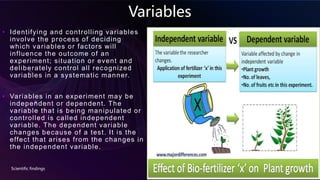
The document describes the scientific method and its steps. It begins by explaining that science is a way of thinking and gathering knowledge about the world that is accurate and reliable. It then outlines the key steps of the scientific method: 1) make observations, 2) come up with a question, 3) develop a hypothesis, 4) conduct an experiment to test the hypothesis, 5) record and analyze results, and 6) draw conclusions. It provides an example of using this method to test if eggs will float or sink, depending on the density of the surrounding water.