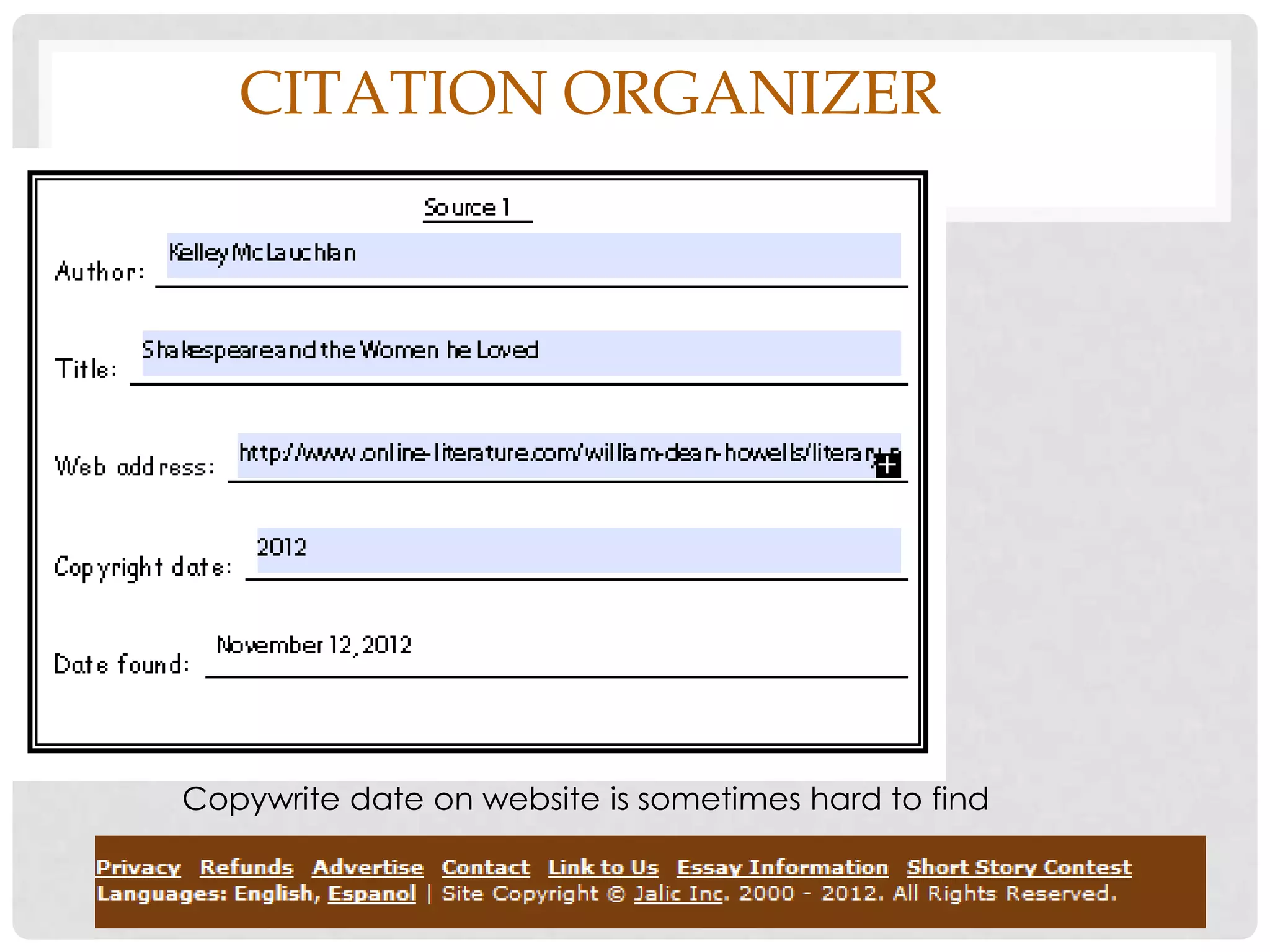
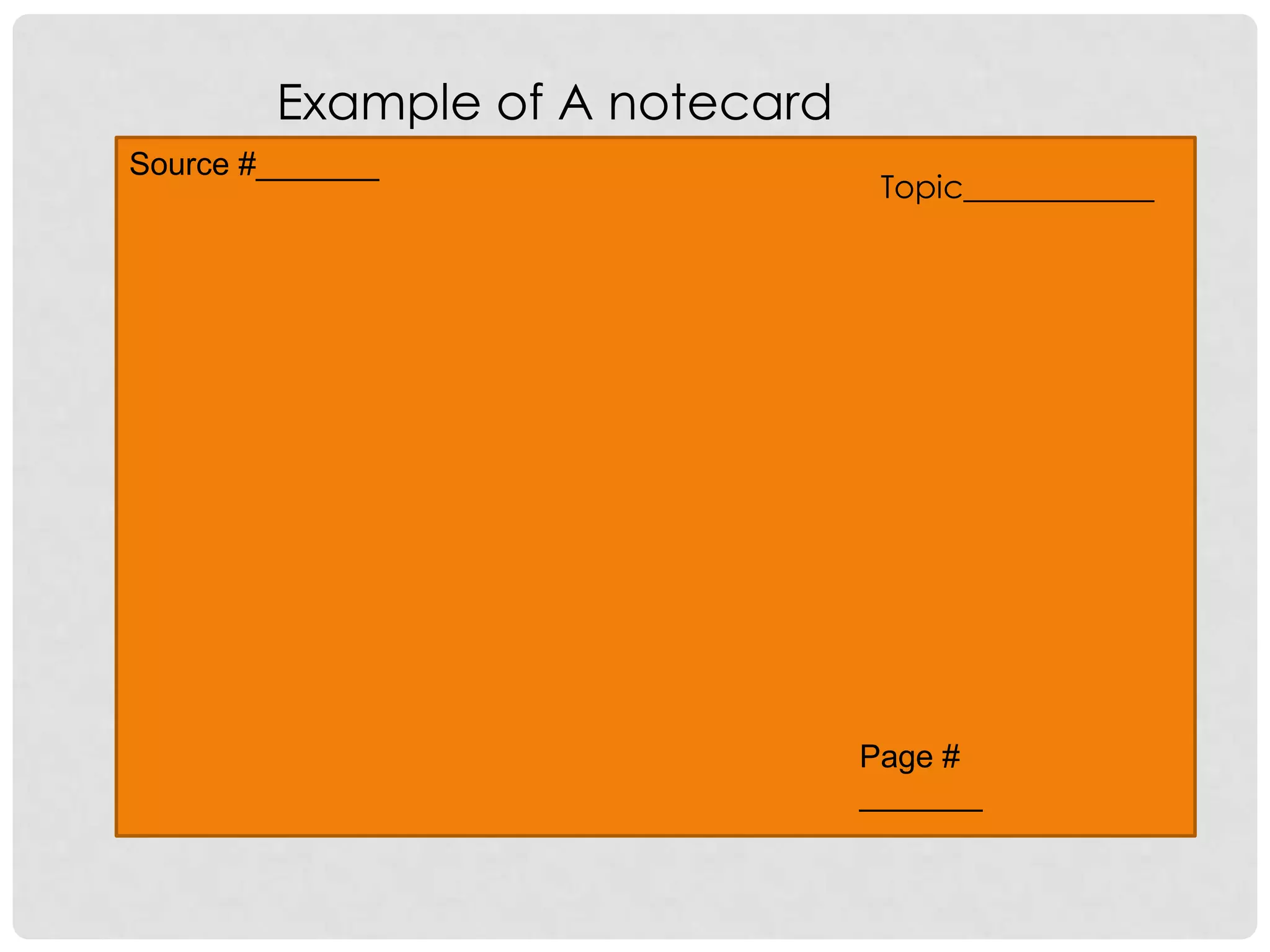
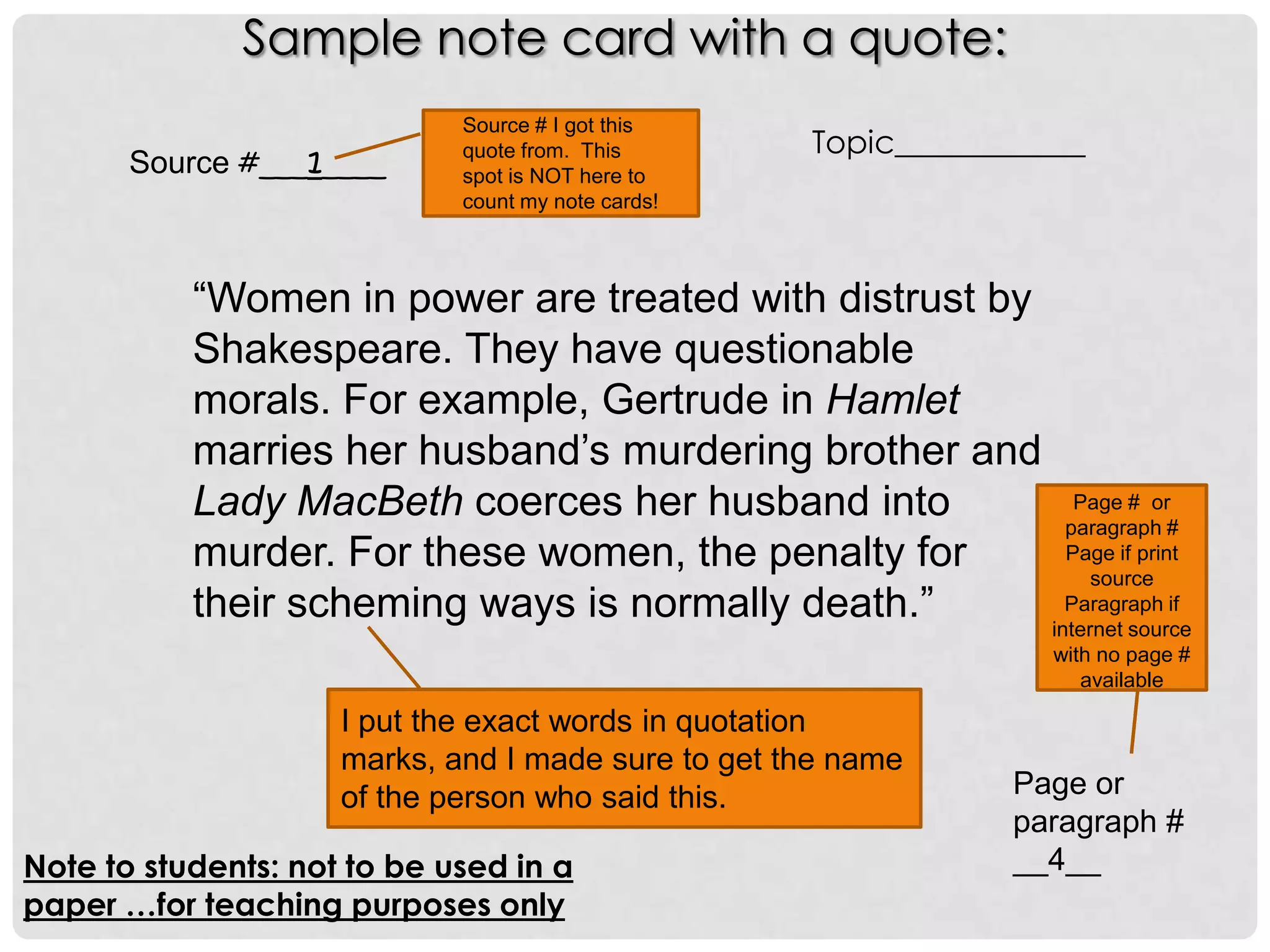
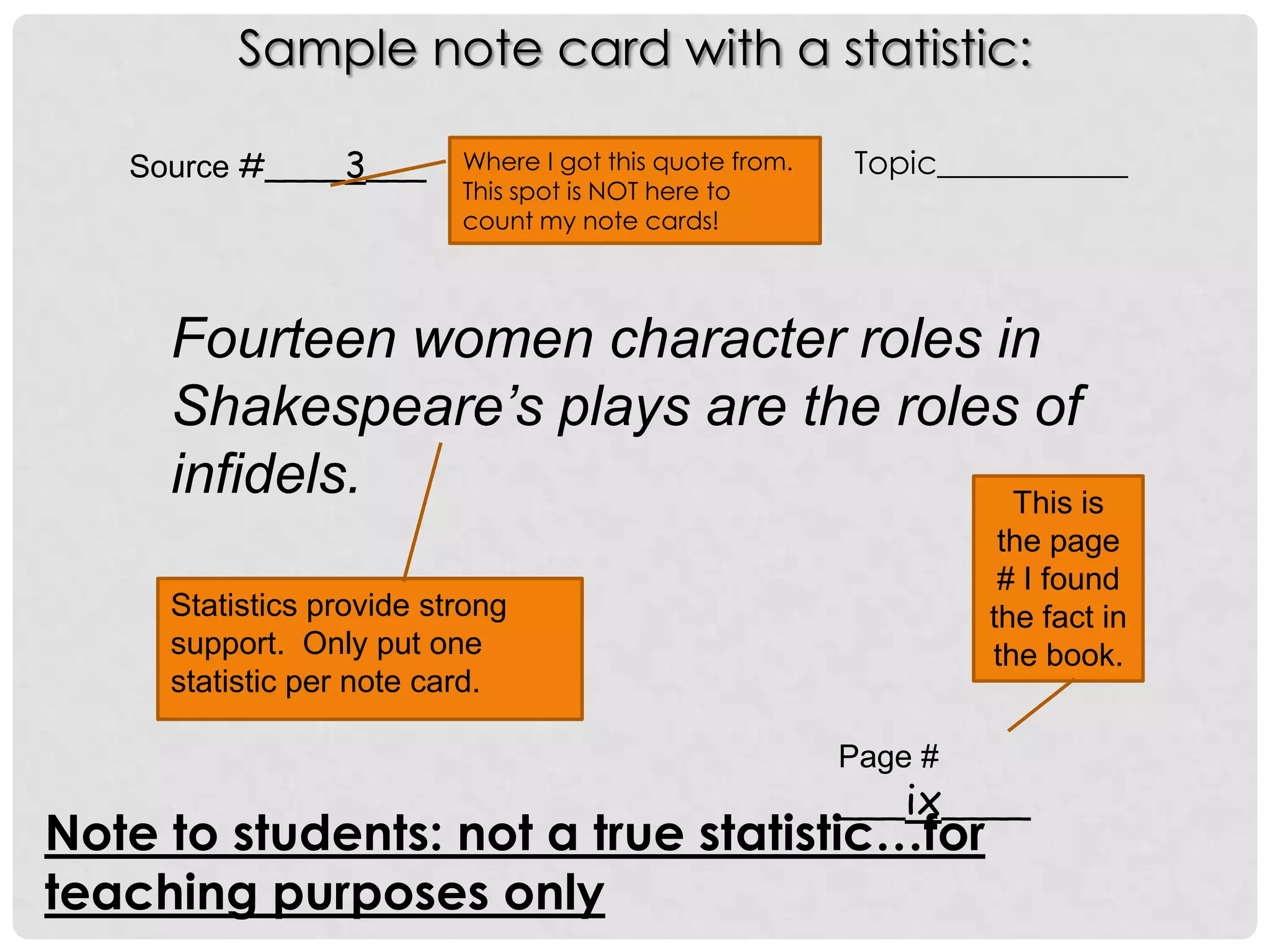
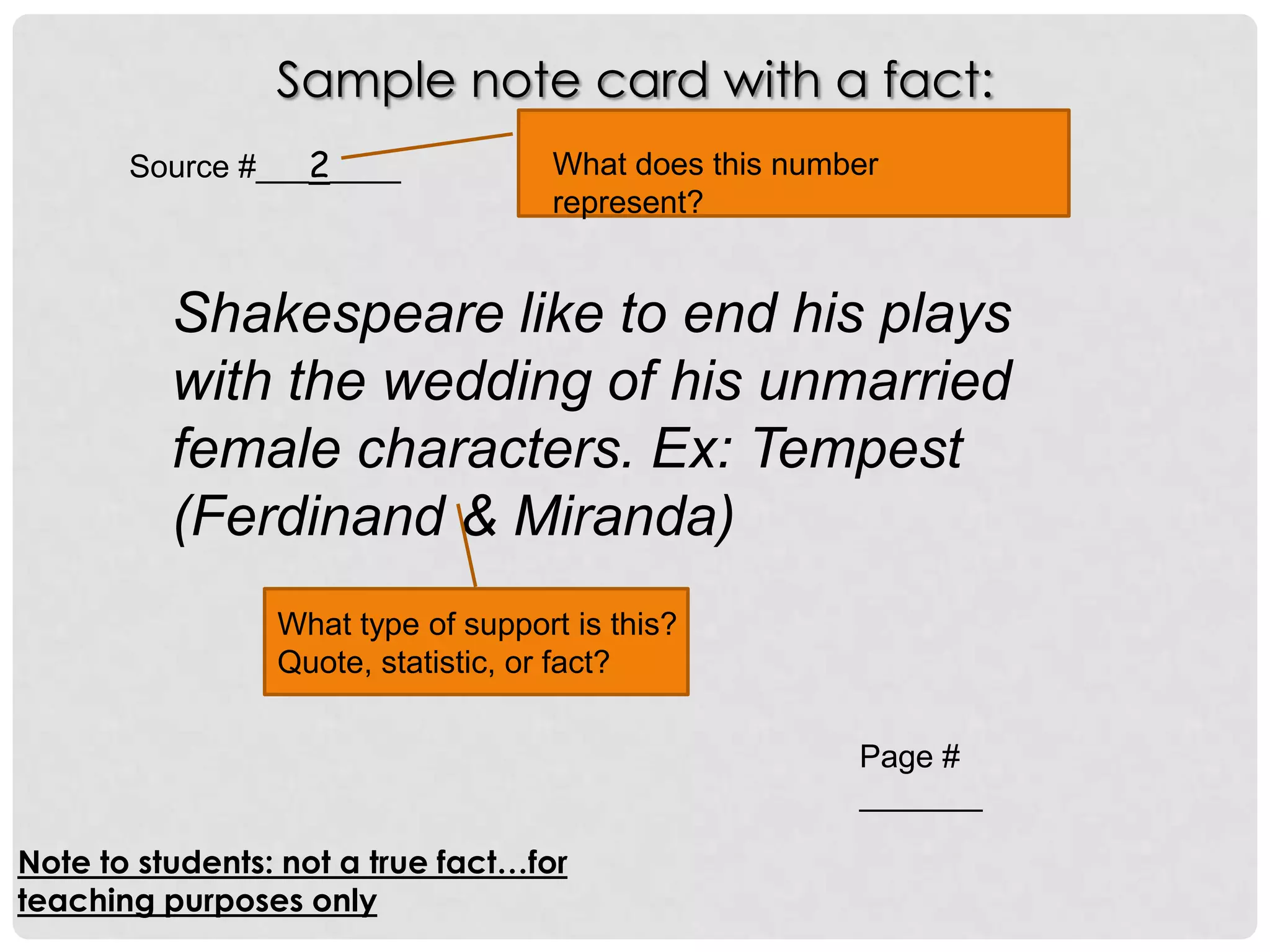
This document provides an overview of how to start researching and writing a research paper. It discusses reviewing the thesis statement, finding and evaluating different types of sources like primary and secondary sources, taking notes on those sources using note cards or electronic files, and analyzing factual and analytical information found in sources. The document emphasizes forming an arguable thesis, using reliable sources like books by experts and avoiding sources like wikis, and properly recording source information to use in the paper and bibliography.