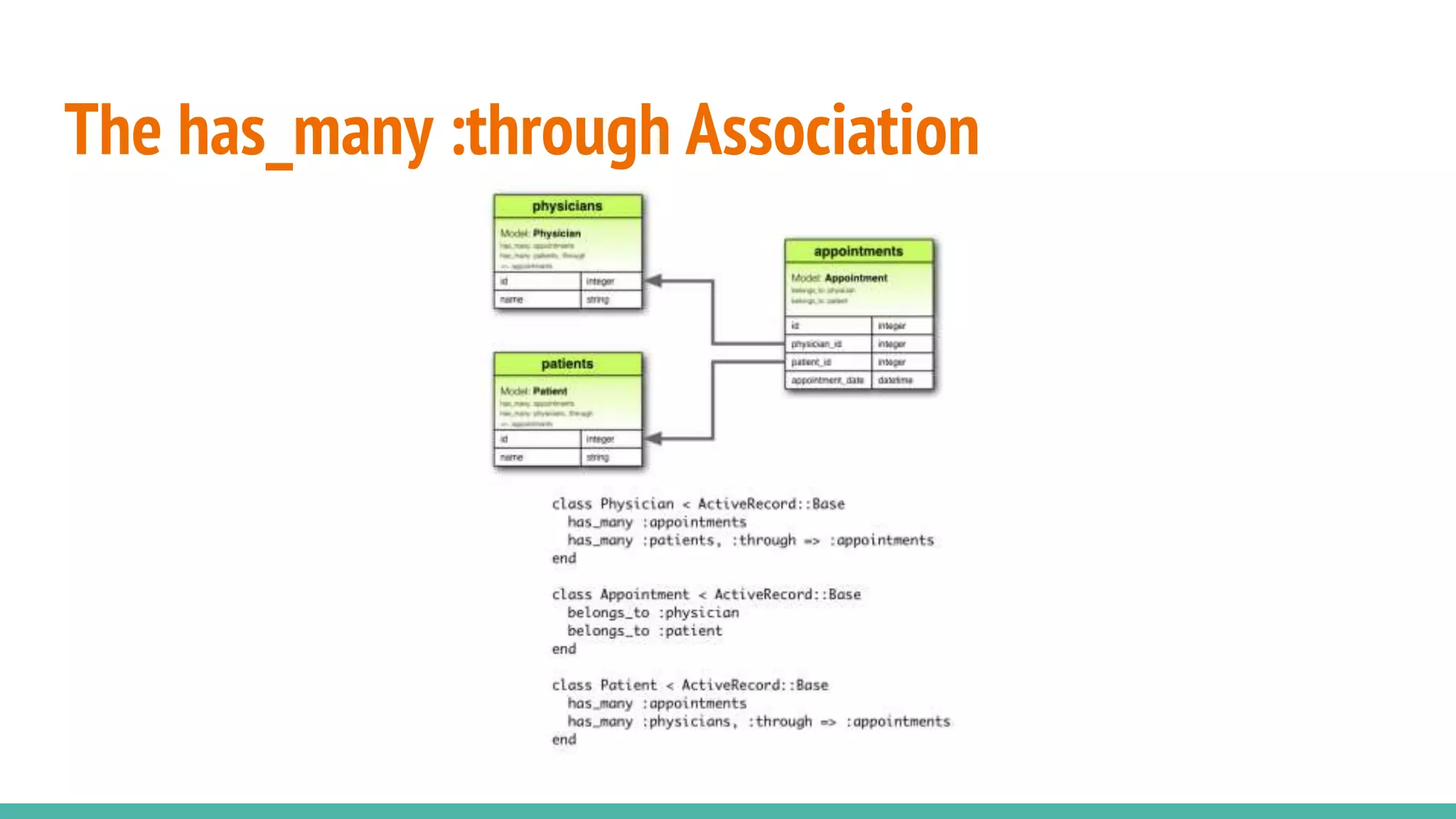
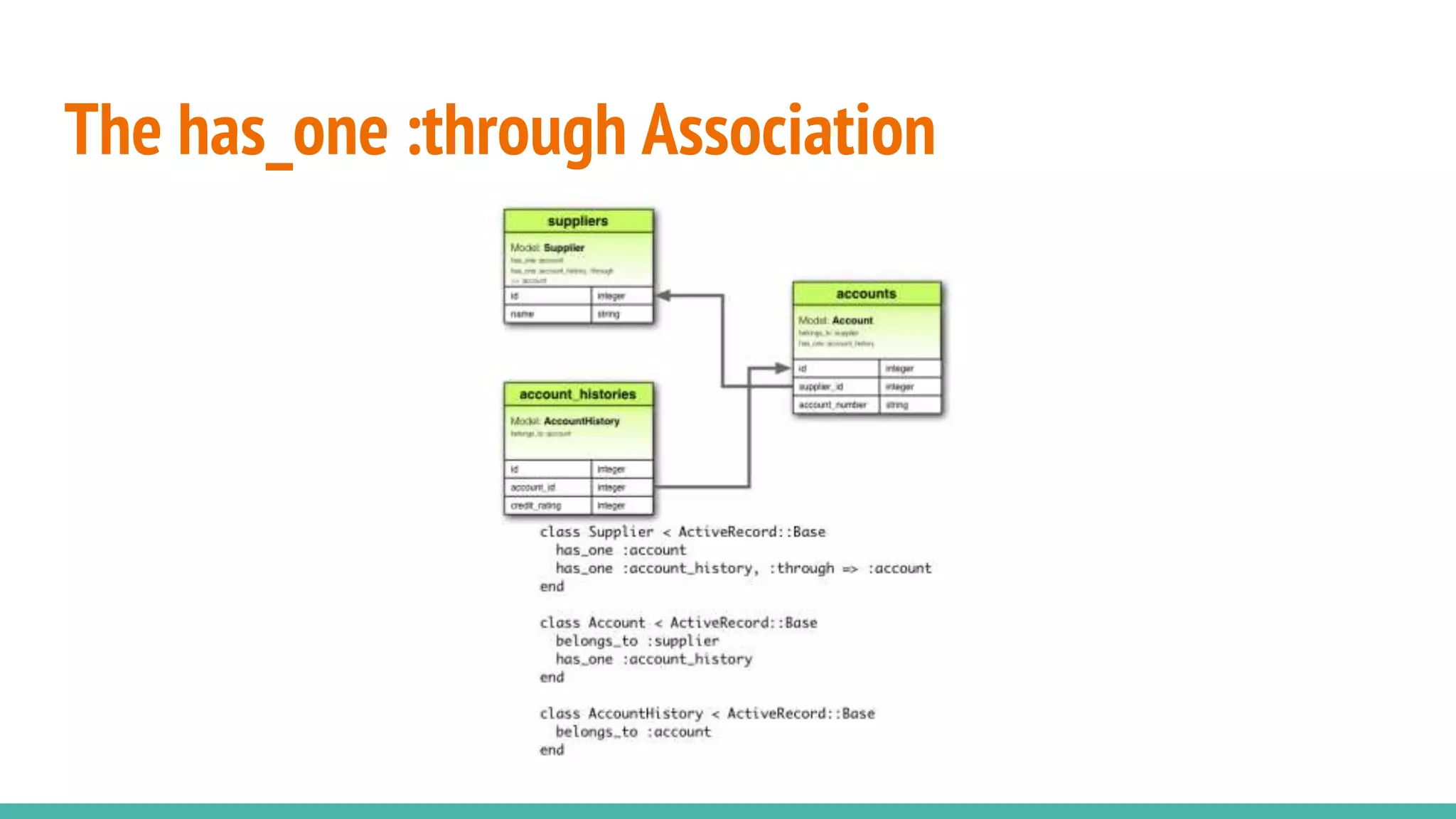
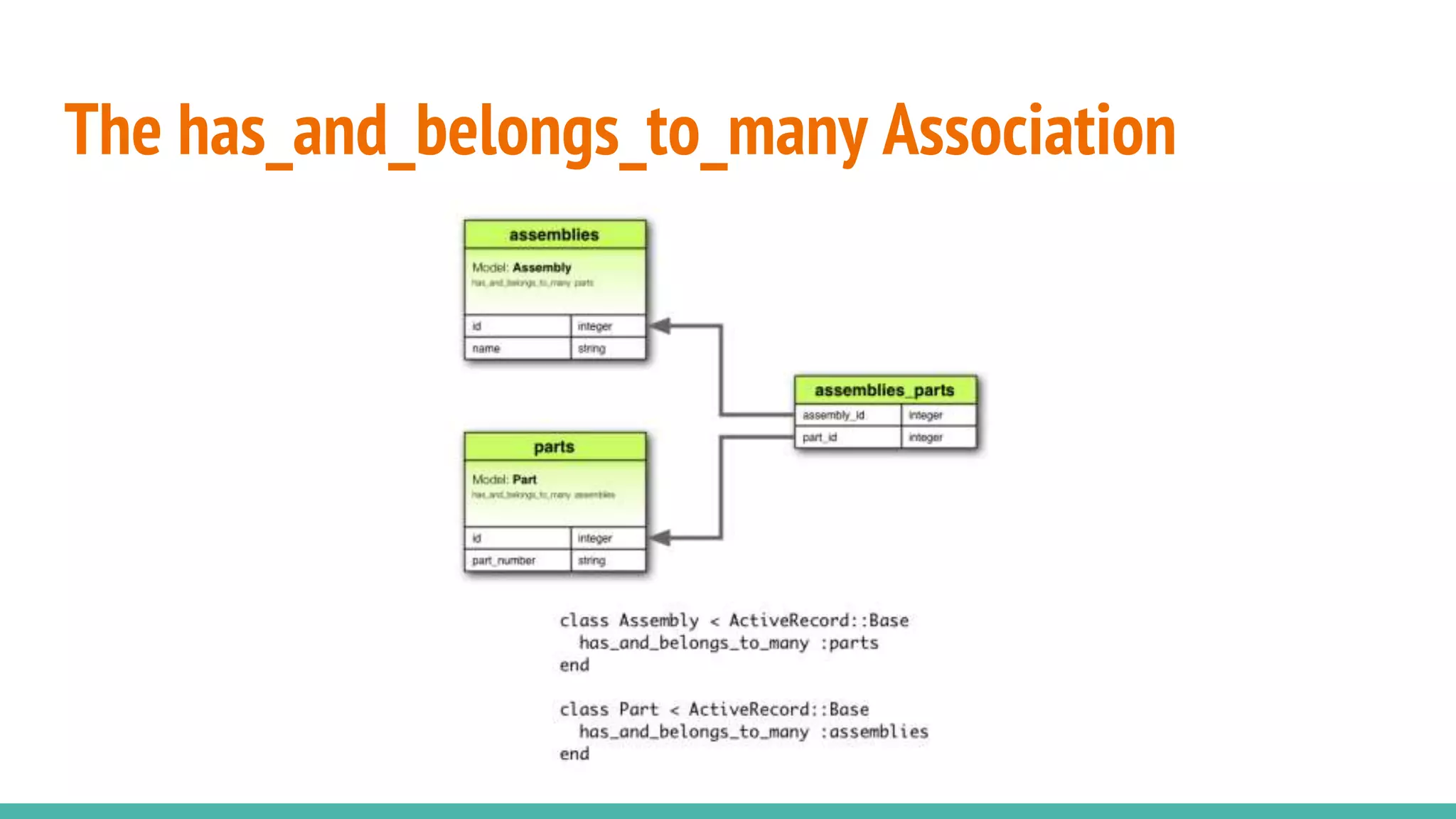
This document provides an overview of Ruby on Rails and how it interacts with databases. It discusses scaffolding which can quickly generate code to view, delete and update database resources. It also covers migrations which allow modifying the database schema and reverting changes. Additionally, it explains that Active Record handles interacting with database data through CRUD operations and defines an object that wraps a database row and encapsulates data access and domain logic. The document then reviews various Rails commands and associations between models.