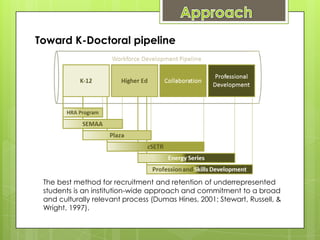
This document discusses the need to develop the energy and engineering workforce through research, education, and skills development programs. It notes that over 50% of the current workforce will retire in the next 10-15 years, creating gaps. Proposed solutions include delivering STEM education from K-12 through doctoral programs, with hands-on learning and research opportunities. Areas of research focus include fossil energy, renewable energy, and climate modeling. The goal is to create an industry-ready and diverse workforce through partnerships between education, government, and industry. Challenges include a lack of pre-implementation data and engineering concepts in K-12 curriculum.