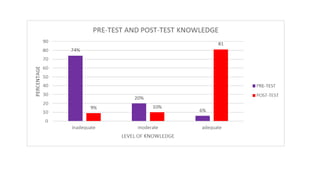
The study assesses the effectiveness of a video-assisted teaching program on organ donation knowledge among engineering students at a Chennai college. Results indicate significant improvement in post-test knowledge scores, with 81% of students achieving adequate knowledge post-intervention. The research highlights the need for increased awareness and educational initiatives to enhance organ donation rates in India.