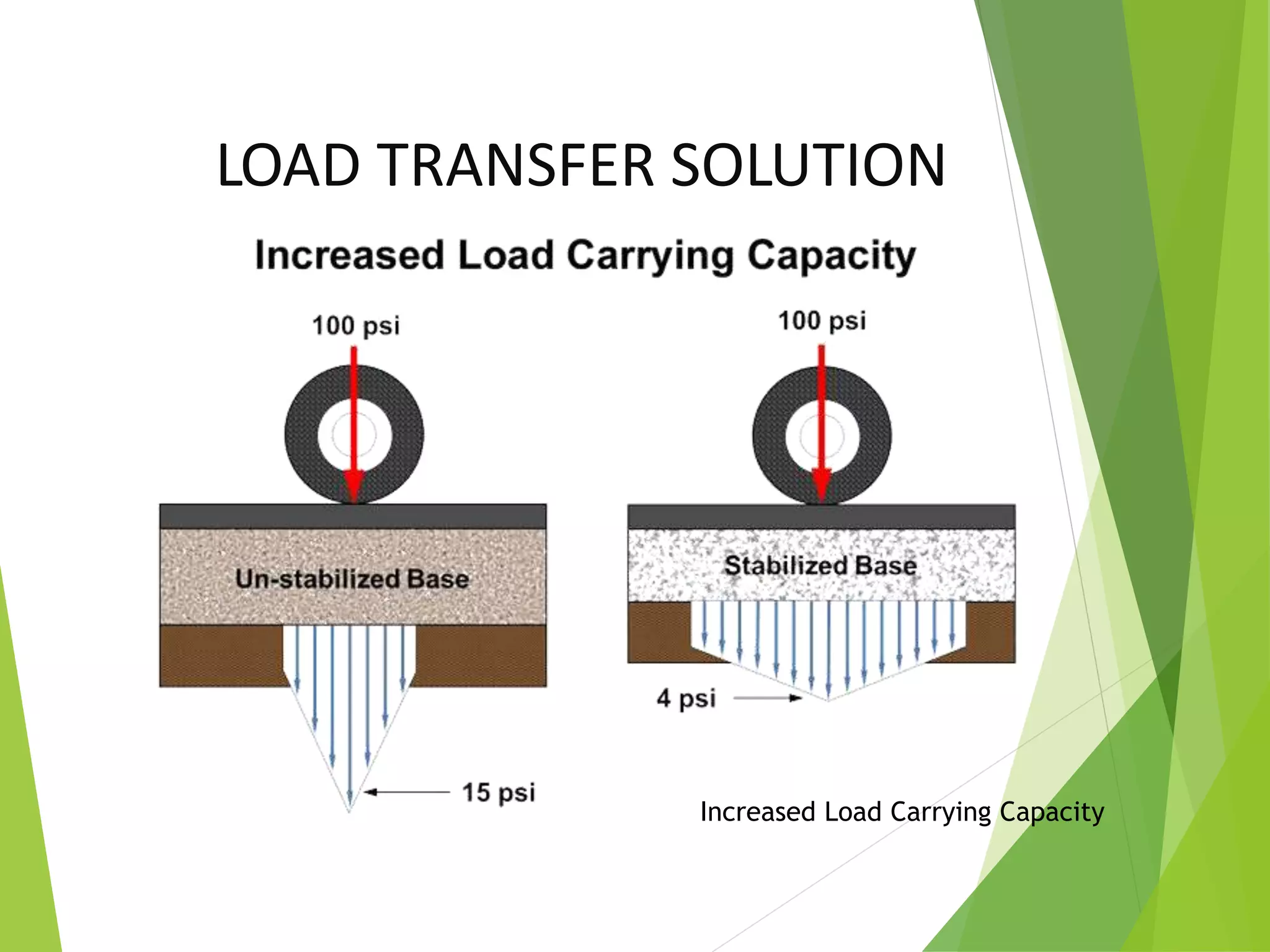
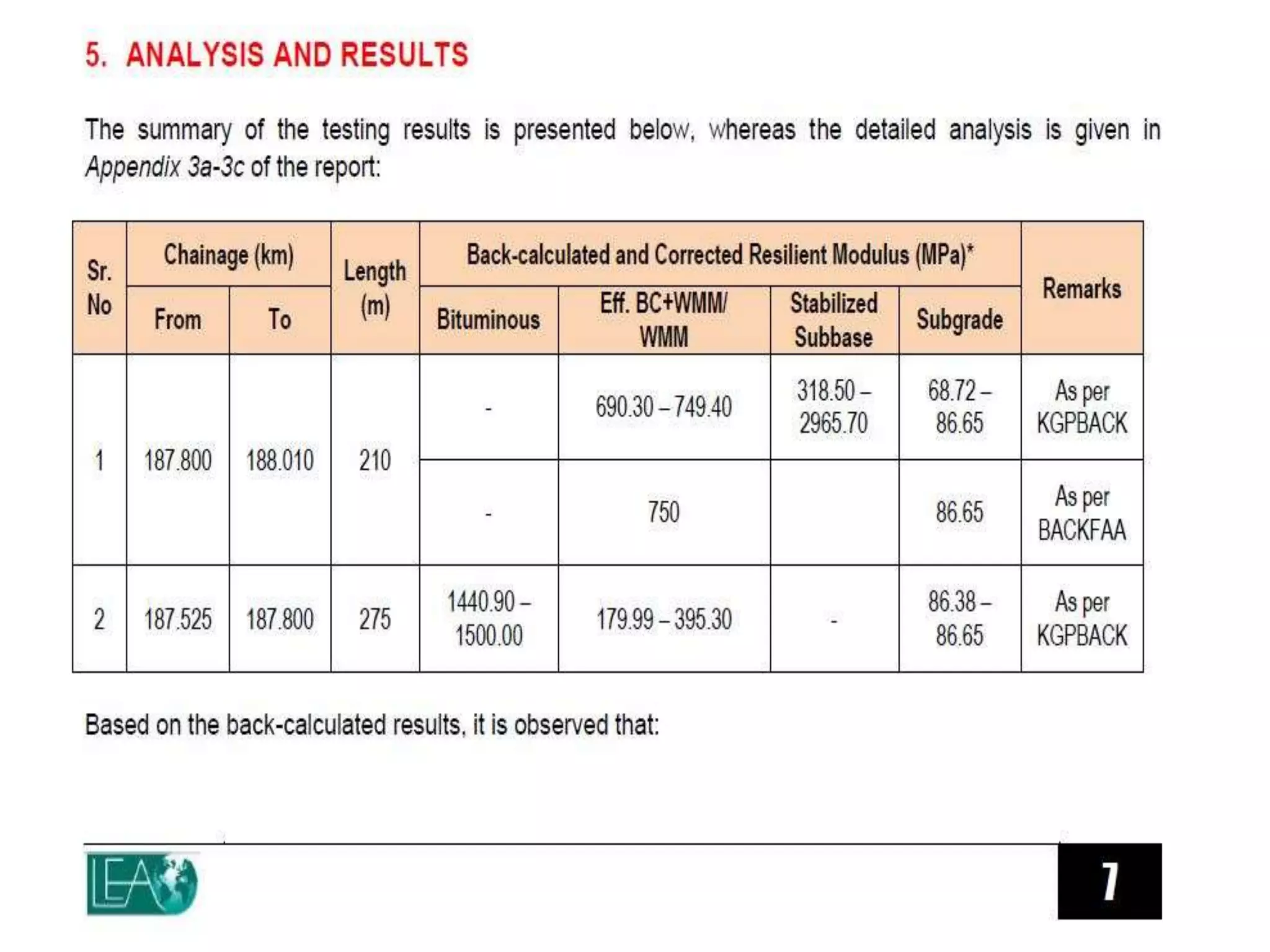
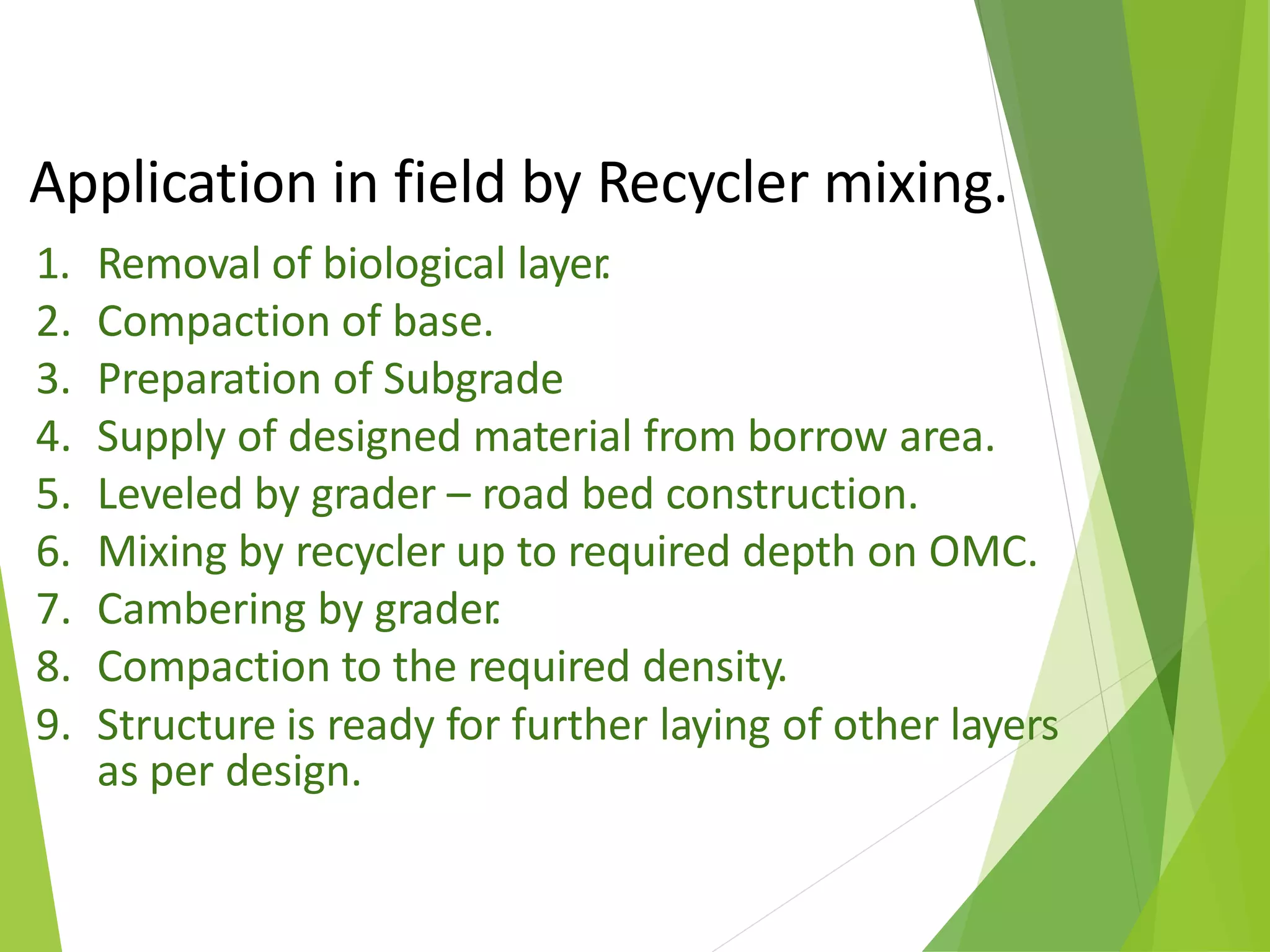
Roadstab technology is a Russian innovation since 1996, specializing in road stabilization and cold reconstruction using a concentrated liquid stabilizer that enhances the structural integrity of roads. The technology offers various advantages including reduced material costs, immediate traffic usability after compaction, and effective performance under challenging conditions such as heavy moisture and temperature fluctuations. Project implementations demonstrate significant cost savings and improved durability compared to conventional road construction methods.