Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times

![Geometric Average nth root of the product of returns for n years Geometric mean = (1+R 1 )x(1+R 2 )x(1+R 3 ) 1/n – 1 = [(1+10%) x (1+ 25%) x(1+(-20%))] 1/3 – 1 [(1.1) x (1.25) x (.8)] 1/3 – 1 (1.1) 1/3 – 1 1.03-1 .03 or 3%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture10retrunandrisk-110530235653-phpapp01/75/Risk-and-Return-5-2048.jpg)
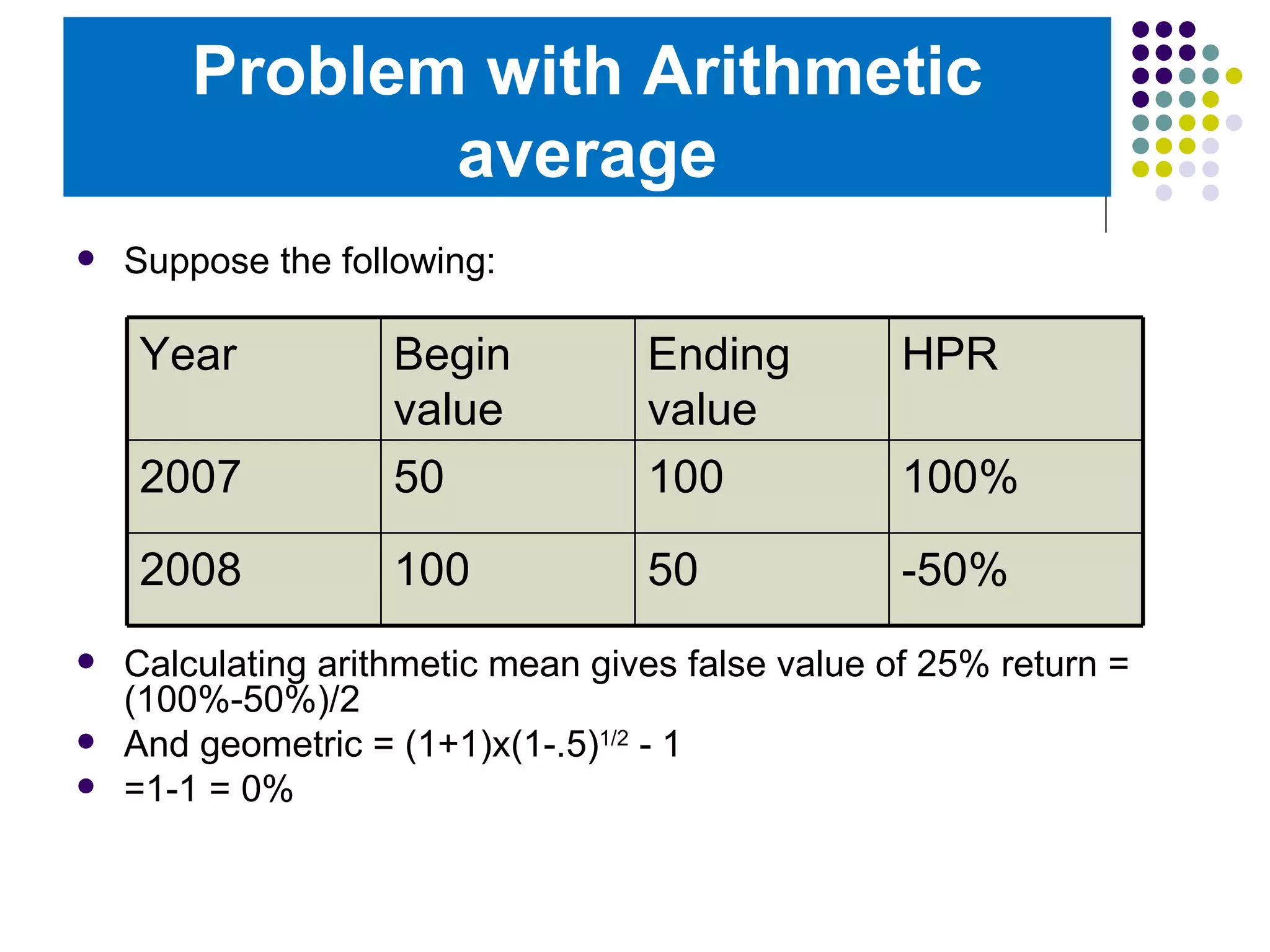

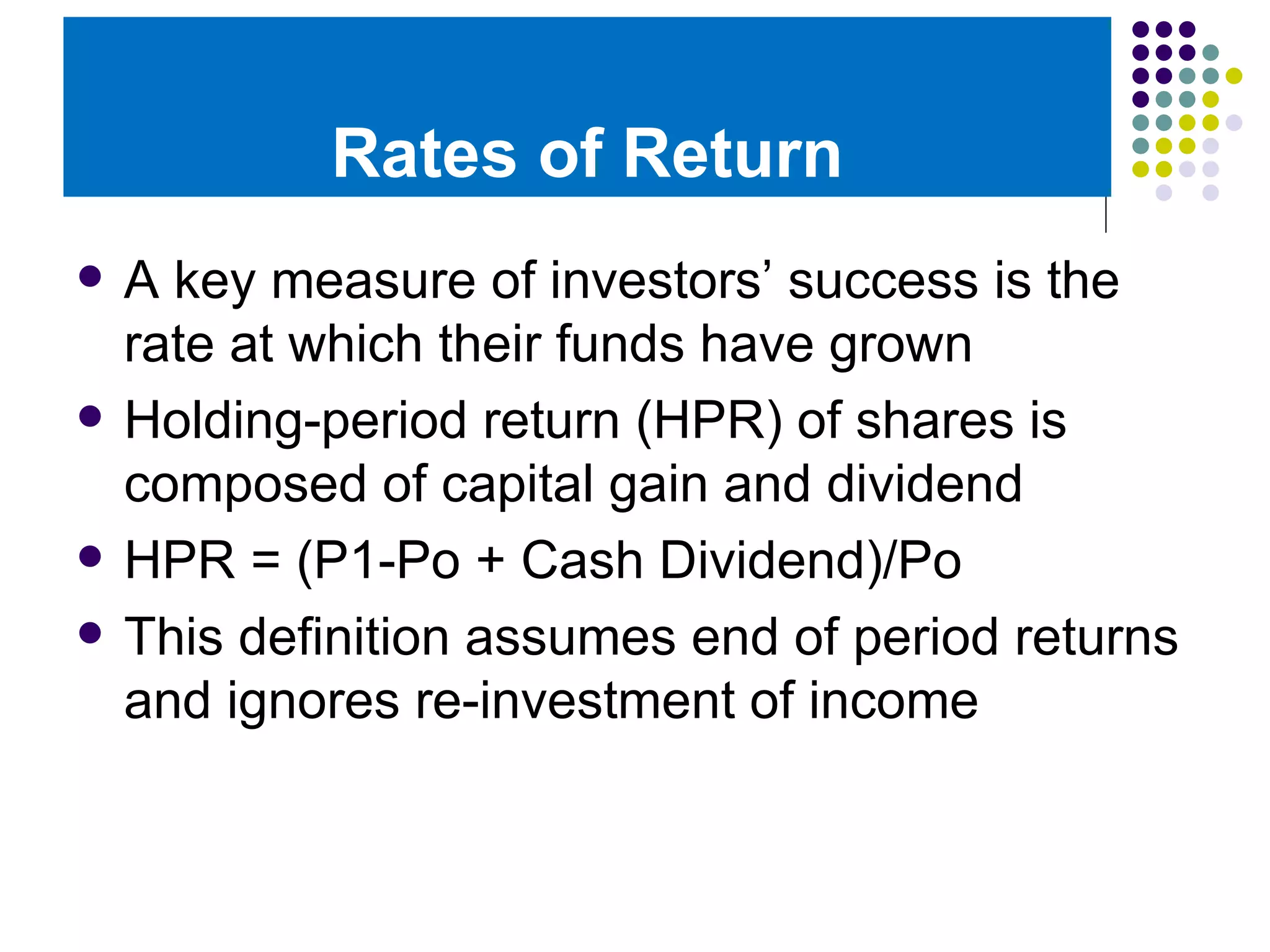
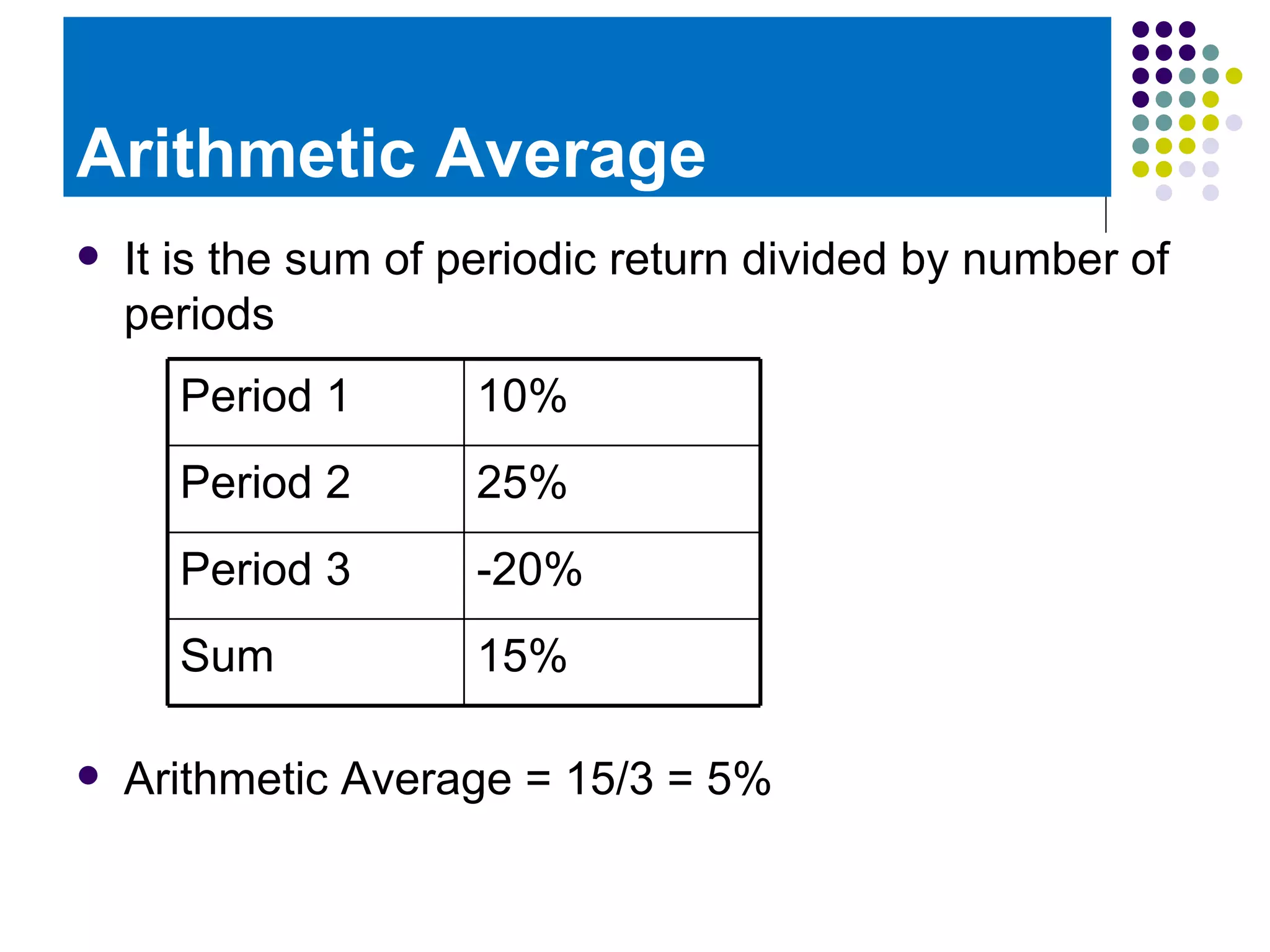
The document discusses different methods for calculating rates of return on investments over time. It defines holding period return as the capital gain plus any cash dividends, divided by the initial price. It also defines dividend yield. There are three main methods discussed: arithmetic average, which simply averages the periodic returns; geometric average, which finds the nth root of the product of 1 plus the rate of return for each period; and dollar weighted return. The geometric average is preferred when returns vary widely from period to period, as the arithmetic average can overstate performance in that case.




![Geometric Average nth root of the product of returns for n years Geometric mean = (1+R 1 )x(1+R 2 )x(1+R 3 ) 1/n – 1 = [(1+10%) x (1+ 25%) x(1+(-20%))] 1/3 – 1 [(1.1) x (1.25) x (.8)] 1/3 – 1 (1.1) 1/3 – 1 1.03-1 .03 or 3%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture10retrunandrisk-110530235653-phpapp01/75/Risk-and-Return-5-2048.jpg)

