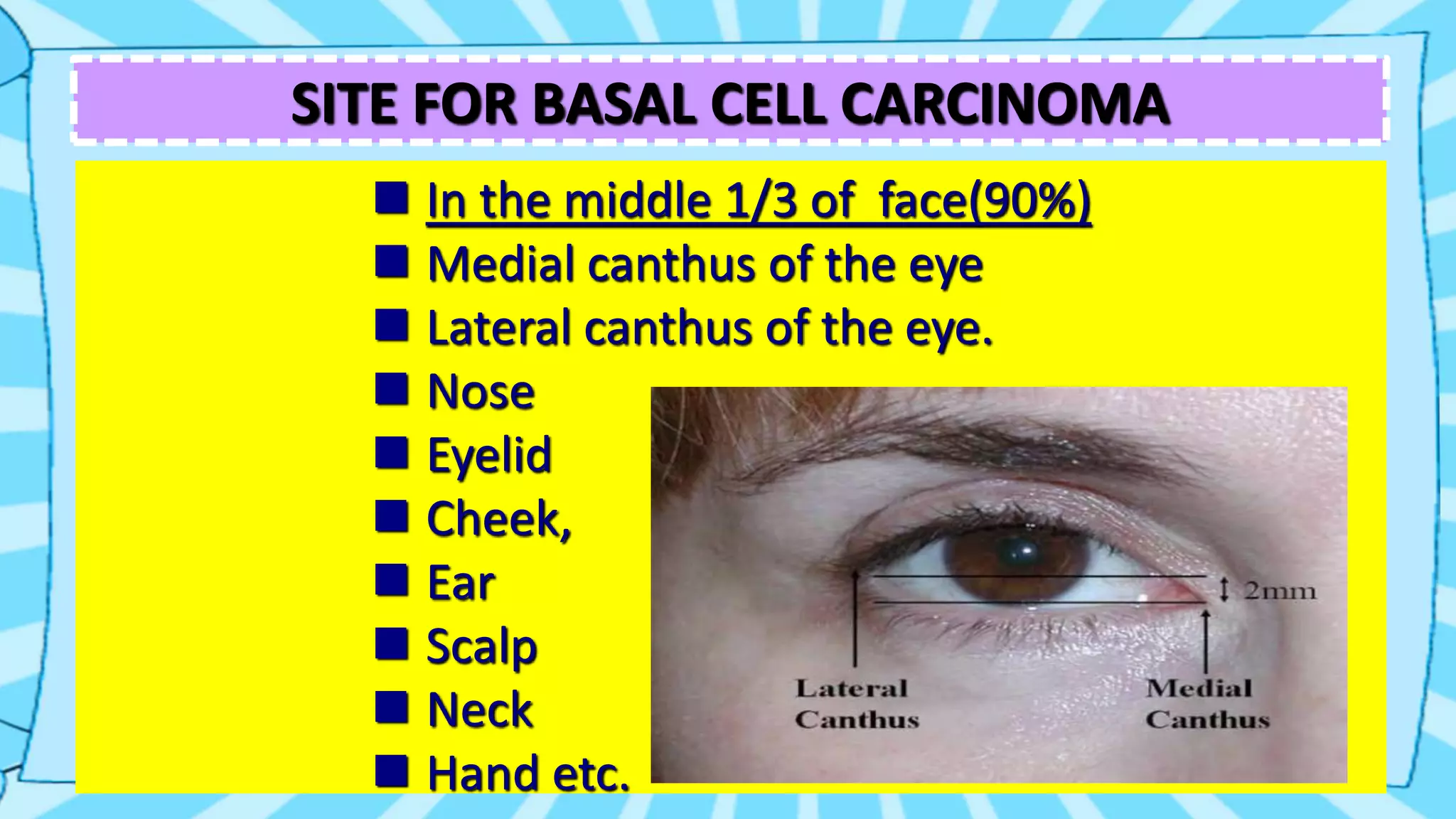
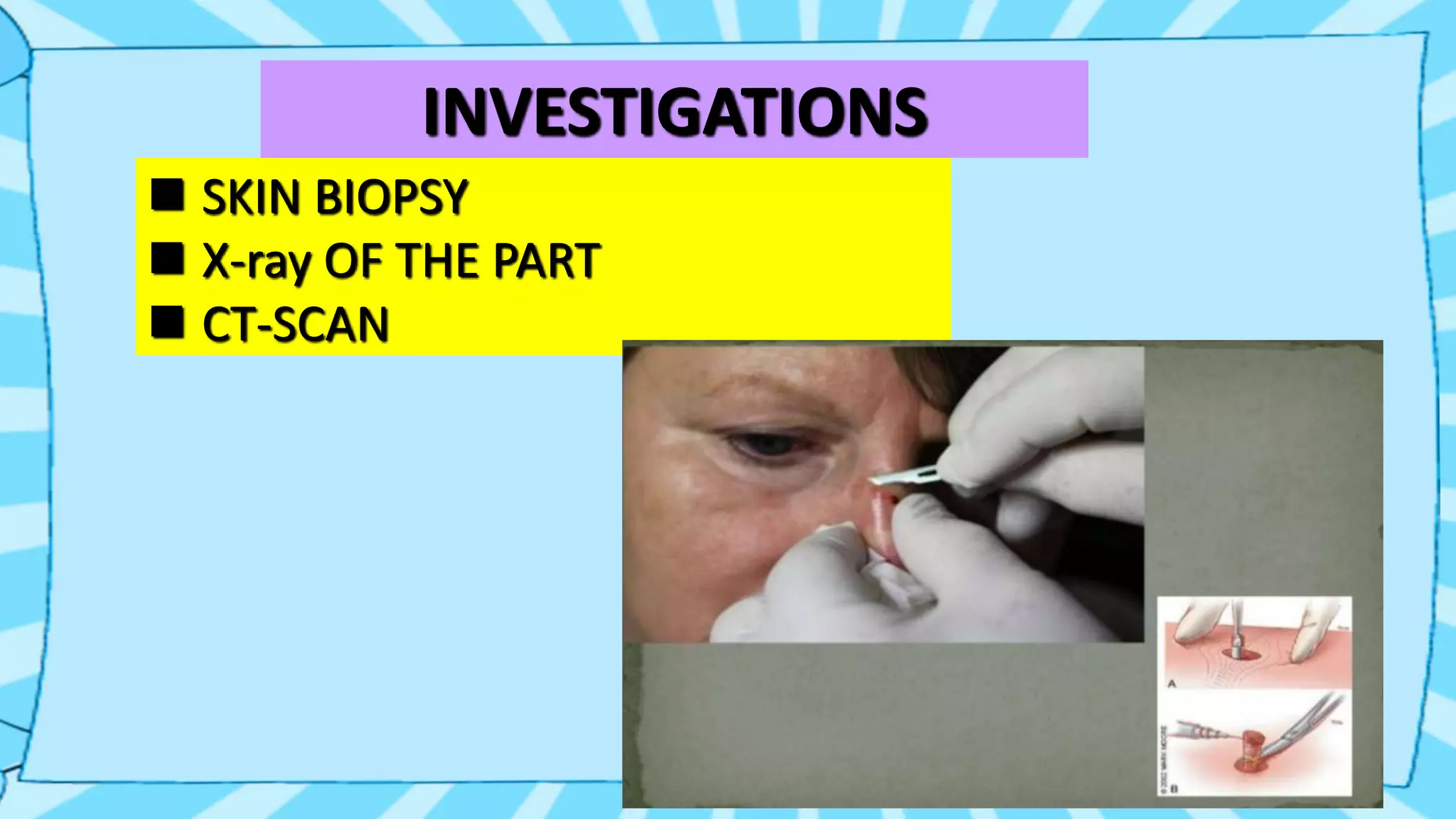
This document summarizes basal cell carcinoma (BCC), the most common skin cancer. BCC is a locally invasive, malignant tumor that arises from basal epidermal cells and hair follicles. It typically appears as a small nodule or ulcer on sun-exposed areas of the head and neck in fair-skinned, older adults. While BCC rarely metastasizes, it can cause significant local tissue destruction if not treated. Treatment options include surgical excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, radiation therapy, or non-surgical procedures like laser vaporization.