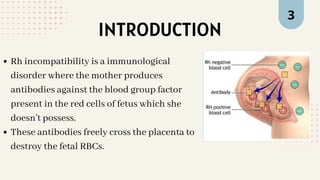
Isoimmunization in pregnancy occurs when an Rh-negative mother produces antibodies against Rh-positive fetal blood, leading to potential fetal complications, particularly in subsequent pregnancies. These antibodies can cause hemolysis of fetal red blood cells, resulting in conditions such as fetal anemia, hydrops fetalis, and jaundice. Recommendations for managing this condition include specific interventions to monitor and protect fetal health.