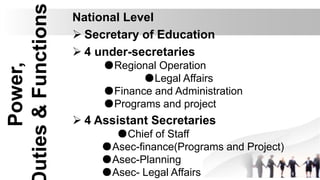
This document establishes a framework for governance of basic education in the country. It renames the Department of Education, Culture and Sports to the Department of Education and defines the roles and responsibilities within the education system. The goals are to provide skills, knowledge and values to students to become productive citizens and establish authority and accountability. It outlines the national, regional, and school level offices and their respective powers, duties and functions.




![Core Competency [kawr.kompet'nsee]
n.
a defined level of expertise that is
essential or fundamental to a particular
job; the primary area of expertise,
specialty; the expertise that allows an
organization or individual to beat it's
competitors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e9c61dfa-f1a1-48a1-9c97-239eb7f73d57-160307110916/85/REPUBLIC-ACT-NO-9155-5-320.jpg)