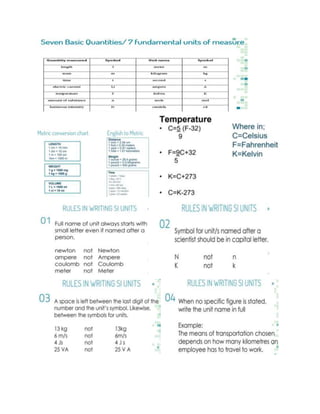
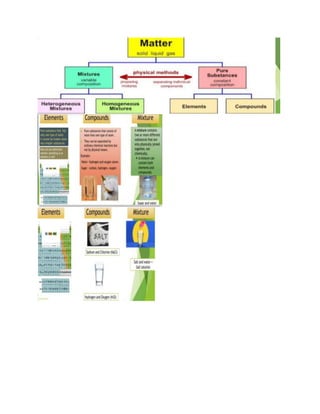
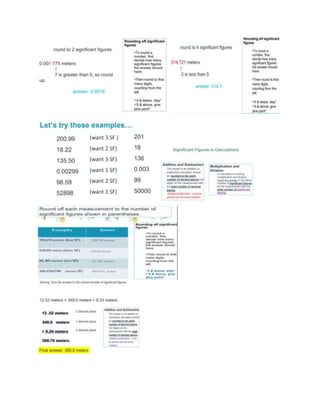
The document discusses the key aspects of science and the scientific method. It defines science as a systematic body of knowledge based on facts obtained through observation and experimentation. The scientific method is then described as a series of steps that scientists use to answer questions and solve problems, including making observations, asking questions, developing a hypothesis, conducting experiments, and drawing conclusions. Non-science is distinguished as involving beliefs, philosophy, or personal opinions rather than being testable. Measurement, matter, and solutions are also briefly covered.