Republics States of Ancient India
- 1. Republican States Sachin Kr. Tiwary
- 3. Theme of the Subject 1.Introduction : 1.Sources: 1.Historical Background: 1.Buddha Views 2.On Republic 1.Important Republics Polity and Administrations of Republics 1. Lichacchavis Sakyas Republican States
- 4. What is Republican State? • A state in which supreme power is held by the people and their elected representatives. • The term democracy is derived from two Greek words 'Demos' and Kratos. • Demos mean “people” and Kratos means “rule”. • In republican system sovereign power is possessed by the people. • The people may delegate power to a single man or a group of selected person.
- 5. Introduction • In ancient Indian Republic and Monarchy system dominant. • Democratic form of the state prevailing in later Vaidik period. • In the sixth century B.C.E. numerous democratic states exists in northern India. • Republics known as: Ganas (group of people)
- 6. Source 1. Buddhist Literature 2. Mahabharata 3. Greek Historians 4. Panini, 5. Katyayan, 6. Patanjali, 7. Arthashashtra 8. Inscriptions 9. Coins Literature Archaeological Living Practices
- 7. Gana and Sangha • Gan: group of people, number of people • Altekar: In Republic control of government was in hands of group of people. • K.P. Jaiswal: Gan – Assembly or Parliament Sangha: • Panini: Sangha is equal to Gana • Kautilya: Sangha is equal to Gana • Buddhist text Majjim Nikaya: Sangha is equal to Gana • Later on sangha restricted to Buddhist religion
- 8. Historicity and Meaning Gana Gana mentions in • Rigveda: forty six times • Atharvaveda: nine times • Brahmans: several times • Smritis: Gana = assemblage of families. • Dr. Jayaswal: Gana as ‘numbers’: • Dr. Jayaswal: Ganarajya = ‘rule of numbers’, ‘the rule of many’. • Buhler: An autonomous corporation of tradesmen • Dr. Fleet: A self-governing community. • Ganarajya = Government by assembly.
- 9. According to Greek Writers 1. Greek historians observed both Monarchy and Republics in ancient India. According to Greek writers 1. Puru was republic 2. Nyasa was also kind of Republic (oligarchy) 3. Lot of Republic states in the area of Indus River
- 10. Republican Elements 1. Vedik Period Rigveda: Sambha and Samitee 2. Later Vedik Period Aitareya Brahman: Vairjaya State
- 11. Sabha & Samiti • The Vedic Period Sabha and Samitee: the twin daughters of Lord Prajaprati, • Samiti 1. Election of the King, 2. Re-election of a king who had been banished and 3. Discussion of the State matters • Sabha 1. the Sabha was its standing body. 2. Elected people
- 12. Later Vedic period Aitareya Brahman • Uttar Kurus and the Uttar-madras had a Virat (Kingless) state. • Vairajya: Kingless • Heads of the founder family, were offered rulership. • Uttar-madras, continued to be republican states upto the 4th Century. CE.
- 13. Historical Period 1. Mahabharata: mentions the rule of the Republics. 2. Panini: Mentions a number of republics 3. Buddhist literature: abounds with references to the republics 4. The Buddha himself was born in a republican people 5. He called the community which he founded “Bhikkhu Sangha”, or the Republic of Bikkhu 6. Avadana sataka अवदान शतक : A merchants told to king who travelled to Deccan from Madhydesha “these are some countries are Gana or republican States. 7. Acharang sutra आचाराांग़ सूत्र: Warned Jain monk to avoid to visit where no kings or Gana form of government. 8. Numerous coins of Yaudehyas, Malvas, Arjunayan bears the name of “Gana” (Arjunayananam Jayah)
- 14. Buddhist literature • In various places of Buddhist literature the main features of the republics have been described. • Magadha King wanted to know the opinion of the Buddha for invading the three Republics of the Vajjis , the Lichchhavis and Videhas, 1. As long as these republics had these strong points the King could not suppress them. 2. He enumerates the strong points as follow……
- 15. Buddha’s View on Republican States 1. To hold full and frequent public Assemblies 2. To meet together in concord, 3. Rise in concord and to carry out their undertakings concord; 4. To enact nothing not already established, 5. Abrogate nothing that has been already enacted and act in accordance with the ancient institutions of the Vajjians as established in former days 6. To honour, esteem, revere, and support the Vajjian elders and hold it a point of duty to harken to their words 7. To support the old shrines in town or country 8. To honour women and not detain them by force or abduction. • This passage thus points out that the requisites for the success of a republic in those days were : 1. The respect of its members for their Parliament, 2. They should meet often and, 3. They were fully attended for their ancient laws, customs and institutions, for seniority and experience and its internal harmony in policy and administration
- 16. Republics form and constitution • A few scholars have expressed the opinion that every adult of the population participated in the administration; • Some others maintain that only Kshatriyas had this right; • Others have expressed the view that only head of a joint-family was allowed to participate in the administration. • Mostly the opinions of scholars are divided on the basis of the above mentioned differences of views.
- 17. Dr Jayaswal’s view on Republic 1. Democracies or pure Gana, wherein the total adult- population participated in the administration; 2. Aristocracies or pure Kula, wherein only some selected families participated in the administration; and 3. Mixed aristocracies and democracies or a mixture of Kula and Gana, wherein the administration was the mixture of the two.
- 18. Dr. Bhandarkar’s view on Republic • The republics were basically divided into two types, 1. Pure republics and 2. Kshatriya aristocracies. • Then each of them was further divided into two parts. • Both the republics and the aristocracies were of two types, 1. Unitary: called City-republics or Nigamas 2. Federal: called State-republics or Janapadas
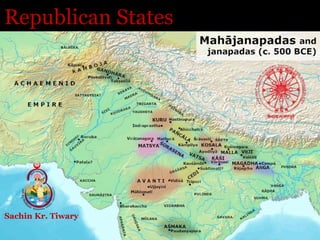
- 19. Important Republics 1. The Mallas of Pava 2. Licchavis of Vaishali 3. The shakya of Kapilvastu 4. The Koliya of Ramagrama 5. The Bhagya of Sunsamagiri 6. The Mauryas of Piphalivana 7. The Kalama of Suputa 8. The Videhas of Mithila 8. The Ghvatrikas of Kollanga 9. The Asmakas, 10. The Malavas, 11. The Kshudrakas, 12. The Arjunayanas, 13. The Mushikas, 14. The Yaudheys 15. The Madrakas
- 21. Administrations of Republics Executive Council Assembly Republics • Limited Members • To handle confidential issues • Large members • General matter of the state • Small size • Bigger size
- 22. Administration of Small Republicans • The Moriya, the Koliyas and the Sakyas were small republics. • Contain a few area (number of villages; modern districts?) • These republic states having assembly hall (Santhagaras) • Members of the Central Assembly probably lived in Capital, near to the Santhagaras. • Each member of the aristocratic order called as a Raja. • Jatka: one of members son called as Upraja. • Sakhya town and villages has their own Assembly meetings (Santhagaras) • Shakya assembly has 500 rajas • Reppublic Pava and Malla also has Assembly hall
- 23. Administration of Bigger Republics • Bigger state like Yaudheyas or the Malvas were divided into a) Provinces, b) Cities, c) Villages. • Each provinces has separate Governor. • The cities also completely autonomous and administrated by their own men. • City council probably consist: Traders, Artisan, Peasants. • In village council, headman of the village probably a member of ruling class. • Members of the Village council may belonged to the different trades and professions.
- 24. Members of the Assembly 1. Members number varies according to the size of state. 2. Yaudheyas: 5000 members 3. Licchhvis: 7707 members 4. Kshudrakas: sent 150 men to negotiate peace with Alexander. 5. Probably every citizen has right to attend the meeting like Greek and Athens 6. Yaudheyas 5000, Licchhvis 7707 members plausibly progenies of the founder members who were probably Raja. 7. Jataka: there were twice 84,000 nobles at Vaishali. 8. Small City like Nyasa had 30 Councilors.
- 25. Role of Assembly 1. To look after general issues of the State 2. To see Social, Economic and Religious system 3. It controlled foreign affairs 4. Entertained foreign Ambassadors 5. Handle the issue of Peace and War Examples: a. 150 Ambassadors Kshudrkas to Alexzander b. Ambashthas elected three brave military leaders to fight against Alexzander
- 26. Procedure of Assembly 1. The members of the assembly framed laws 2. Discussion was carried out all important matters 3. Decision on issues was made by a majority vote. 4. If there was no unanimity of opinion and elected the members of the executive. 5. Then, probably by open or secret ballot.
- 27. Assembly Hall • At Assembly Hall various issue of state were discussed • Political issues • Religious issues • Social issues • Economic issues • Assembly divided by various parties • Decision was taken by Presidents • Example: a) Lichchhavis: invited Buddha for opening of new Assembly Hall b) Malla of Kushinagar: Discuss the funeral of Buddha. • In big republics like Licchavis and Ambashtha decision was taken on opinion of elders not by vote.
- 28. Executive Council • According to some writers there was an Executive council/Committee to deal, important issues. • To maintain secrecy • Like war and peace • Treaty • Warfare plans and • Foreign policy • Secret Service • Treasury • Justice • Police and Revenue
- 29. Executive Council मांत्री पररषद • Members varies as per size and traditions • Small Malla republic had 4 members • Lichchhavis :9 members (Assembly Members 7707) • Videha had 18 members • Patanjali: Panchakah (5), Dasakah (10) and vimsakah (20) • Mahavagga: five different kind of Sangha with executive had four, five , ten, twenty etc. members.
- 30. Qualifications of members of Executive Council: i. Executive must capable to guide the State ii. They should be well-versed in warfare activity iii. Capable enough to guide a state in emergency iv. Energetic in action v. Firm in Resolutions vi. Well grounded in the laws, customs and tradition of the country. vii. Later times members seems hereditary
- 31. Members of the Executive Council • The members of the Assembly may elected the members of the Executive Council, • They like modern Commander-in-Chief of the forces, • The Treasurer, etc. • Members of Executive Council discussed important matters of the state such as that of peace and war. • The members of the Executive Council were called Rajana and • The head of Executive Council was sometimes given the title of Raja (King).
- 32. Rules of Procedure • A Buddhist chapter required a quorum of 20. • Similar rule may prevailed in political assembly of Republics • The Sanghmukhya (President) of the assembly • He was initiated and presided debate of parties • He should be strict and neutral • In Buddhist Sangha motion was thrice proposed and passed. • In case of difference of opinions voting was done
- 33. Voting Rights • In Buddhist sangha voting was done by secret method (gulhaka) • Sometimes by whispering method (sakarnajapakam) • Sometime, open method (vivatakam) • Voting tickets were various colour • A person called Salaka-grahka collected them • Subsequently, tickets were counted by the President • Probably similar process was followed by republics
- 34. The Sakyas of Kapilavastu • This was an important republican state of ancient India. • It was situated near the border of Nepal in the Terai region of the Himalayas. • Mahatma Buddha belonged to the family of the Sakyas. • The republican state of the Sakyas had a federal constitution. • Its head was elected and was given the title of King. • Every Sakya adult participated in its administration and all important matters were decided by the assembly of all. • Attendance of a fixed number of members was necessary to complete the quorum. • The Sakya republic had eighty thousand families living within its territories and had several cities as well.
- 39. The Lichchavis of Vaisali: • It considered first Republic of the World. • It was the largest and the most powerful republican state of that time. • Vaisali was the capital of the Lichchhavis, • Wherein lived nearly 42,000 families and was a beautiful and prosperous city. • The head of the state was elected and was titled King. • It had another 7,707 Rajans who were, probably, the chief officers of their territories. • It was such a powerful state that Ajatasatru, the ruler of the Magadha, had to make military and diplomatic preparations for years before he could succeed in annexing it. • And that, too, could be achieved when his diplomacy succeeded in dividing the Lichchhavis.
- 42. Ideal Republic • According to the Shantiparv: 1. Adults shall be properly educated 2. Youth were taught proper manners 3. They must follows the path of virtue 4. Experiences statemen should be valor 5. They should given proper administrative posts 6. They shall be responsible for delicate and secrecy issues 7. Spies and ambassadors were selected with great care 8. Attention must paid for growth for economy of the state. 9. Ensure the prosperity of the state and the people.
- 43. Administration of Republican states As per Buddhist Sanga • Sangha consisting number of monks • Chief of Sangha called “Vinayghar” • Regular meetings were held • Subject of meeting were discussed thoroughly • In state of conflict, it was read three times • Those agree remained mute • If dispute persistent, long discussion were held • For voting colorful flags were used.
- 44. Republic Administrations Republic Central Assembly Deals with the general issues Large number of members Voting was done on important issue Executive Council Deals with the Delicate issues Elders considerations Limited numbers Smaller or Bigger
- 45. End of Republics • Internal weaknesses • Mahabharat: violation of rules, internal dispute • Mutual conflicts in-between • Process of slow voting • Key post become hereditary • K.P. Jaiswal: rise of powerful kingdoms • Rising power of Magadha • Surrounded by Powerful Monarch • At last were destroyed by the imperial Guptas
- 46. Conclusion • Evidence of one of the oldest republics of the World. • Along with monarchy, Republics were also main administrative system • Republics of ancient India shows sophisticated administration. • Republics permitted all respectable citizens in administration and framing of laws. • Republican generally followed the broad pattern of elections. • Cities, villages probably had their own autonomous system of governance.
