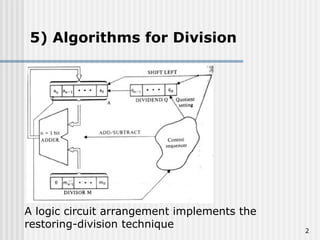
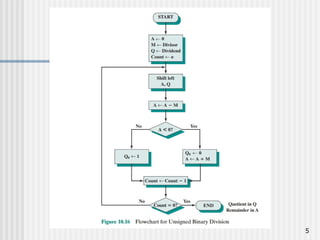
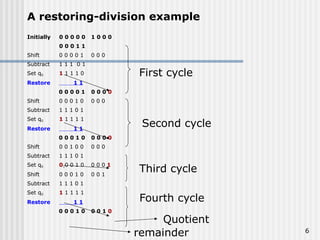
The document describes two algorithms for division: restoring and non-restoring. The restoring-division algorithm involves shifting and subtracting, with a restoration step if subtraction is unsuccessful, while the non-restoring algorithm simplifies this by shifting and either subtracting or adding based on the sign of the result. Both algorithms assume positive values for the divisor and dividend and include examples and references for further reading.