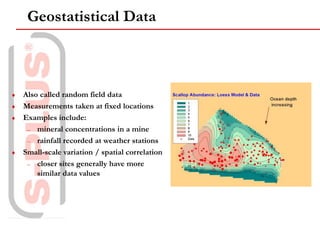
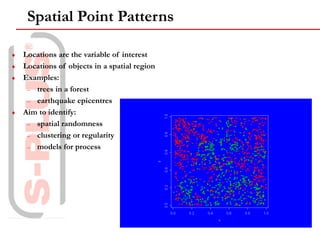
The document discusses spatial analysis and visualization software called S-PLUS SpatialStats. It provides an overview of the software's capabilities including tools for analyzing different types of spatial data like point patterns, lattice data, and geostatistical data. It also describes additional S-PLUS modules that can be used for tasks like spatial statistics, linking S-PLUS with GIS software, and environmental statistics.