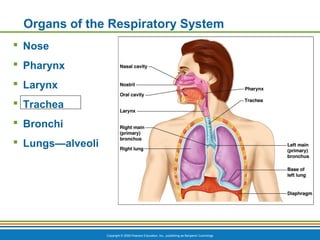
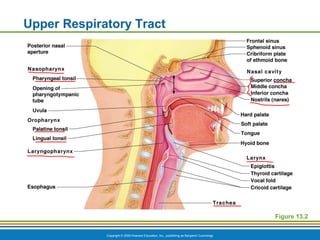
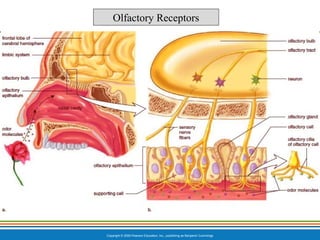
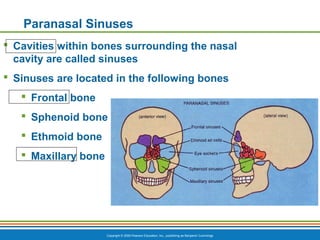
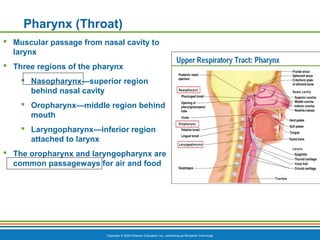
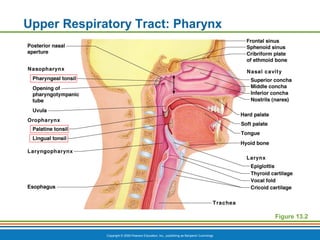
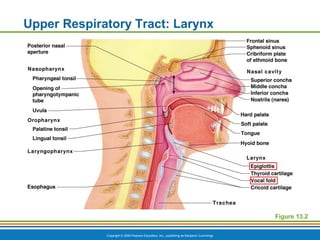
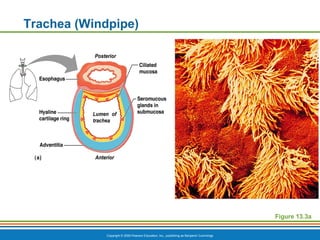
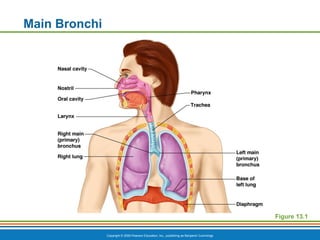
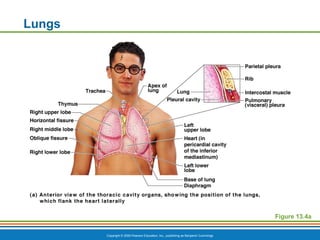
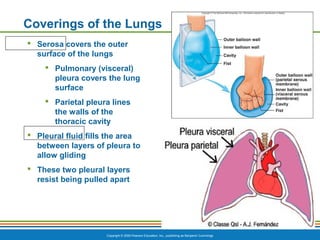
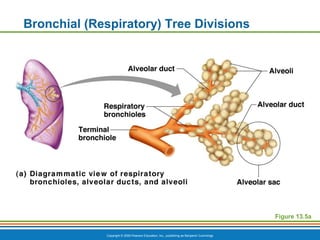
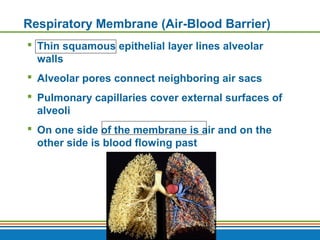
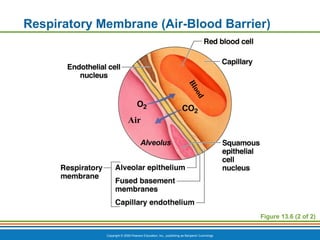
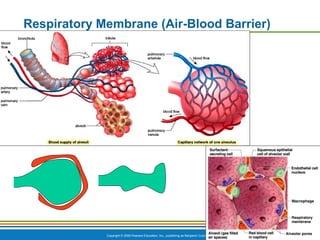
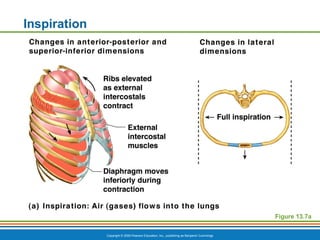
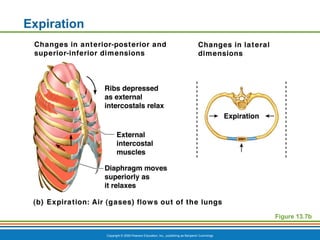
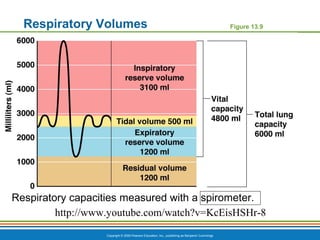
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the respiratory system. It describes the major organs that make up the respiratory tract, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It explains that the primary functions of the respiratory system are to oxygenate blood and expel carbon dioxide through gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. It also provides details on the mechanics of breathing through the processes of inspiration and expiration.