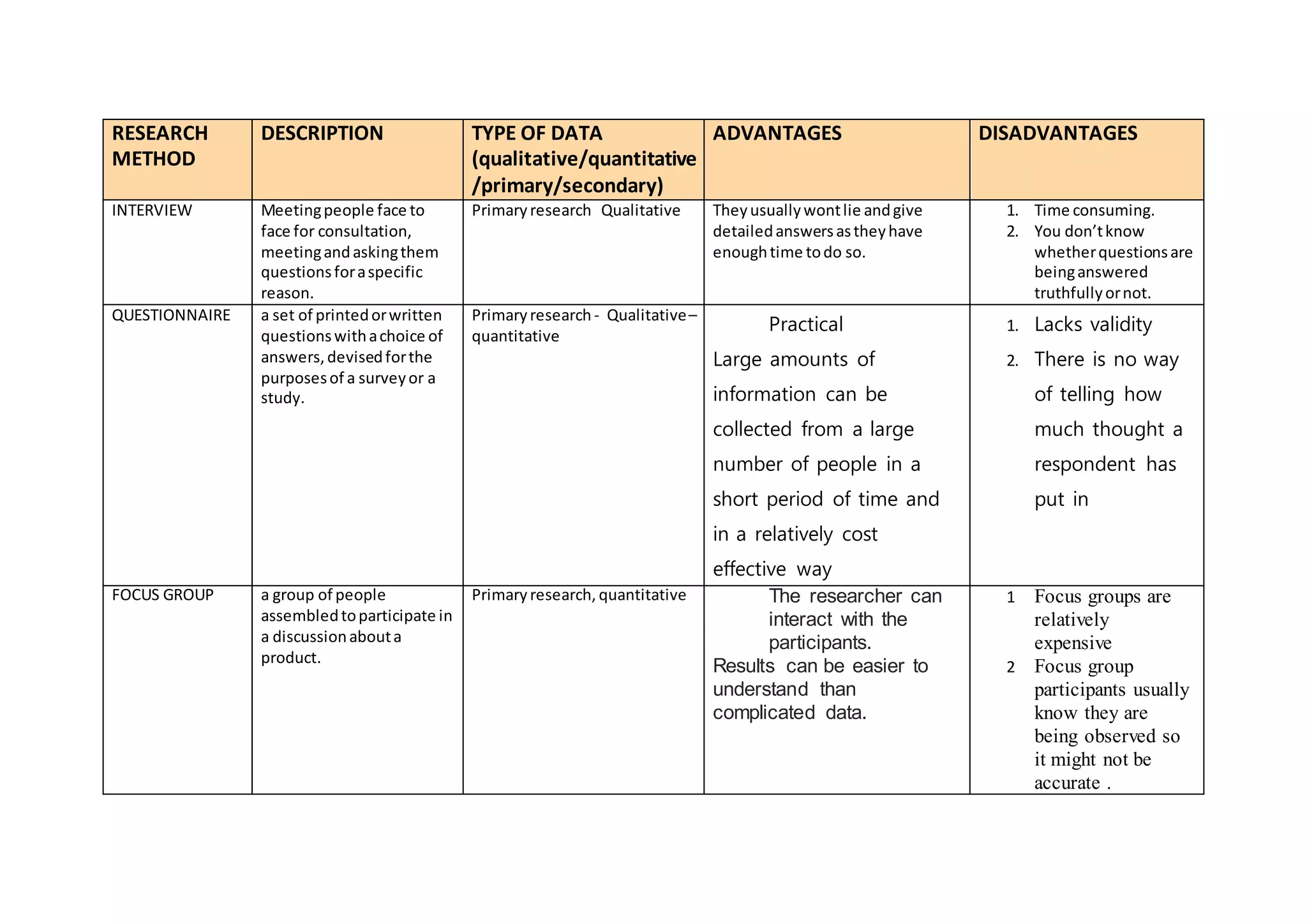
This document describes and compares several common research methods: interviews, questionnaires, focus groups, surveys, internet research, and library research. It outlines the type of data each collects (qualitative vs. quantitative), as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Interviews collect primary qualitative data face-to-face but can be time-consuming. Questionnaires collect both qualitative and quantitative primary data from many people quickly but lack validity. Focus groups allow interaction but participants may not be accurate. Surveys can reach many but responses may not be honest. Internet research has a large scope but information may not be accurate. Library research relies on reliable sources but access can be limited.